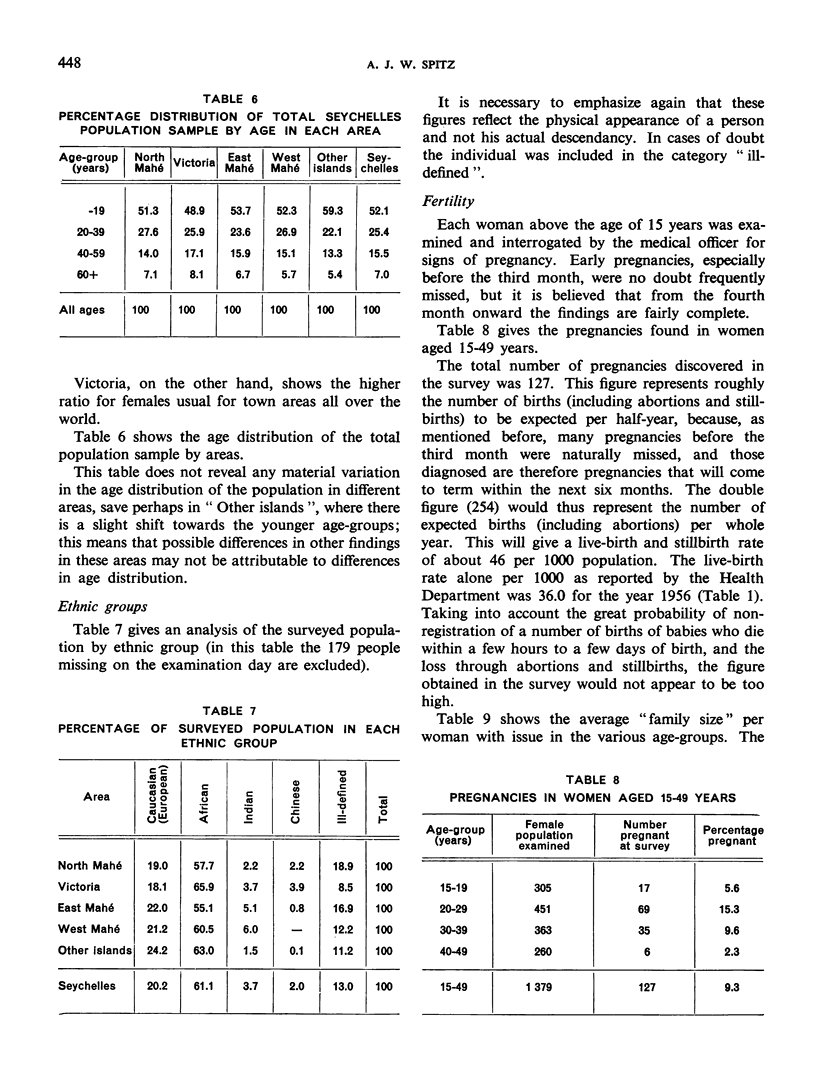
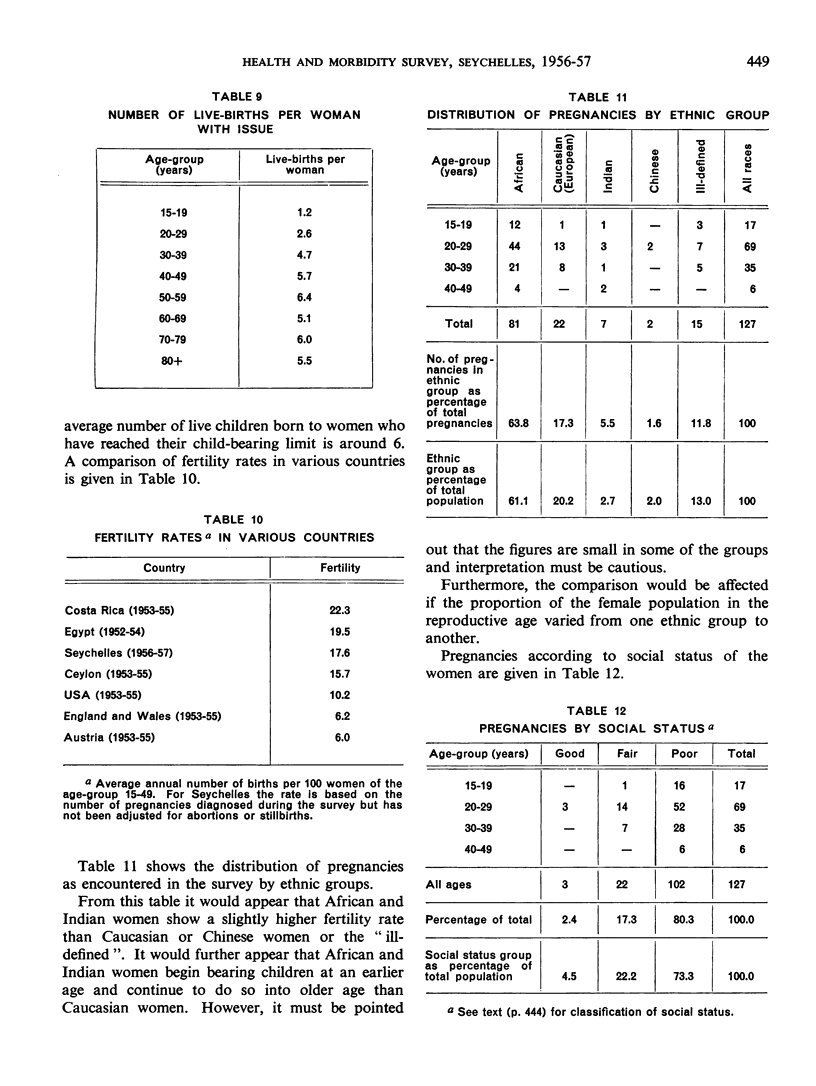
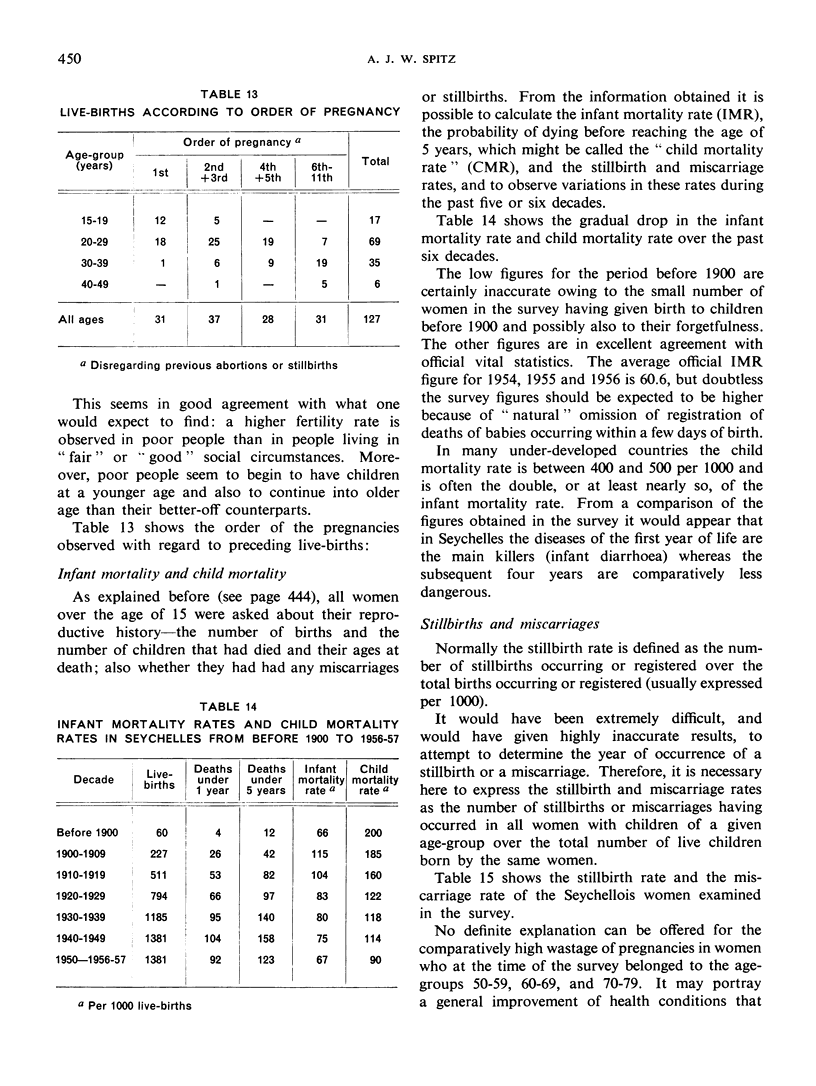
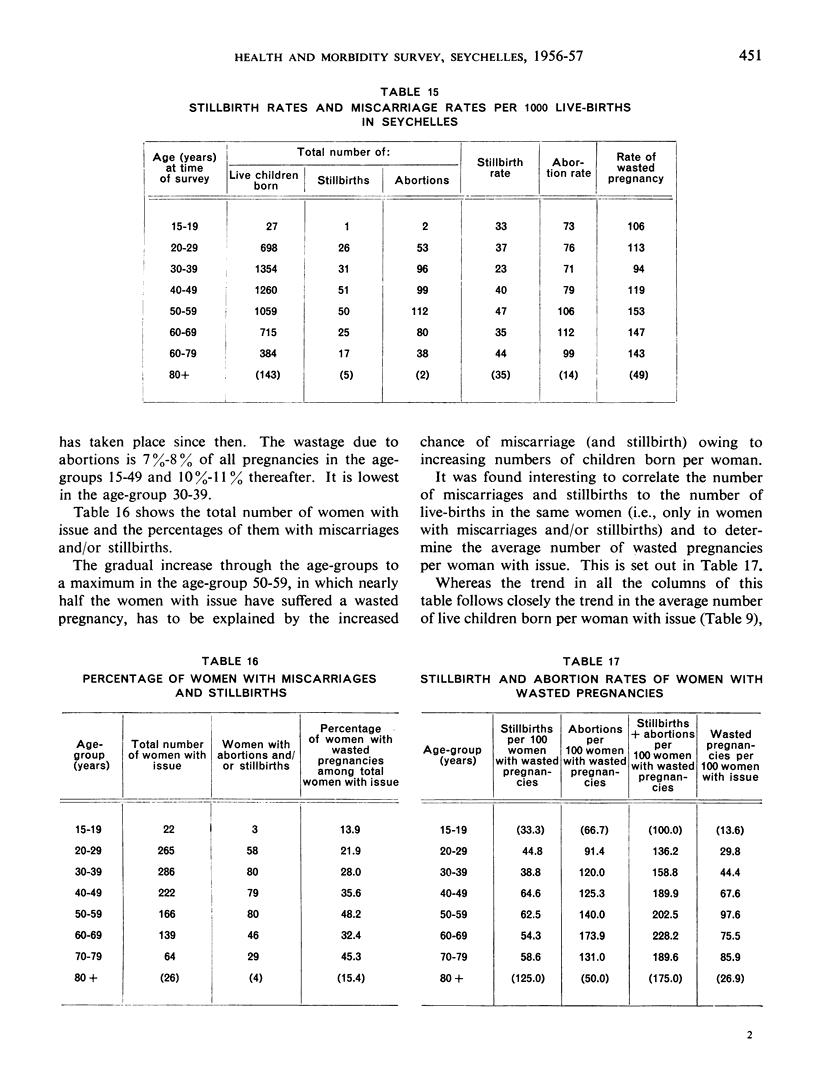
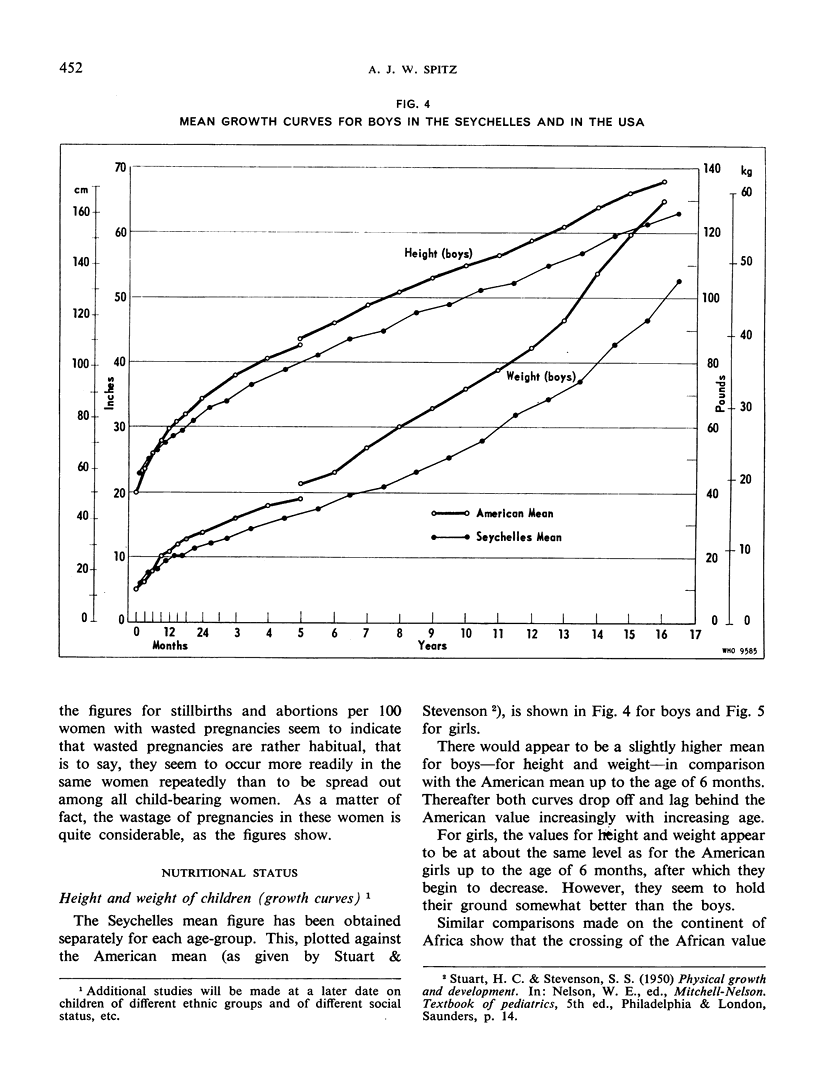
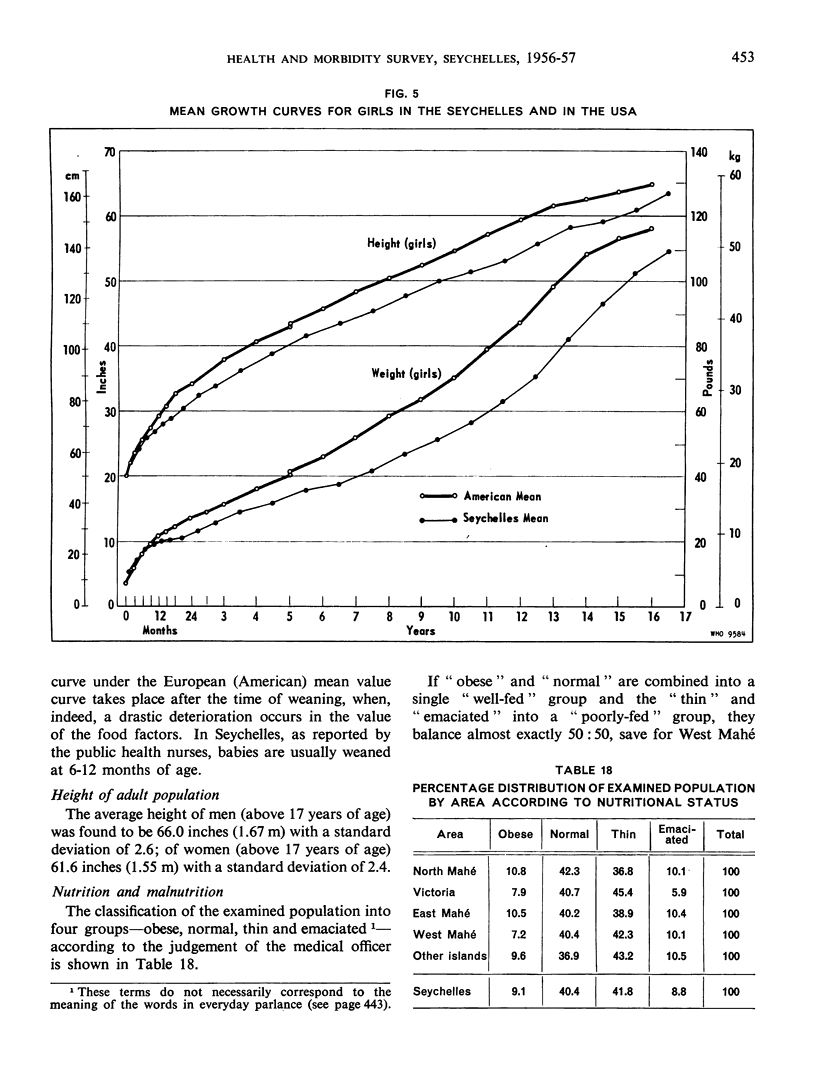
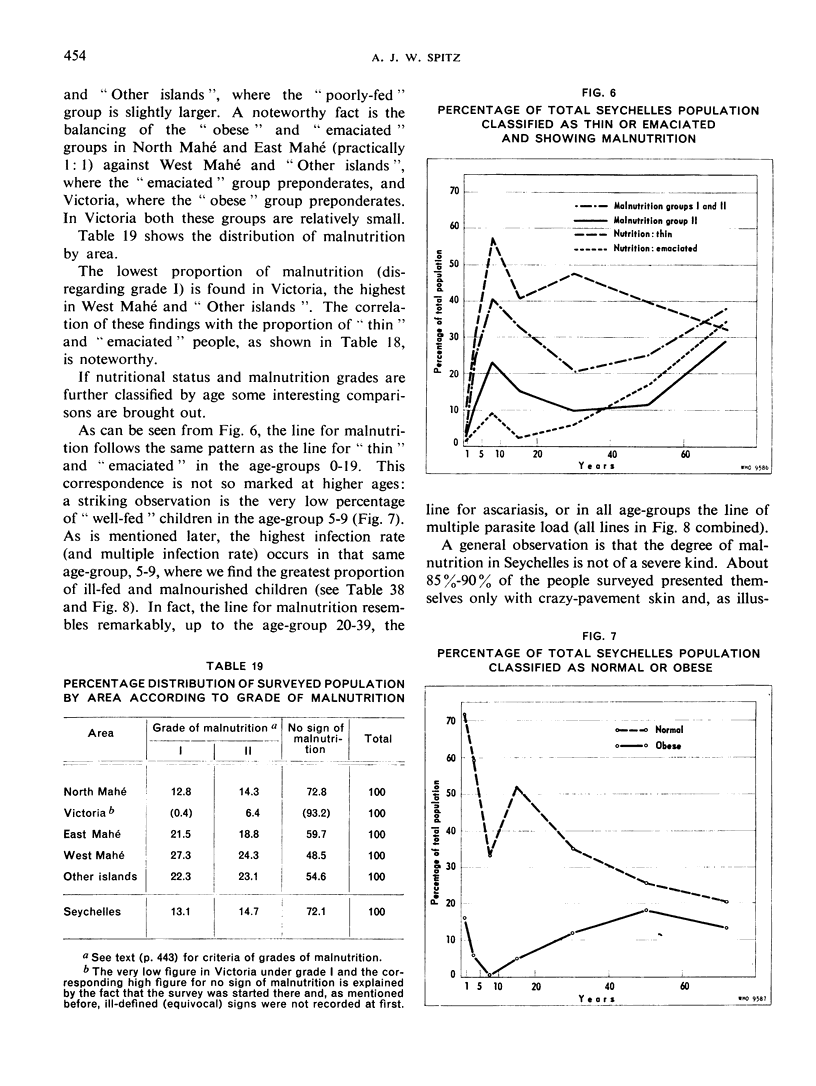
