Abstract
In his comprehensive monograph on plague, published by WHO in 1954, Dr Pollitzer pointed out that despite the marked drop in the incidence of this disease in recent years, he considered it impossible for various reasons to be complacent about the situation. Since this monograph appeared, plague has shown a truly spectacular decrease, but in case this is partly the outcome of a natural periodicity of the infection, the author still feels that the disease ”should be given continued attention by those interested in global public health”. To this end he summarizes here the latest information on the subject, his review covering not only works published since 1954, but also some earlier literature (particularly from the USSR) which was not available to him at the time of preparation of his monograph.
Full text
PDF







































































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGARWALA S. C., SAGAR P., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Studies in the enzyme make up of Pasteurella pestis. I. Determination of amino acids by virulent and avirulent strains. Indian J Med Res. 1956 Jul;44(3):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGARWALA S. C., SAGAR P., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Studies in the enzyme make up of Pasteurella pestis. II. Phosphatase activity of virulent and avirulent strains. Indian J Med Res. 1956 Oct;44(4):593–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AJL S. J., REEDAL J. S., DURRUM E. L., WARREN J. Studies on plague. I. Purification and properties of the toxin of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Aug;70(2):158–169. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.2.158-169.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AJL S. J., RUST J., Jr, HUNTER D., WOEBKE J., BENT D. F. Preparation of serologically homogeneous plague murine toxin and its reactions with physical, chemical and enzymatic agents. J Immunol. 1958 Jun;80(6):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AJL S. J., WOEBKE J., RUST J., Jr Inhibition of keto acid oxidation by plague toxin. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):449–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.449-452.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMES C. T., QUAN S. F., RYCKMAN R. E. Triatominae in experimental transmission of plague. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 Sep;3(5):890–896. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1954.3.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMIES C. R. The envelope substance of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):259–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANISIMOV P. I. Tsitologiia chumnogo mikroba v protsesse ego izmenchivosti. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1958 Aug;29(8):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: an antigen determining virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Oct;37(5):481–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W., YATES M. The effects of biochemical mutation on the virulence on Bacterium typhosum: the induction and isolation of mutants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Dec;31(6):703–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER E. E., SOMMER H., FOSTER L. E., MEYER E., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. I. The isolation and characterization of the soluble antigen of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):131–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., DAVIS D. H., DEVIGNAT R., GIRARD G., GOHAR M. A., KARTMAN L., MEYER K. F., PARKER M. T., POLLITZER R., PRINCE F. M. Recommended laboratory methods for the diagnosis of plague. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;14(3):457–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., EFTEKHARI M. Techniques de récolte, de manipulation et d'élevage des puces de rongeurs. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;16(2):436–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., SEYDIAN B., MOFIDI C., BAHMANYAR M., POURNAKI R. Sur la résistance a la peste de certaines espèces de rongeurs sauvages. I. Faits observés dans la nature. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Oct;85(4):411–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNETT S. A., BATHARD A. H. Population dynamics of sewer rats. J Hyg (Lond) 1953 Dec;51(4):483–491. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400036767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENT D. F., ROSEN H., LEVENSON S. M., LINDBERG R. B., AJL S. J. Elemental and amino acid composition of purified plague toxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):178–181. