Abstract
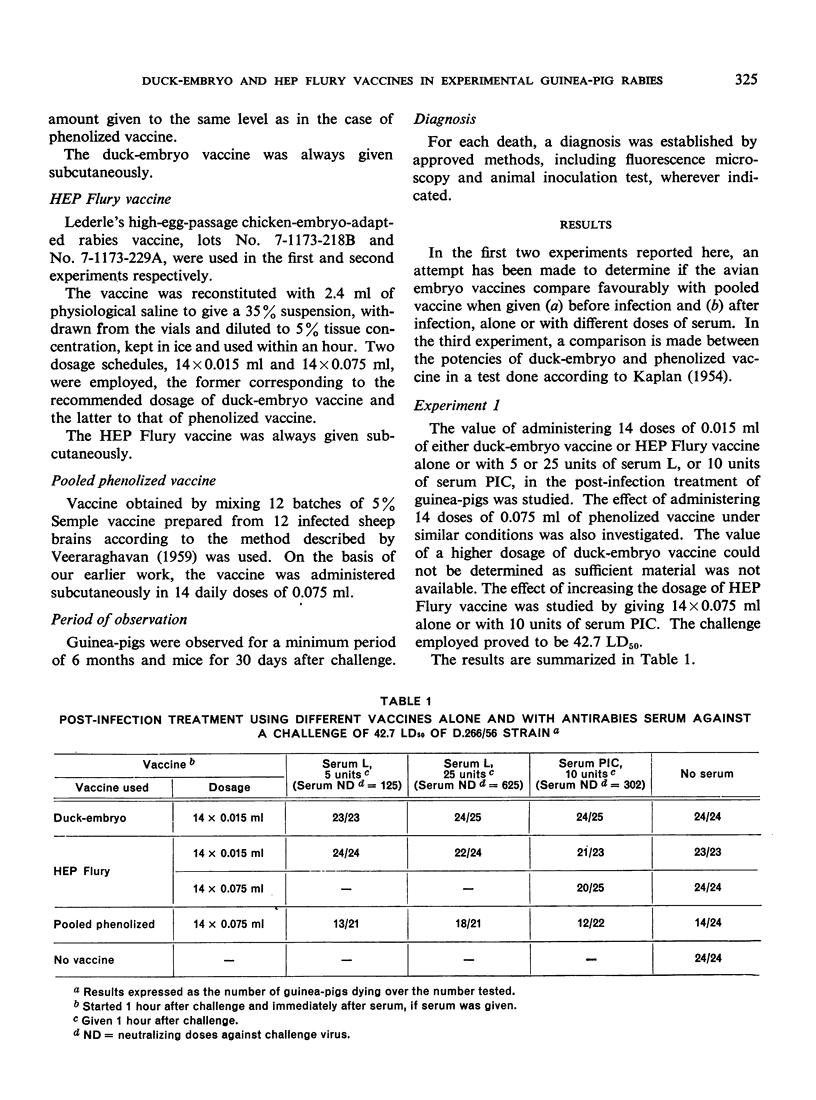
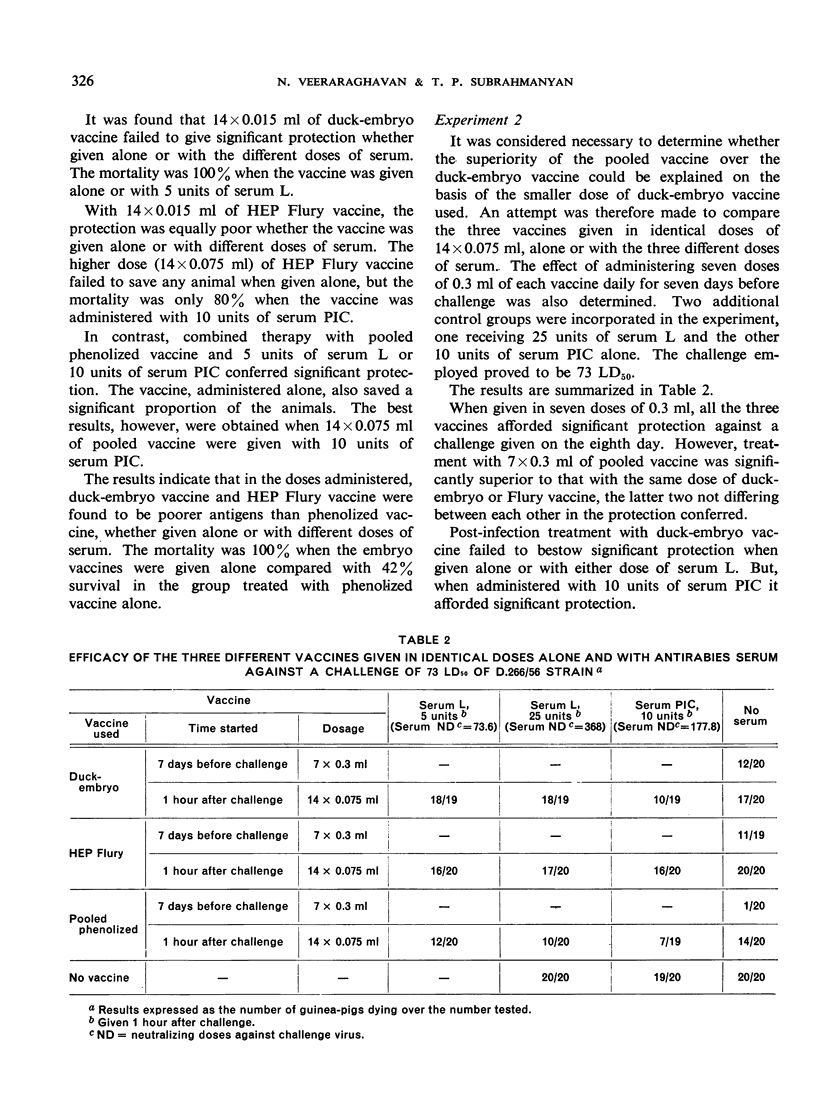
The authors have compared the value of multiple doses of duck-embryo and HEP Flury vaccine with that of pooled 5% sheep-brain vaccine in experimental rabies infection in guinea-pigs. They found that the duck-embryo vaccine given in a dosage corresponding to 14 ml of 10% vaccine (the dosage recommended for human treatment), either alone or with antirabies serum, gave no protection and that, even when administered in a dosage corresponding to 140 ml of 5% pooled vaccine, both the duck-embryo and the HEP Flury vaccines, whether alone or with serum, conferred little protection. Pooled phenolized vaccine under identical conditions gave good results. The immunogenicity of duck-embryo and HEP Flury vaccines, given before infection, was also inferior to that of pooled vaccine; and the duck-embryo vaccine was found to be a poorer antigen than the pooled vaccine in mouse potency tests.
The authors conclude that the dosage of duck-embryo vaccine recommended for human treatment is inadequate and that the HEP Flury vaccine in its present form is unsuitable for post-infection treatment.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON G. R., SCHNURRENBERGER P. R., MASTERSON R. A., WENTWORTH F. H. Avian embryo rabies immunization I. Duck-embryo vaccine administered intradermally in man. Am J Hyg. 1960 Mar;71:158–167. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULBERTSON C. G., PECK F. B., Jr, POWELL H. M. Duck-embryo rabies vaccine; study of fixed virus vaccine grown in embryonated duck eggs and killed with beta-propiolactone (BPL). J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Dec 8;162(15):1373–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEAN D. J., SHERMAN I. Potency of commercial rabies vaccine used in man. Public Health Rep. 1962 Aug;77:705–710. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX J. P. Prophylaxis against rabies in humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):480–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG M., CHILDRESS J. Vaccination against rabies with duck-embryo and Semple vaccines. J Am Med Assoc. 1960 May 28;173:333–337. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020220007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY G. L., KEMP G. E., WOOD E. G. A fatal case of rabies in a woman bitten by an insectivorous bat. Public Health Rep. 1960 Apr;75:317–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H., BLACK J., NELSEN D. J. Studies on chick-embryo-adapted-rabies virus. VI. Further changes in pathogenic properties following prolonged cultivation in the developing chick embryo. J Immunol. 