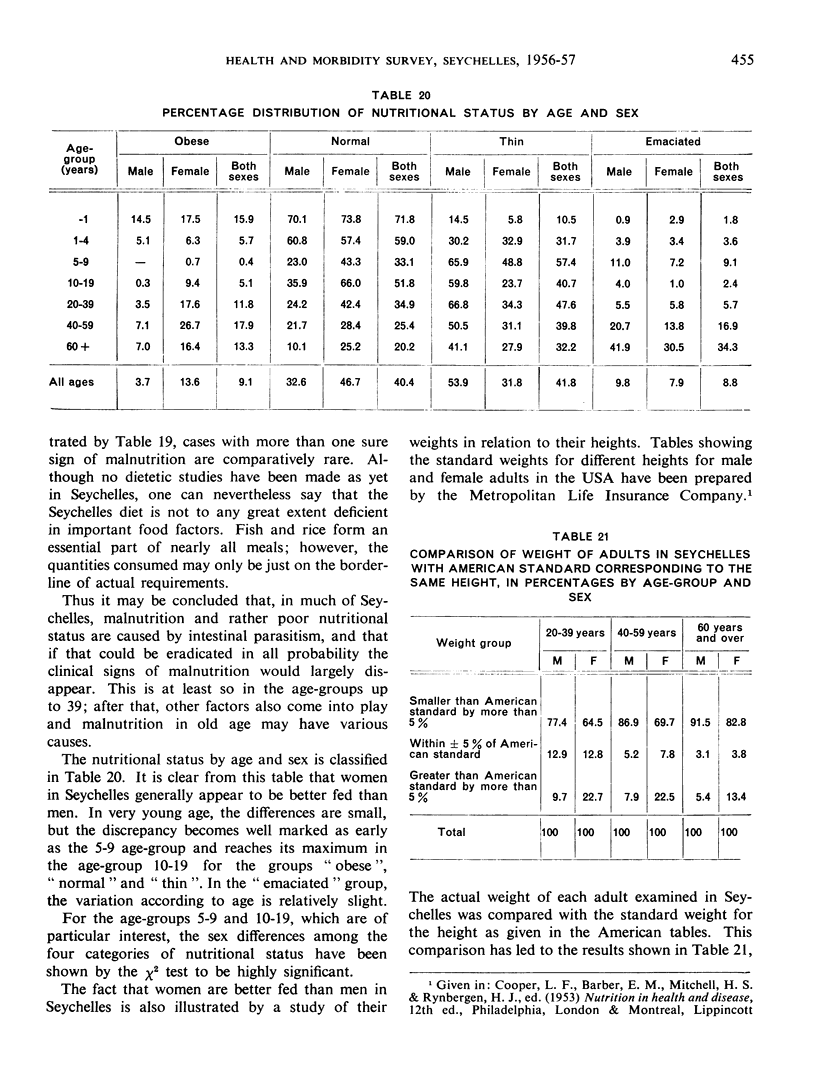
Abstract
Adequate knowledge of existing health and morbidity conditions is the basis for all planning of future health services. For this reason, a health and morbidity survey of the population of the Seychelles was carried out in 1956-57 under the joint auspices of the Seychelles Government and the World Health Organization. Statistical sampling methods were used and the information was obtained by the household interview method. Health, morbidity and relevant demographic data were thus disclosed for the first time for Seychelles. Basic information was obtained on: general morbidity of the population, including dental and nutritional status, malnutrition, incidence of intestinal diseases and other easily diagnosable conditions; growth and weight curves of children up to the age of 16; haemoglobin levels; erythrocyte sedimentation rates; general living conditions such as housing and overcrowding, social status and latrine arrangements; the connexion of soil pollution with the incidence of amoebiasis and helminthiasis; and lastly, the incidence of the sickle cell trait, eosinophilia and positive serological reactions to the Chediak test (for manifest or latent syphilis). The findings are presented with a minimum of remarks and interpretation.
Full text
PDF