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY E. W., LARTHE Y., TAYLOR A. The effect of particle size on the toxicity of alpha-naphthyl thiourea (antu) to albino rats. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Sep;53(3):328–334. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENDT R. F. Some physiological and immunological properties of Pasteurella pestis recovered from aerosols. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):217–223. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.217-223.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHAGAVAN N. V., CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Further studies of antigenic structure of Pasteurella pestis in gels. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Mar;91(3):353–356. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLANC G. Une opinion non conformiste sur le mode de transmission de la peste. Rev Hyg Med Soc. 1956 Sep;4(6):535–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. W. The insecticide-resistance problem: a review of developments in 1956 and 1957. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;18(3):309–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYGOO E. R., COURDURIER J. Action in vitro des antibiotiques sur 101 souches malgaches de Pasteurella pestis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Jul;89(1):118–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYGOO E. R., COURDURIER J. Comportement des souches malgaches de Pasteurella pestis a l'égard du rhamnose. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Dec;89(6):688–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYGOO E. R., COURDURIER J. Test sur souris de l'efficacité du vaccin E.V. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):939–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYGOO E. R. Le diagnostic de la peste par inoculation à la souris de produits pathologiques additionnés de pénicilline. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1956 May-Jun;49(3):409-13; discussion, 413-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. An antigen determining virulence in Pasteurella pestis. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):426–427. doi: 10.1038/177426b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: attempts to induce mutation from avirulence to virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):129–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: comparative behaviour of virulent and avirulent strains in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):134–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: the development of resistance to phagocytosis in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):286–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The effects of loss of different virulence determinants on the virulence and immunogenicity of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):278–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. Virulence of Pasteurella pestis. Nature. 1957 Jun 15;179(4572):1246–1247. doi: 10.1038/1791246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., WHEELER C. M., SUYEMOTO W., SHIMADA T., YAMAKAWA Y. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in various flea species. I. Infection of flea species with avirulent strains of Past. pestis. J Infect Dis. 1956 Jan-Feb;98(1):103–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., CROCKER T. T., MEYER K. F. Electron microscopic study of the extracellular materials of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1956 Dec;72(6):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.6.851-857.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. VII. A hemagglutination test with the protein fraction of Pasteurella pestis: a serologic comparison of virulent and avirulent strains with observations on the structure of the bacterial cells and its relationship to infection and immunity. J Immunol. 1954 Apr;72(4):282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. X. Specific precipitation of Pasteurella pestis antigens and antibodies in gels. J Immunol. 1955 Jun;74(6):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. XI. A study of the immunogenicity and toxicity of eleven avirulent variants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Infect Dis. 1955 Mar-Apr;96(2):145–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H. Studies on immunization against plague. IV. The method of the hemagglutination test and some observations on the antigen. J Immunol. 1952 Dec;69(6):587–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEVALIER A., GIRARD G. Comportement de Pasteurella pestis à l'égard du rhamnose; a propos de la communication de E.R. Brygoo et J. Courdurier. