Abstract
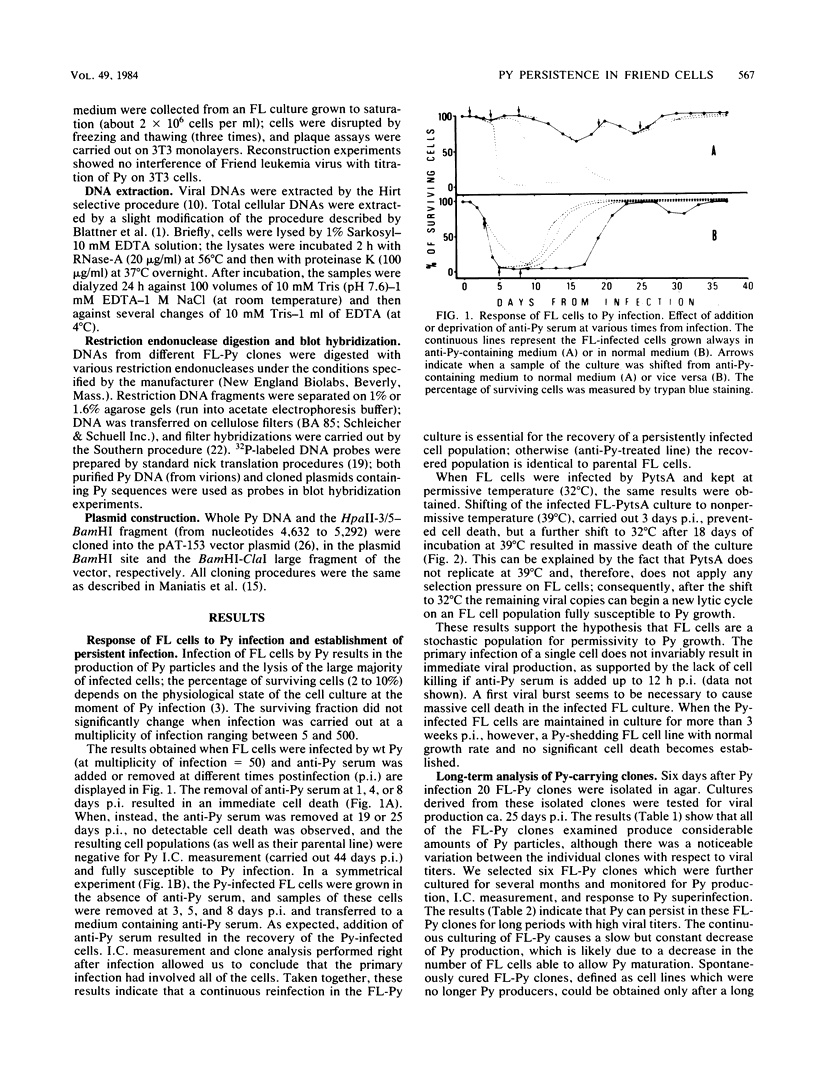
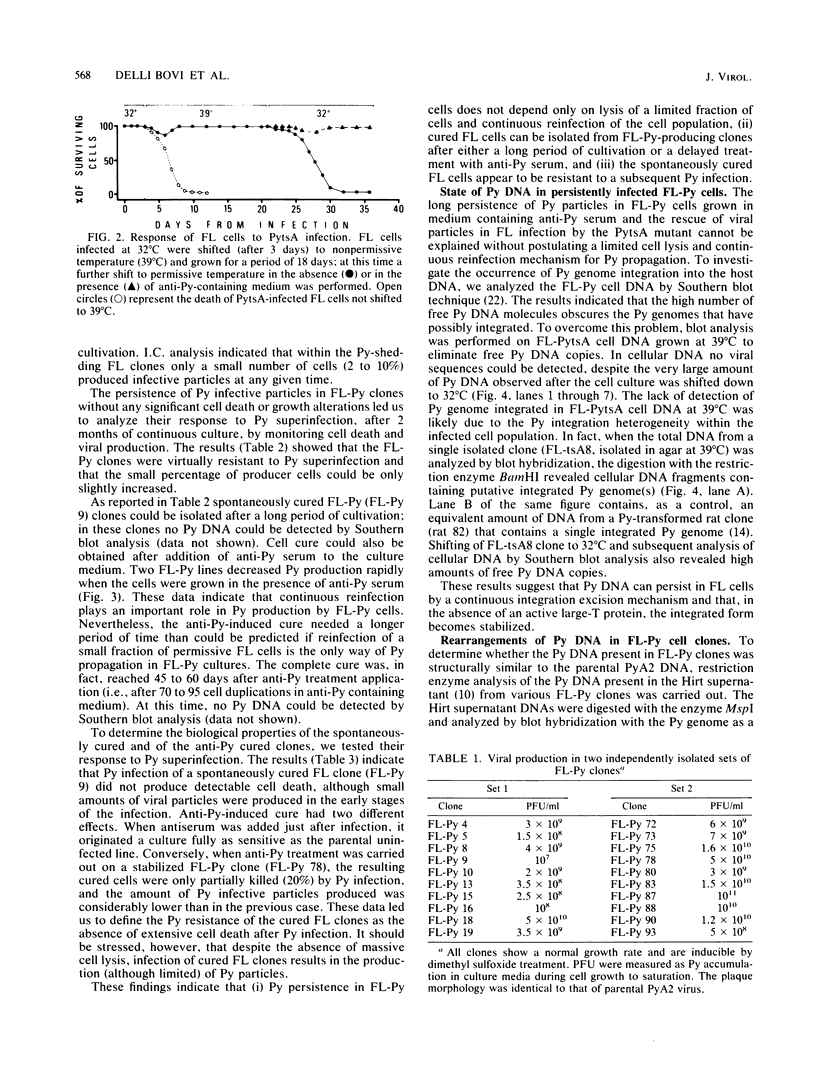
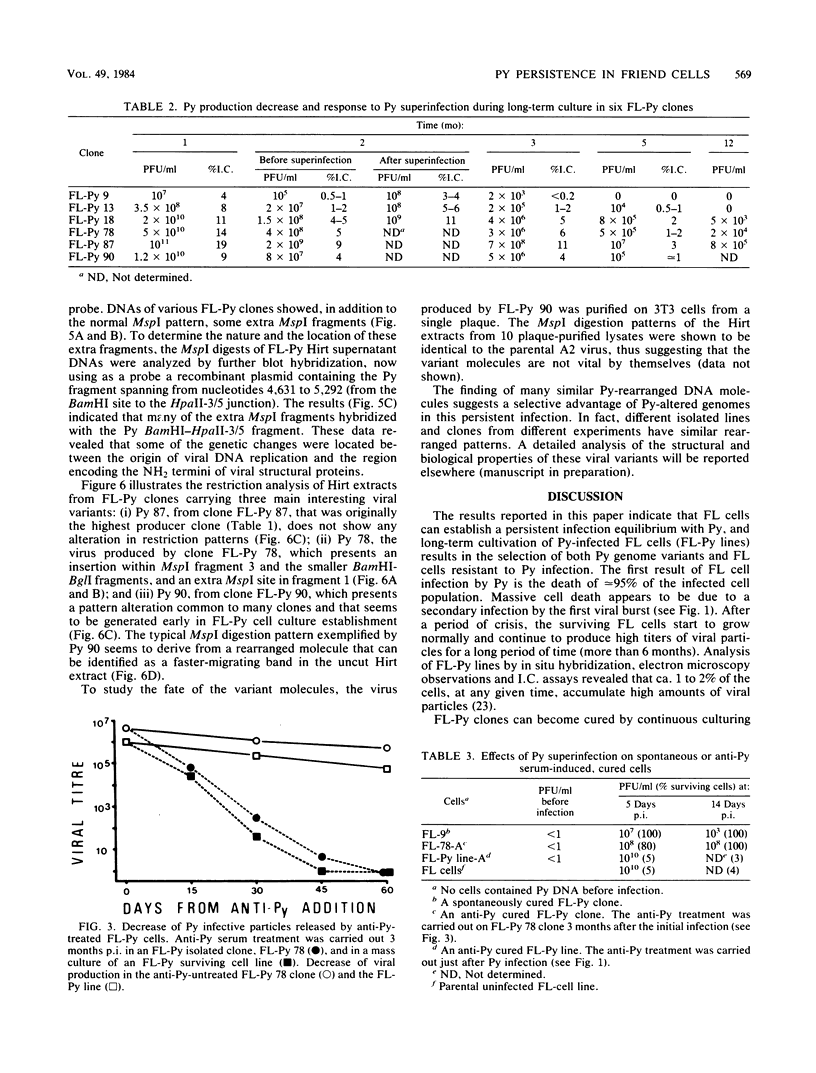
Infection of Friend erythroleukemic (FL) cells by polyomavirus (Py) invariably results in the selection of persistently infected FL-Py cell lines and clones. Anti-Py serum treatment of FL-Py lines and clones leads to the loss of Py genome and consequent cell cure. Conversely, cure has not been obtained in FL-PytsA cell lines (isolated after infection by a Py thermosensitive early mutant) and their derivative clones cultivated for a long time at nonpermissive temperature (39 degrees C), where viral large-T protein is inactive. Rescue of viral particles has always been obtained after shifting cells to 32 degrees C. Integrated viral genomes were detected by blot hybridization in an FL-PytsA clone at 39 degrees C. Long-term observation of FL-Py cell lines and their derivative clones reveals a reciprocal selection mechanism (coevolution) between the viral and the cellular populations, resulting in either a completely virus-free Py-resistant FL cell line (cure) or in a continuously Py-shedding line bearing Py genome variants. Structural analysis of these viral populations has been carried out, and some viral variants have been isolated and characterized. On the basis of the results obtained, the possible mechanisms of Py persistence in FL cells will be discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccara M., Kelly F. Etude de la sensibilité au virus du polyome et à SV40 de plusieurs lignées cellulaires de tératocarcinome. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Feb-Mar;129(2):227–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant of polyoma virus. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):605–617. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Linney E. Mutation near the polyoma DNA replication origin permits productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Vasseur M., Montreau N., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Polyoma DNA sequences involved in control of viral gene expression in murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):720–722. doi: 10.1038/290720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M., Vasseur M., Blangy D. Expression of polyoma early functions in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells depends on sequence rearrangements in the beginning of the late region. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90625-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly F., Condamine H. Tumor viruses and early mouse embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;651(2-3):105–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-419X(82)90009-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C. Papovaviral persistent infections. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Dec;46(4):384–425. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.4.384-425.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Friend C. Persistent infection of Friend erythroleukemia cells with vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4805–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Levine A. J. Isolation and characterization of polyoma host range mutants that replicate in nullipotential embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taddei C., Delli Bovi P., Giordano R., Amati P. Ultrastructural observations of polyoma infected Friend erythroleukemic cells. Microbiologica. 1982 Oct;5(4):333–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Chowdhury K., Chang K. S., Israel M., Ito Y. Isolation and characterization of polyoma virus mutants which grow in murine embryonal carcinoma and trophoblast cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1521–1527. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur M., Kress C., Montreau N., Blangy D. Isolation and characterization of polyoma virus mutants able to develop in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1068–1072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Banerji J., Schaffner W. Analysis of the transcriptional enhancer effect. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):911–919. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]