Abstract
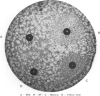
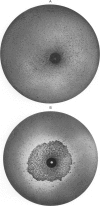
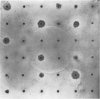
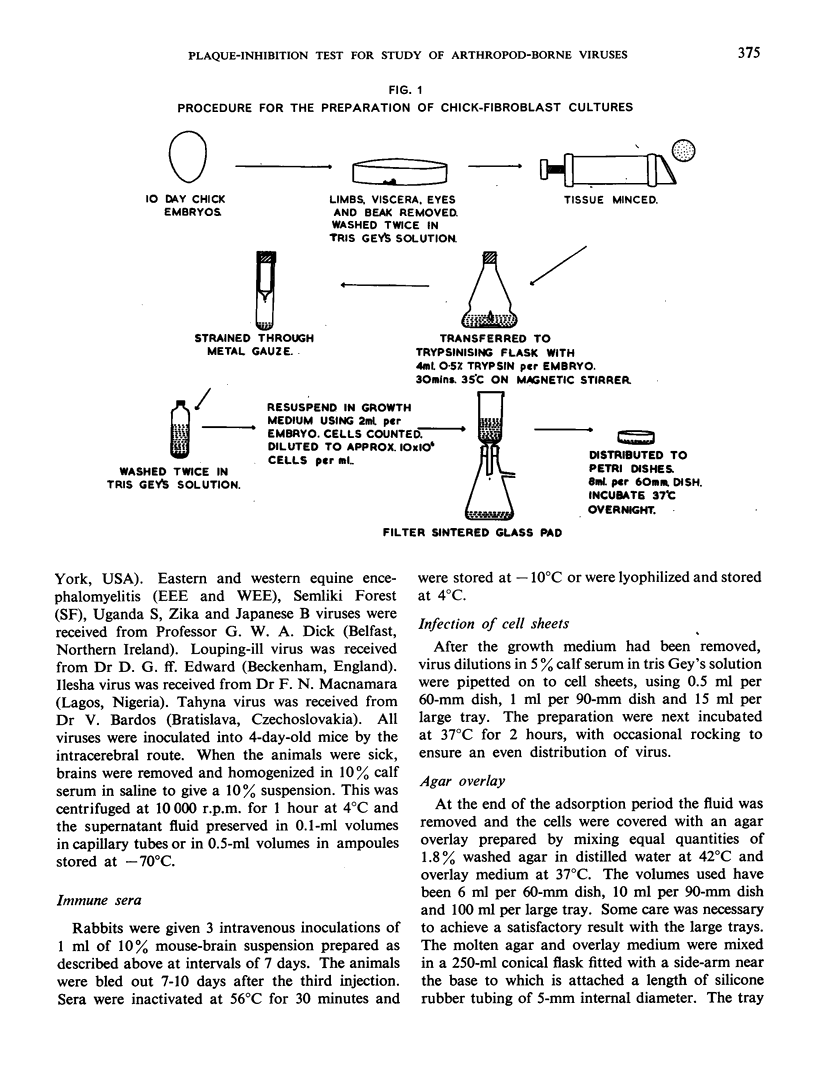
The plaque-neutralization method developed by Dulbecco and co-workers for the study of the virus of western equine encephalomyelitis in cultures of chick fibroblasts, though probably unequalled for accuracy, has not been adopted for general use in laboratories engaged in research on the arthropod-borne viruses, for two reasons: (a) the belief that the technique would be suitable only for viruses with a powerful cytopathic effect on chick-embryo cells, and (b) the laborious procedures involved.
The simple plaque-inhibition test described in this paper was devised with the requirements of the field or diagnostic laboratory in mind; while less precise than Dulbecco's method, this test is sufficiently accurate for many purposes and is far less laborious. The range of applicability of the technique is discussed, the author claiming that it can be used both as a qualitative test for the presence of neutralizing antibodies to a particular plaque-producing virus and as a test for the identification of unknown plaque-producing viruses.