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Aug;91(2):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., DAVIES D. A. A protein antigen associated with smooth colony forms of some species of Pasteurella. Nature. 1957 Oct 26;180(4591):863–864. doi: 10.1038/180863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., DAVIES D. A. An antigenic analysis of Pasteurella pestis by diffusion of antigens and antibodies in agar. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Mar 27;144(918):109–134. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., DAVIES D. A., HUTCHISON A. M. The serological specificities of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis somatic antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):129–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUTKHOW C., SCHULZ K. H. A demonstration project of plague control in a south-east Asian township in 1950. J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Nov;59(11):267–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A. A specific polysaccharide of Pasteurella pestis. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):105–116. doi: 10.1042/bj0630105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A. The smooth and rough somatic antigens of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):118–128. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS D. E. The characteristics of global rat populations. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951 Feb;41(2):158–163. doi: 10.2105/ajph.41.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS D. E. The characteristics of rat populations. Q Rev Biol. 1953 Dec;28(4):373–401. doi: 10.1086/399860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS D. H. Plague in South Africa: a study of the epizootic cycle in gerbils (Tatera brantsi) in the northern Orange Free State. J Hyg (Lond) 1953 Dec;51(4):427–449. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400036718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERTEVA I. I. Deistvie protivochumnoi syvorotki na chumnoi mikrob v probirke i v organizme zhivotnogo. II. Vliianie protivochumnoi syvorotki na fagotsitoz chumnogo mikroba v organizme zhivotnogo. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1958 Feb;29(2):105–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVIGNAT R., BOIVIN A. Deux milieux complexes pour la différentiation des trois variétés de Pasteurella pestis, et de P. pseudotuberculosis. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1953;46(5):627–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
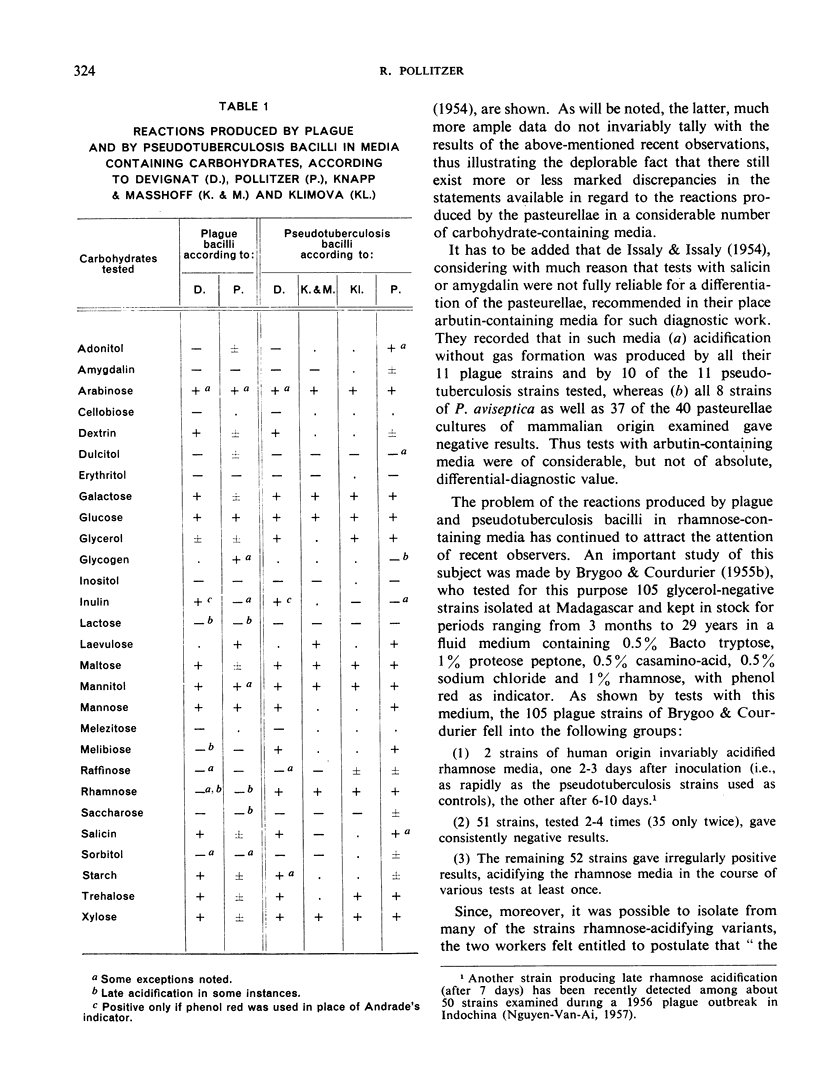
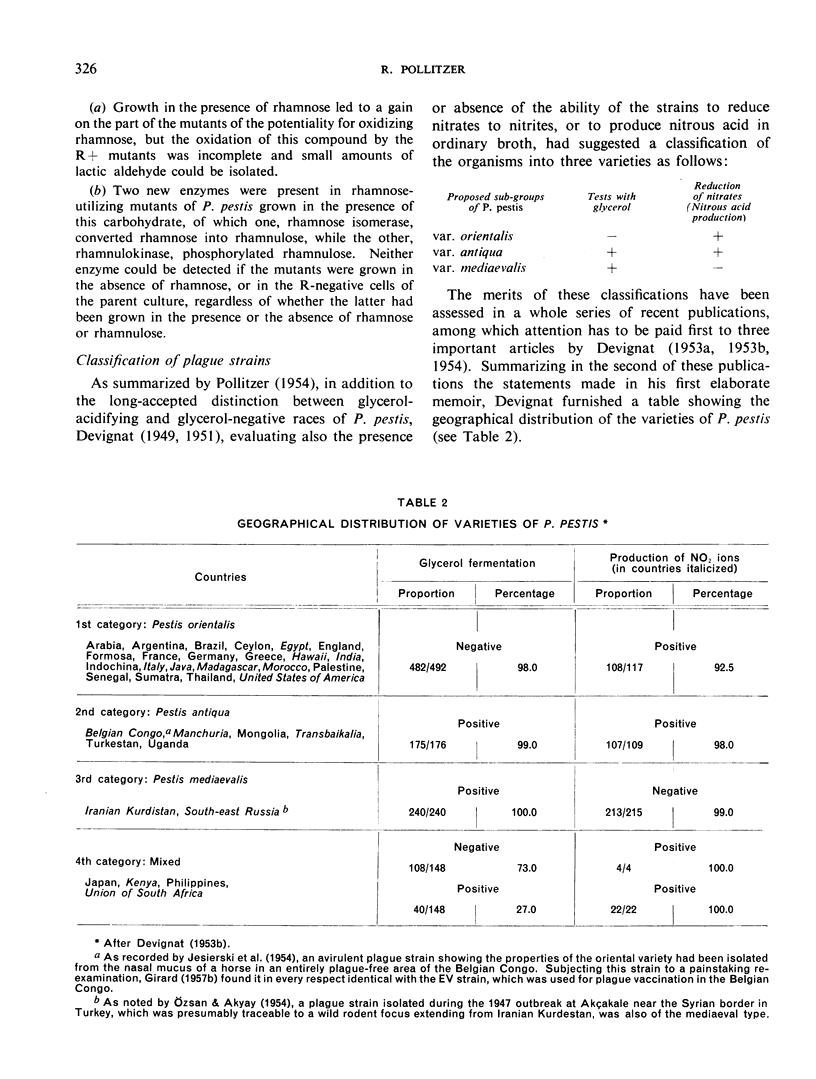
- DEVIGNAT R. Comportement biologique et biochimique de P. pestis et de P. pseudotuberculosis. Bull World Health Organ. 1954;10(3):463–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVIGNAT R. Répartition géographique des trois varietes de Pasteurella pestis. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1953;16(3):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVIGNAT R. Variétés de l'espèce Pasteurella pestis; nouvelle hypothèse. Bull World Health Organ. 1951;4(2):247–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DZHAPARIDZE M. N., KULIKOVA V. L. Vliianie chumnogo mikroba na nekotorye storony metabolizma vospriimchivykh k chume zhivotnykh. I. Deistvie fermentnykh ingibitorov trikarbonovogo tsikla na zhivotnykh, porazhennykh toksinom chumnogo mikroba. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1958 Sep;29(9):122–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRENKRANZ N. J., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. VIII. Study of three immunizing preparations in protecting primates against pneumonic plague. J Infect Dis. 1955 Mar-Apr;96(2):138–144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRENKRANZ N. J., WHITE L. P. Hepatic function and other physiologic studies in monkeys with experimental pneumonic plague. J Infect Dis. 1954 Nov-Dec;95(3):226–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/95.3.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBEL R. E., THAINEUA M. A flea and rodent control program for plague prevention in Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1957 Mar;6(2):280–293. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1957.6.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. Diffusible antigens in staphylococcal cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Jun;31(3):358–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., CHEN T. H., LEVY J. B., FOSTER L. E., MEYER K. F. Virulence in Pasteurella pestis. Science. 1954 Mar 26;119(3091):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3091.