Abstract
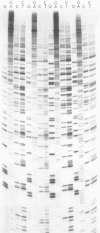
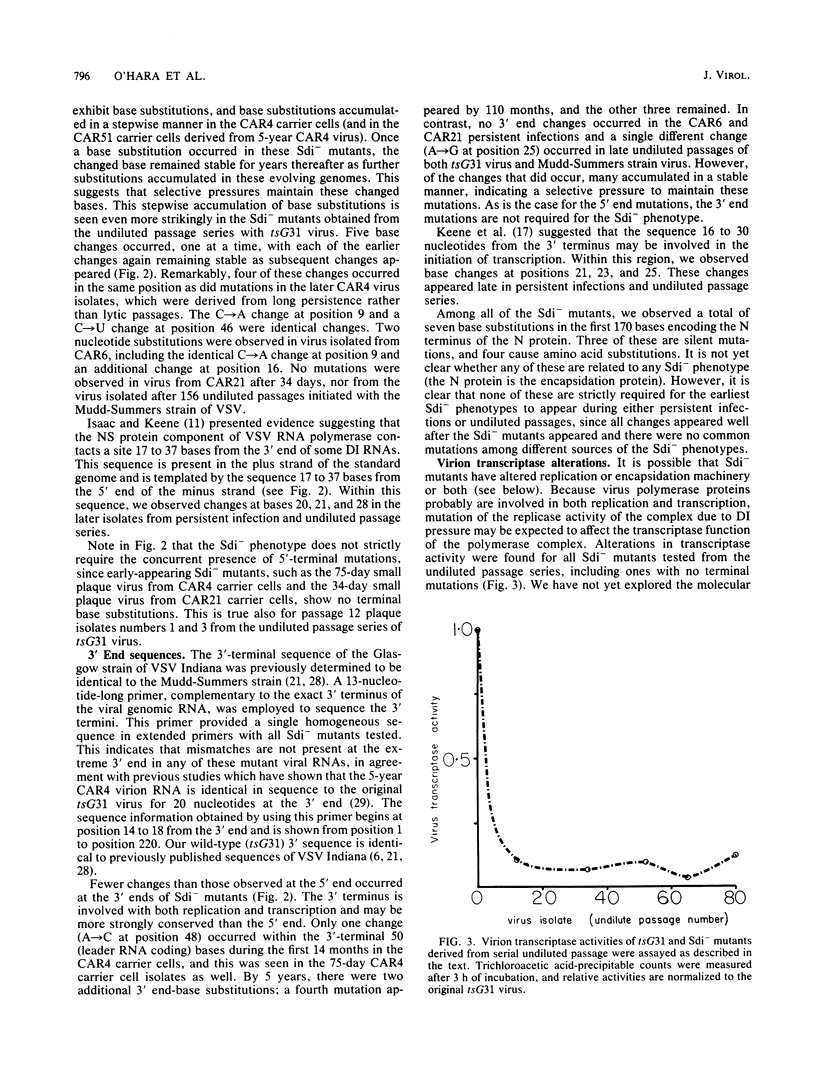
We have studied the evolution of sequences which include the RNA polymerase binding sites at the 5' and 3' termini of vesicular stomatitis virus mutants (Sdi-) resistant to defective-interfering particles. We observed a striking stepwise accumulation of stable base substitutions within the area of replication initiation at the 5'-terminal 54 nucleotides of Sdi- mutants isolated at intervals from persistent infections and undiluted lytic passage series. Fewer mutations accumulated in the region of transcription initiation at the 3' end and in those portions of the N and L protein coding cistrons examined. The termini changes are not strictly required to obtain the Sdi- phenotype. However, it is possible that they represent stepwise compensatory changes to accommodate Sdi- mutations affecting viral replication or encapsidation gene products or both. These results have important implications for RNA virus genome evolution.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. N protein of vesicular stomatitis virus selectively encapsidates leader RNA in vitro. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Holland J. J. Studies on the in vitro transcription and translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):106–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Perrault J. Sequence signal involved in the generation of an internally deleted defective interfering RNA from vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6919–6930. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Zinder N. D. Interference resistant mutants of phage f1. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey T. K., Youngner J. S. Novel phenotype of RNA synthesis expressed by vesicular stomatitis virus isolated from persistent infection. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):167–174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.167-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Greene J. R., Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus N and NS proteins. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.529-535.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodyski F. M., Holland J. J. Viruses isolated from cells persistently infected with vesicular stomatitis virus show altered interactions with defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):627–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.627-631.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodyski F. M., Nichol S. T., Spindler K. R., Holland J. J. Properties of DI particle resistant mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus isolated from persistent infections and from undiluted passages. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac C. L., Keene J. D. RNA polymerase-associated interactions near template promoter sequences of defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):241–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.241-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Ike Y., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Solid phase synthesis of polynucleotides. VI. Further studies on polystyrene copolymers for the solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1755–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Pfau C. J. Viral pathogenesis and resistance to defective interfering particles. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):311–313. doi: 10.1038/283311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai A., Matsumoto S. Interfering and noninterfering defective particles generated by a rabies small plaque variant virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. Terminal sequences of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA are both complementary and conserved. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):167–174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.167-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Thornton B. J., Emerson S. U. Sequence-specific contacts between the RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus and the leader RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Keene J. D., Schubert M. The origins of defective interfering particles of the negative-strand RNA viruses. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Rittenhouse L., Perrault J., Summers D. F., Kolakofsky D. Plus and minus strand leader RNAs in negative strand virus-infected cells. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A. Sequence of 200 nucleotides at the 3'-terminus of the genome RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3199–3211. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Arentzen R., Huang T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. IV. Usage of polystyrene resins for the synthesis of polydeoxyribonucleotides by the phosphostriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5507–5517. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J. Origin and replication of defective interfering particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:151–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. The genetics of vesiculoviruses. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):1–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01314447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Bishop D. H. Determination of the molecular weight of animal RNA viral genomes by nuclease digestions. I. Vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective T particle. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):969–983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.969-983.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J. Sequences of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA in the region coding for leader RNA, N protein mRNA, and their junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4793–4797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands K., Grabau E., Spindler K., Jones C., Semler B., Holland J. Virus protein changes and RNA termini alterations evolving during persistent infection. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Keene J. D., Herman R. C., Lazzarini R. A. Site on the vesicular stomatitis virus genome specifying polyadenylation and the end of the L gene mRNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):550–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.550-559.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Holland J. J. Persistent vesicular stomatitis virus infection mediates base substitutions in viral RNA termini. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):420–428. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.420-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Perrault J., Holland J. J. The nucleotide sequence of the 5' terminus of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3923–3931. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa D., Chanda P. K., Banerjee A. K. Unique mode of transcription in vitro by Vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Schlesinger S. Defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus do not interfere with the homologous virus obtained from persistently infected BHK cells but do interfere with Semliki Forest virus. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):840–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.840-844.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Lazzarini R. A. Analysis of the recombination event generating a vesicular stomatitis virus deletion defective interfering particle. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):766–772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.766-772.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]