1954 Jan;72(1):94–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., SOAVE O. A., NAKAMURA K., KELLOGG G. H., Jr A fatal human case of rabies following the bite of a rabid bat (Lasionycteris noctivagans). Isolation and identification of the virus from vector and victim. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jan;55:89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK F. B., Jr Rabies vaccine experience during the recent Marion County epizootic. J Indiana State Med Assoc. 1959 Sep;52:1455–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL H. M., CULBERTSON C. G. Action of rabies vaccine derived from embryonated duck eggs against street virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:801–803. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL H. M., CULBERTSON C. G., PECK F. B., Jr Tests of duck embryo (DE) rabies vaccine against street virus in rabbits and guinea pigs. J Indiana State Med Assoc. 1960 Jul;53:1307–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEGSEGGER J. M., BLACK J., SHARPLESS G. R. Primary antirabies immunization of man with HEP flury virus vaccine. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1961 May;51:706–716. doi: 10.2105/ajph.51.5.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNURRENBERGER P. R., ANDERSON G. R., RUSSELL J. H., WENTWORTH F. H. Avian embryo rabies immunization. II. A comparison of the antigenicity of high egg-passage and duck-embryo vaccines administered intradermally in man. Am J Hyg. 1961 Jul;74:1–6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB M. P., FOX J. P., CONWELL D. P., ROBINSON T. A. Avianized rabies virus vaccination in man. Bull World Health Organ. 1954;10(5):823–835. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEERARAGHAVAN N., BALASUBRAMANIAN A., SUBRAHMANYAN T. P. Advances in rabies treatment; an experimental evaluation. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(6):943–962. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEERARAGHAVAN N. Improvement of the antigenicity of antirabies vaccine by pooling checked by post-challenge vaccination of guinea-pigs. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20(1):121–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEERARAGHAVAN N., SUBRAHMANYAN T. P. Value of antirabies vaccine with and without serum against severe challenges. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;22:381–391. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