Full text
PDF





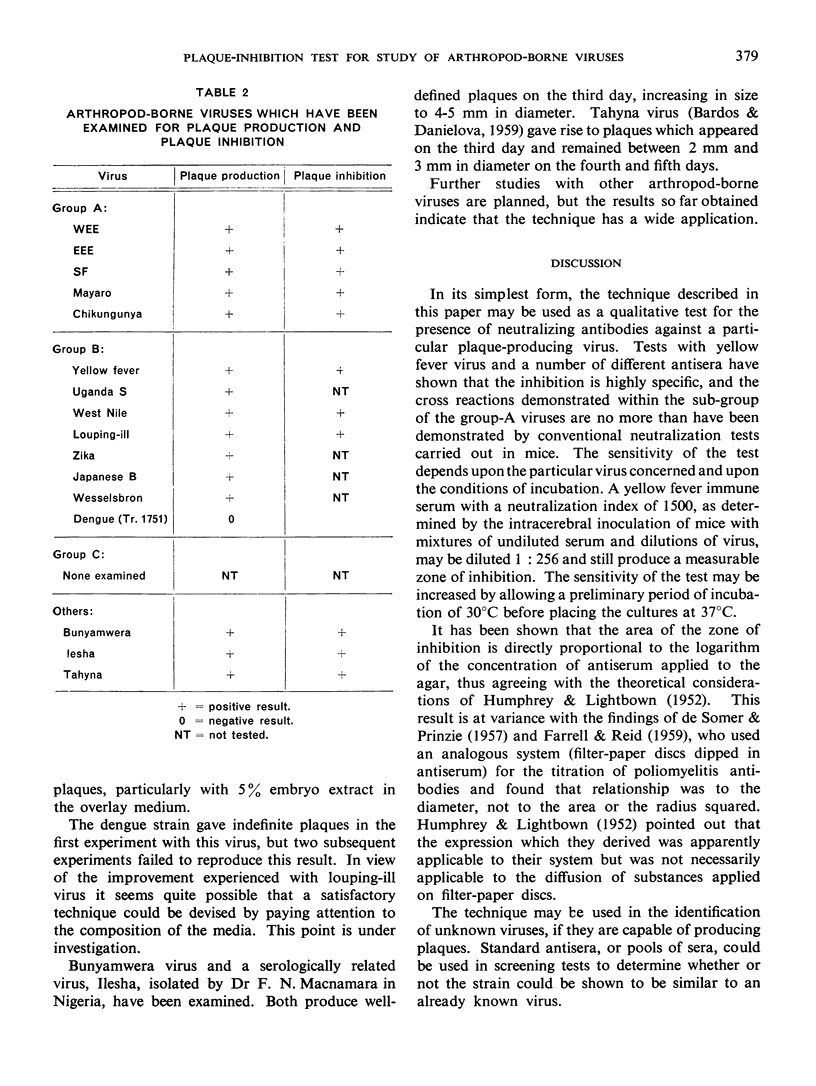

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARDOS V., DANIELOVA V. The Tahyna virus--a virus isolated from mosquitoes in Czechoslovakia. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1959;3:264–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SOMER P., PRINZIE A. Poliomyelitis virus neutralizing antibodies determination by filter paper discs on solidified bottle cultures. Virology. 1957 Oct;4(2):387–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M., STRICKLAND A. G. A study of the basic aspects of neutralization of two animal viruses, western equine encephalitis virus and poliomyelitis virus. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):162–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R. Production of Plaques in Monolayer Tissue Cultures by Single Particles of an Animal Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Aug;38(8):747–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.8.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRELL L. N., REID D. B. Disc-plate assay of poliomyelitis antibodies. Can J Public Health. 1959 Jan;50(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., LIGHTBOWN J. W. A general theory for plate assay of antibiotics with some practical applications. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Aug;7(1-2):129–143. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-1-2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKERNOT R. H., DE MEILLON B., PATERSON H. E., HEYMANN C. S., SMITHBURN K. C. Middelburg virus; a hitherto unknown agent isolated from Aedes mosquitoes during an epizootic in sheep in the eastern Cape Province. S Afr J Med Sci. 1957 Dec;22(4):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHTBOWN J. W., SULITZEANU D. The assay of penicillin in blood-serum using Sarcina lutea. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(4-5):553–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S. A plaque technique for the titration of yellow fever virus and antisera. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Nov;53:458–466. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(59)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S. Plaque production with yellow fever and related arthropodborne viruses. Nature. 1959 Apr 11;183(4667):1069–1070. doi: 10.1038/1831069b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT J. R., GAJDUSEK D. C., SCHAFFER M., GORRIE R. H. Epidemic jungle fever among Okinawan colonists in the Bolivian rain forest. II. Isolation and characterization of Uruma virus, a newly recognized human pathogen. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Jul;8(4):479–487. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1959.8.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]