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., GIBOR A., LEVY J. B. Adaptive control of terminal respiration in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1954 Aug;68(2):146–151. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.2.146-151.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., LEVY J. B., GIBOR A. Some enzymatic changes accompanying the shift from anaerobiosis to aerobiosis in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1954 Aug;68(2):178–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.2.178-185.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., LEVY J. B. Induced synthesis of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes as correlated with the oxidation of acetate and glucose by Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):418–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.418-431.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E. Mutation to rhamnose utilization in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 May;73(5):641–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.5.641-648.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E. Physiological basis for rhamnose utilization by a mutant of Pasteurella pestis. II. A single mutational event leading to the production of two enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Sep;71(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E. The irreversibility of methionine synthesis from cysteine in pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1952 May;63(5):675–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.5.675-680.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Ingraham L. MEIOTROPHIC MUTANTS OF Pasteurella Pestis AND THEIR USE IN THE ELUCIDATION OF NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 May 15;43(5):369–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAUCONNIER J. La décomposition de l'urée en milieu synthétique de Ferguson par Past. pseudotuberculosis, réaction nouvelle de différenciation des agents étiologiques de la peste et de la pseudotuberculose. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Jul;79(1):104–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOCH H. Quelques remarques au sujet des résistances de divers insectes, notamment Anopheles darlingi, au D. D. T. et autres insecticides. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(4):555–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., HIGUCHI K. Synthesis of the fraction I antigenic protein by Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.209-216.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX I. Murine typhus fever and rat ectoparasites in Puerto Rico. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Sep;5(5):893–900. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1956.5.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUI G. M., LAWTON W. D., JANSSEN W. A., SURGALLA M. J. Response of guinea pig lungs to in vivo and in vitro cultures of Pasteurella pestis. J Infect Dis. 1957 Jan-Feb;100(1):103–107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/100.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUI G. M., OGG J. E., WESSMAN G. E., SURGALLA M. J. Studies on the relation of cultural conditions and virulence of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):714–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.714-717.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUMI H., KANEKO H., SAYAMA E. Antigenic substance of Pasteurella pestis concerning hemagglutination. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1954 Dec;7(6):621–629. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.7.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
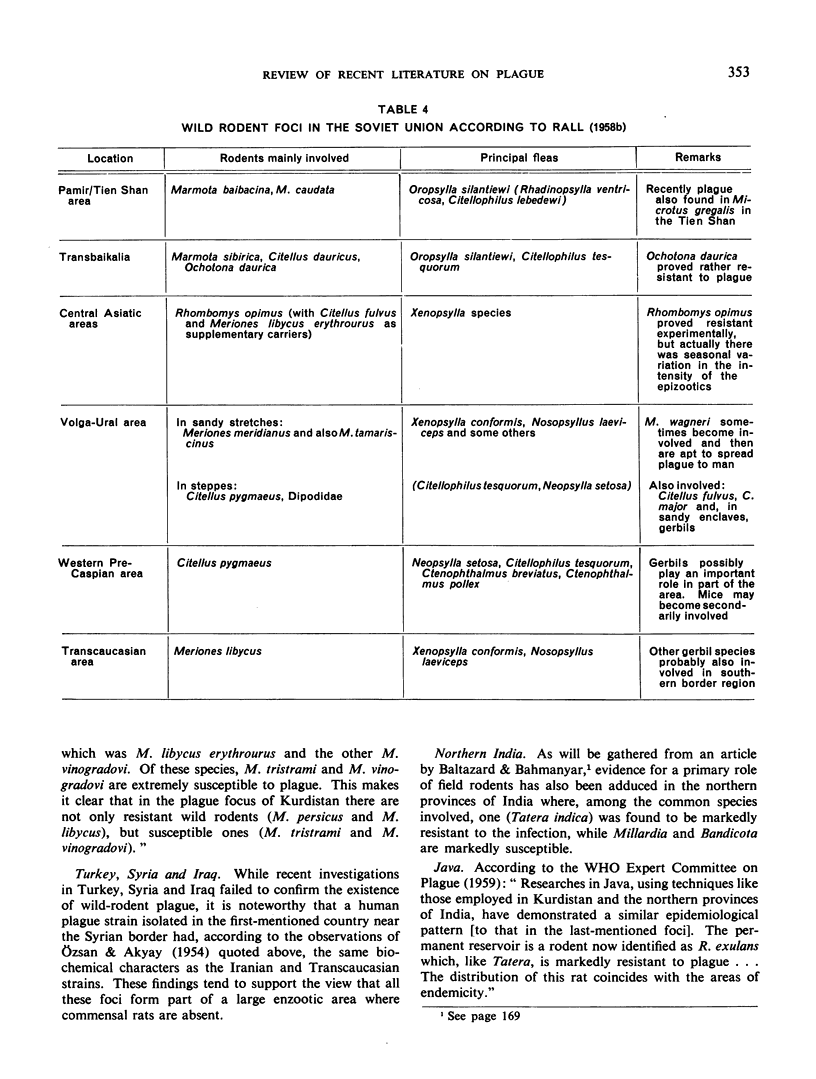
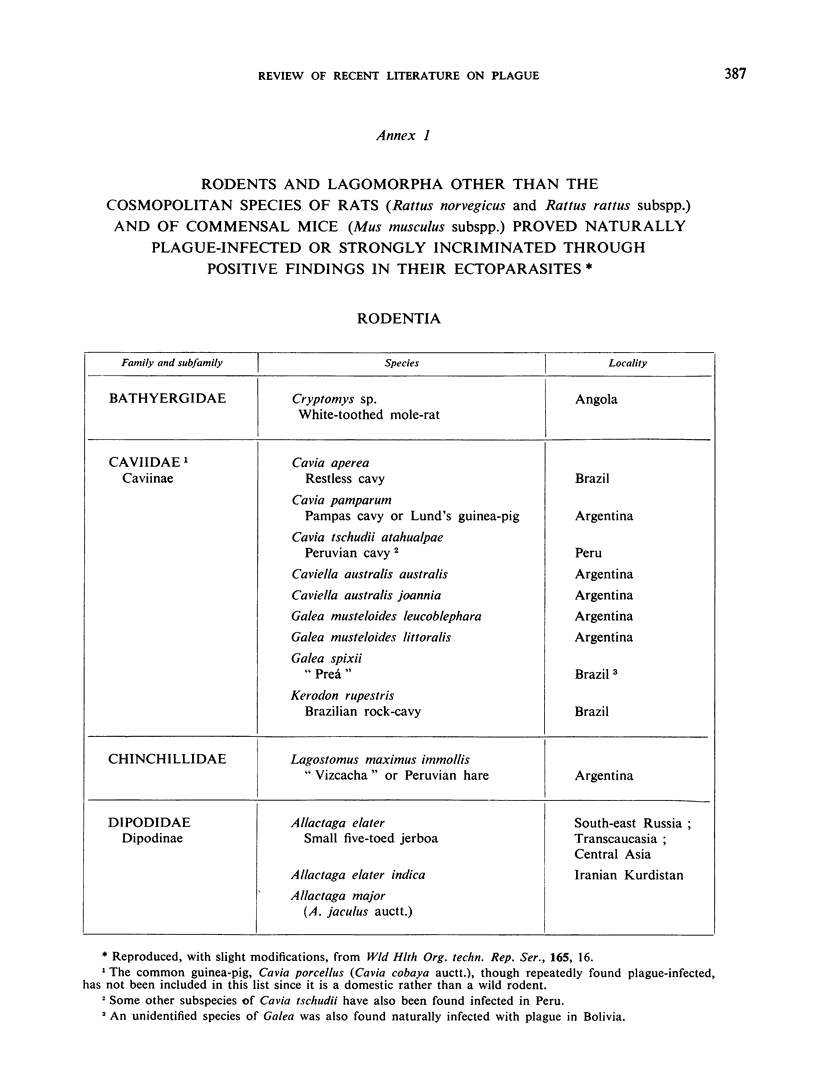
- GARNHAM P. C. C. Distribution of wild-rodent plague. Bull World Health Organ. 1949;2(2):271–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Caractères généraux des mutants pseudolysogènes sélectionnés chez Pasteurella pestis par les bactériophages; déduction épidémiologiques. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1957;151(6):1068–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Comportement de deux souches de Pasteurella pestis de la variété continentale (glycérol positive) après 50 passages par le rat blanc; premières déductions épidémiologiques. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(3):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Considerations sur une souche de Pasteurella pestis, isolée à partir d'un cheval au Congo Belge; son étroit apparentement à la souche EV (Girard et Robic). Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1957 May-Jun;50(3):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Données numériques sur la densité microbienne d'une rate de souris morte de peste septicémique. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1958 Mar-Apr;51(2):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G., GALLUT J. Au sujet de la latence dans la croissance de Pasteurrella pestis en bouillon. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Sep;85(3):372–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Le sérum antipesteux, associé aux antibiotiques, garde ses indications dans les formes hypertoxiques de la peste. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1953;46(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Le virus-vaccin E. V. confère une protection égale vis-a-vis de l'infection pesteuse expérimentale provoquée par les trois variétés de Pasteurella pestis. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(4):475–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Les trois variétés du bacille pesteux (Pasteurella pestis); intérêt épidémiologique de cette notion. Maroc Med. 1954 Nov;33(354):1016–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Méthodes permettant de différencier P. pestis de P. pseudotuberculosis; possibilité d'uniformiser ces méthodes. Bull World Health Organ. 1953;9(5):645–653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD G. Plague. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1955;9:253–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.09.100155.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODNER K. Toxic end products from Pasteurella pestis. II. Toxin yields as influenced by conditions of growth. J Infect Dis. 1955 Nov-Dec;97(3):246–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/97.3.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRATZ N. G. A rodent ectoparasite survey of Haifa port. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):328–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRENIER P., RAGEAU J. Rongeurs et puces en Nouvelle-Calédonie. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1956 Sep-Oct;49(5):827–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNNISON J. B., LARSON A., LAZARUS A. S. Rapid differentiation between Pasteurella pestis and Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis by action of bacteriophage. J Infect Dis. 1951 May-Jun;88(3):254–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTWELL W. V., SCOTT K. G., KARTMAN L. Observations on flea transfer between hosts; a mechanism in the spread on bubonic plague. Science. 1958 Apr 11;127(3302):814–814. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3302.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHIDA T. Effect of pituitary adrenocorticotropic and growth hormones on the resistance of rats infected with Pasteurella pestis. J Exp Med. 1957 Jul 1;106(1):127–143. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECKLY R. J., ANDERSON A. W., ROCKENMACHER M. Lyophilization of Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Jul;6(4):255–261. doi: 10.1128/am.6.4.255-261.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B., GRAINGER W. E., ST A D'SOUZA J. Results of a plague investigation in Kenya. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1953 Nov;47(6):503–521. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(53)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B. Zoonoses as a study in ecology; with special reference to plague, relapsing fever, and leishmaniasis. Br Med J. 1956 Sep 22;2(4994):669–673. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4994.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENTSCH H. F. Zusätzliche Massnahmen in der Pestbekämpfung. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1955 Jun;163(2-3):173–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. C. The significance of insecticide resistance in vector control programs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1952 May;1(3):371–388. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1952.1.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., CARLIN C. E. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. I. A casein hydrolyzate medium for the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.122-129.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., CARLIN C. E. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. II. A defined medium for the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):409–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.409-413.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOESSLY G. F. Studies on immunization against plague. XII. Natural resistance of chickens and pigeons. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1954;17(6):720–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOESSLY G. F., WALKER D. L., LARSON A., MEYER K. F. Experimental bubonic plague in monkeys. I. Study of the development of the disease and the peripheral circulatory failure. Acta Trop. 1955;12(3):240–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDENRIED R., MORLAN H. B. Plague-infected fleas from northern New Mexico wild rodents. J Infect Dis. 1955 Mar-Apr;96(2):133–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDENRIED R., QUAN S. F. Susceptibility of New Mexico rodents to experimental plague. Public Health Rep. 1956 Oct;71(10):979–984. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYER B. H., COURDURIER J. Detection of plague antigens in tissues of persons dead from plague. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(6):758–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH A., WOLLMAN E. Définition de quelques termes relatifs a la lysogénie. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN W. A., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. A study of the fate of Pasteurella pestis following intracardial injection into guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1958 Sep-Oct;103(2):183–187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESIERSKI A., FAIN A., DEVIGNAT R. Isolement au Congo Belge, à partir du cheval, d'une souche insolite de Pasteurella pestis var. orientalis. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop (1920) 1954 Aug 31;34(4):469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
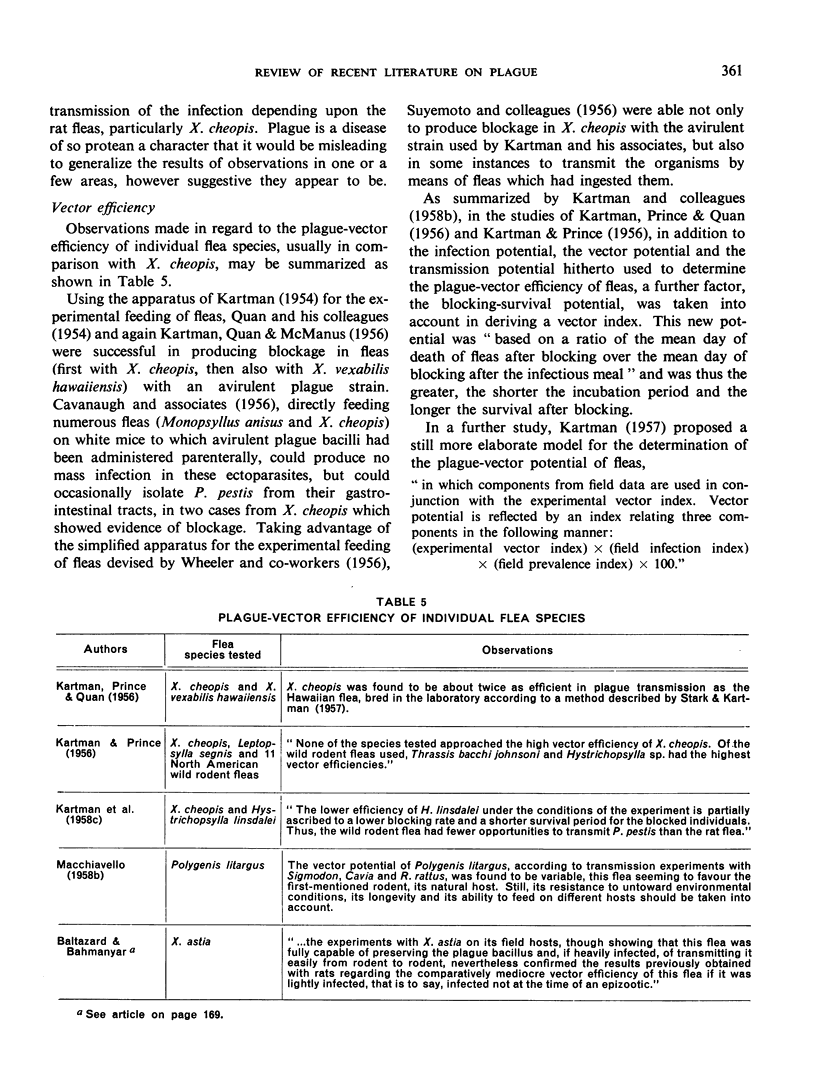
- KARTMAN L., MCMANUS A. G., QUAN S. F. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. IV. Experimental blocking of Xenopsylla vexabilis hawaiiensis and Xenopsylla cheopis with an avirulent strain. Exp Parasitol. 1956 Sep;5(5):435–440. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(56)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., MILES V. I., PRINCE F. M. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco bay area of California. I. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jan;7(1):112–124. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M., QUAN S. F., STARK H. E. New knowledge on the ecology of sylvatic plague. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):668–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M., QUAN S. F. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas, comparative plague-vector efficiency of Xenopsylla vexabilis hawaiiensis and Xenopsylla cheopis. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;14(4):681–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M., QUAN S. F. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. VII. The plague-vector efficiency of Hystrichopsylla linsdalei compared with Xenopsylla cheopis under experimental conditions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 May;7(3):317–322. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. V. The experimental plague-vector efficiency of wild rodent fleas compared with Xenopsylla cheopis, together with observations on the influence of temperature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Nov;5(6):1058–1070. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1956.5.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. 1. An apparatus for the experimental feeding of fleas. Exp Parasitol. 1954 Nov;3(6):525–537. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(54)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L. The concept of vector efficiency in experimental studies of plague. Exp Parasitol. 1957 Nov;6(6):599–609. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(57)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPPIE J., COCKING E. C., SMITH H. A non-toxic complex from Pasteurella pestis which immunises both guineapigs and mice. Lancet. 1958 Feb 1;1(7014):246–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPPIE J., SMITH H., COCKING E. C. Lethality for guinea pigs of ultrasonic extracts of Pasteurella pestis: its relationship to death of guinea pigs from plague. Nature. 1957 Nov 23;180(4595):1136–1136. doi: 10.1038/1801136a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHUNDANOV L. E., KOLESNIK V. S., PLETNIKOVA G. P. K voprosu o sravnitel'noi immunogennoi effektivnosti protivochumnoi syvorotki i ee globulinovykh fraktsii. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1958 Jul;29(7):110–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPP W. Ein Beitrag zur Beweglichkeit von Past. Pseudotuberculosis. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1956;142(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPP W., MASSHOFF W. Zur Atiologie der abszedierenden retikulozytären Lymphadenitis, einer praktisch wichtigen, vielfach unter dem Bilde einer akuten Appendizitis verlaufenden Erkrankung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1954 Aug 27;79(35):1266–1271. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1119840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOROBKOVA E. I. Deistvie glikokola na chumnoi mikrob. III. O prirode chumnogo toksina i ego znachenii v aktivnoi immunizatsii. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1957 Nov;28(11):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUPFERBERG L. L., HIGUCHI K. Role of calcium ions in the stimulation of growth of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):120–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.120-121.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., TRAPANI R. J. A hemagglutination test for plague antibody with purified capsular antigen of Pasteurella pestis. Am J Hyg. 1954 Mar;59(2):150–156. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., WEIMBERG R., DOWLING J. H., EVENSON M., ROCKENMACHER M., WOLOCHOW H. The oxidative dissimilation of serine by Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1954 Mar;67(3):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.3.369-376.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOOSJES F. E. Is the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout) responsible for the disappearance of plague from Western Europe? Doc Med Geogr Trop. 1956 Jun;8(2):175–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCHIAVELLO A. Estudios sobre peste selvática en América del Sur. I. Concepto y clasificación de la peste selvática. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1955 Oct;39(4):339–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCHIAVELLO A. Estudios sobre peste selvática en América del Sur. II. Peste selvatica en la region fronteriza del Peru y Ecuador. 2. El foco de peste selvática del distrito de Lancones, departamento de Piura, Peru. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1957 Sep;43(3):225–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCHIAVELLO A. Estudios sobre peste selvática en América del Sur. III. Peste selvática en la cordillera de Huancabamba, Perú. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1958 Jun;44(6):484–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCHIAVELLO A. Estudios sobre peste selvática en América del Sur. IV Transmisión experimental de la peste por Polygenis litargus. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1958 Aug;45(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCHIAVELLO A. Reservoirs and vectors of plague. J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 Dec;57(12):294–concl. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCRUMB F. R., Jr, LARSON A., MEYER K. F. The chemotherapy of experimental plague in the primate host. J Infect Dis. 1953 May-Jun;92(3):273–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/92.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCRUMB F. R., Jr, MERCIER S., ROBIC J., BOUILLAT M., SMADEL J. E., WOODWARD T. E., GOODNER K. Chloramphenicol and terramycin in the treatment of pneumonic plague. Am J Med. 1953 Mar;14(3):284–293. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERCIER S., RAZAFINDRAKOTO J. B. Bilan de trois années de campagnes de désinsectisation domestique à Tanarive. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1953;46(3):463–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K. F. The natural history of plague and psittacosis. Public Health Rep. 1957 Aug;72(8):705–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKULIN M. A. K voprosu ob epidemiologicheskikh osobennostiakh chumy. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1957 Oct;28(10):142–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES V. I., KINNEY A. R. An apparatus for rapid collection of fleas from rodent nests. J Parasitol. 1957 Dec;43(6):656–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES V. I., KINNEY A. R., STARK H. E. Flea-host relationships of associated Rattus and native wild rodents in the San Francisco Bay area of California, with special reference to plague. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1957 Jul;6(4):752–760. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1957.6.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHR C. O., SMITH W. W. Eradication of murine typhus fever in a rural area: preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;16(2):255–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY K. F. An ecological appraisal of host-ectoparasite relationships in a zone of epizootic plague in Central California. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1957 Nov;6(6):1068–1086. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1957.6.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEL R., GIRARD G. Indications et limites de la réaction d'hémagglutination protéinique dans la peste. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1955;48(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGG J. E., FRIEDMAN S. B., ANDREWS A. W., SURGALLA M. J. Factors influencing the loss of virulence in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.185-191.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1949;26(4):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1949.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUDIN J. B. Specific precipitation in gels and its application to immunochemical analysis. Methods Med Res. 1952;5:335–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRY W. R. An interference phenomenon caused by Pasteurella pestis. J Hyg (Lond) 1956 Jun;54(2):227–233. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004448x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATEL T. B., RODDE S. T. Use of D.D.T. as a plaque control measure in the Bombay State. Ind Med Gaz. 1952 May;87(5):217–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE F. E., LARSON A., FOSTER W. L., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. IX. The effect of cortisone on mouse resistance to attenuated strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Infect Dis. 1955 Mar-Apr;96(2):168–173. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEDROLA GIL G. La peste en la actualidad; sus avances y sus problemas. Med Colon. 1956 May 1;27(5):411–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KARTMAN L., McMANUS A. G. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. II. Experimental blocking of Xenopsylla cheopis with an avirulent strain of P. pestis. Science. 1954 Dec 31;120(3131):1101–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3131.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., MCMANUS A. G., MEYER K. F. Comparisons of sulfisoxazole with sulfadiazine, and thiocymetin with chloramphenicol, in chemotherapy of experimental plague in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955 Nov;4(6):1028–1036. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1955.4.1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., VON FINTEL H., McMANUS A. G. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco Bay area of California. II. Efficiency of bacterial culture compared to animal inoculation as methods for detecting Pasteurella pestis in wild rodent fleas. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jul;7(4):411–415. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANSOM J. P., KRUEGER A. P. Chronic pneumonic plague in Macaca mulatta. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 Nov;3(6):1040–1054. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1954.3.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANSOM J. P., QUAN S. F., HOGGAN M. D., OMI G. Antigenic comparisons of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Feb;88(2):173–176. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANSOM J. P., QUAN S. F., OMI G., HOGGAN M. D. The role of serum proteins in gel-precipitin patterns of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1955 Oct;75(4):265–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANSOM J. P. Some aspects of relationship between antigens of Pasteurella pestis and Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Dec;93(3):551–554. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., AJL S. Metabolic reaction of Pasteurella pestis. II. The fermentation of glucose. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):298–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.298-302.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., AJL S. Metabolic reactions of Pasteurella pestis. III. The hexose monophosphate shunt in the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):713–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.713-718.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., AJL S. Metabolic reactions of pasteurella pestis. I. Terminal oxidation. J Bacteriol. 1954 Apr;67(4):379–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.4.379-386.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAXENA K. C., SAGAR P., AGARWALA S. C., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Studies in the enzyme make-up of Pasteurella pestis. IV. Transamination reactions in virulent and avirulent strains. Indian J Med Res. 1957 Apr;45(2):161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
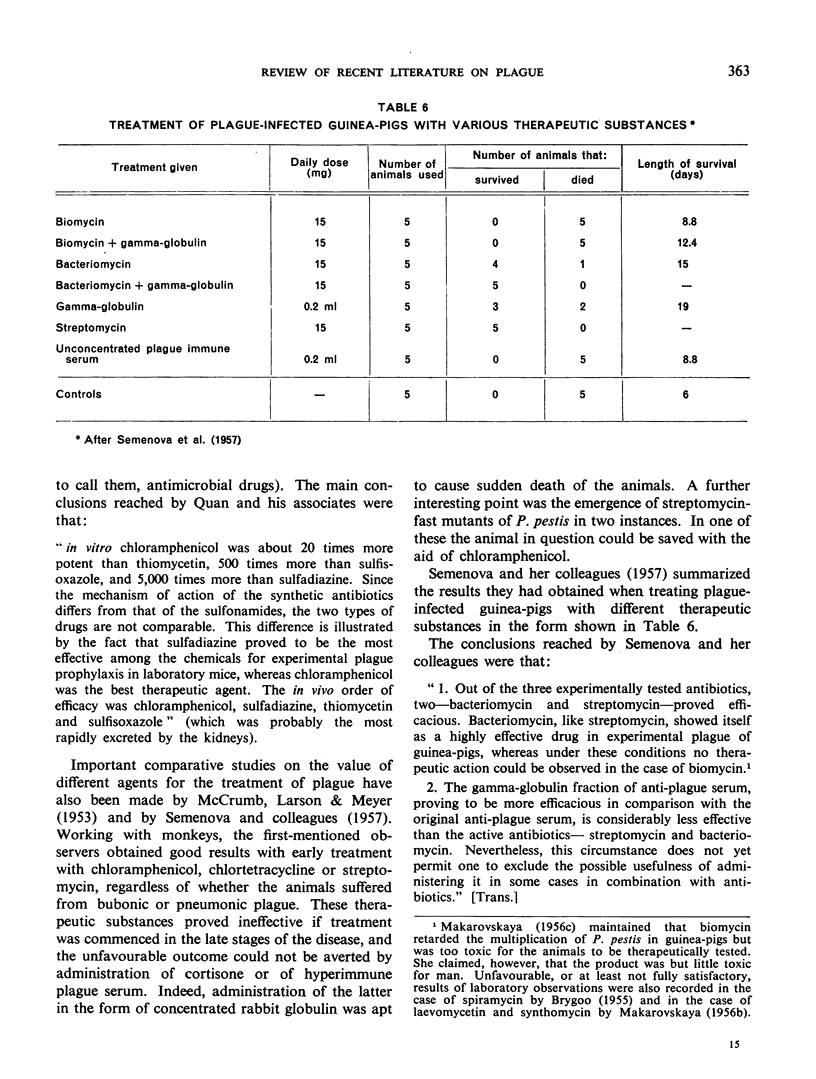
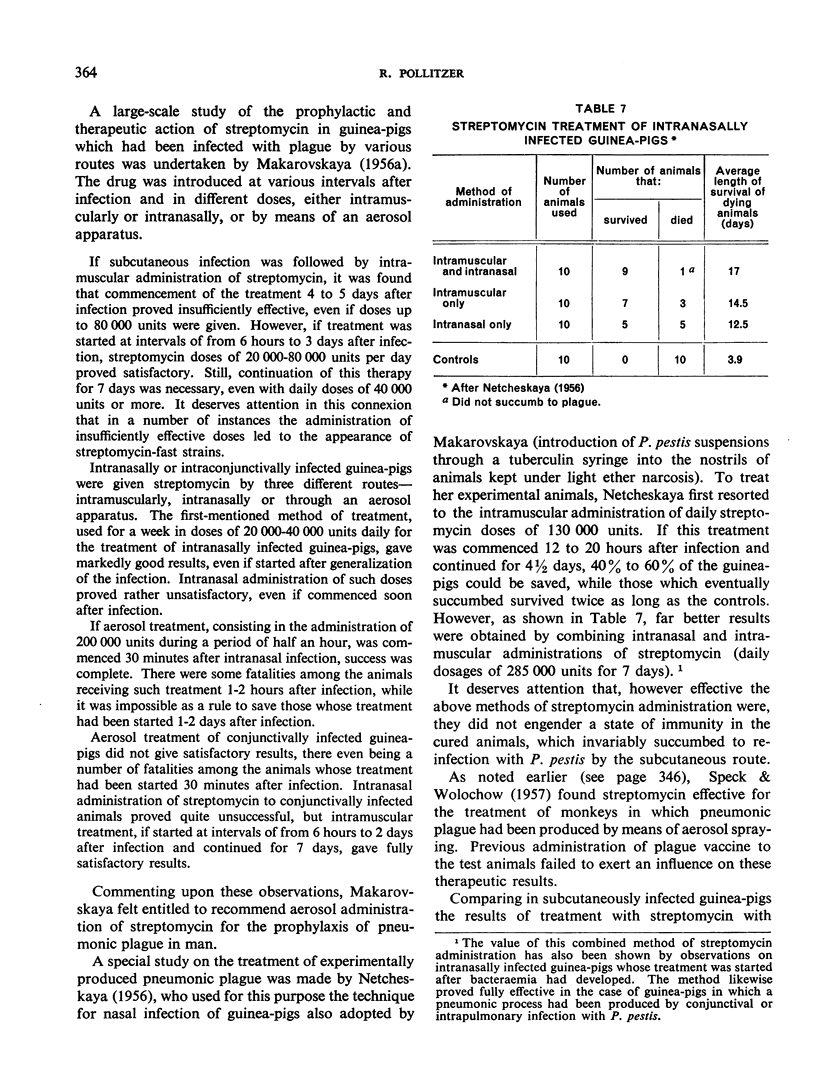
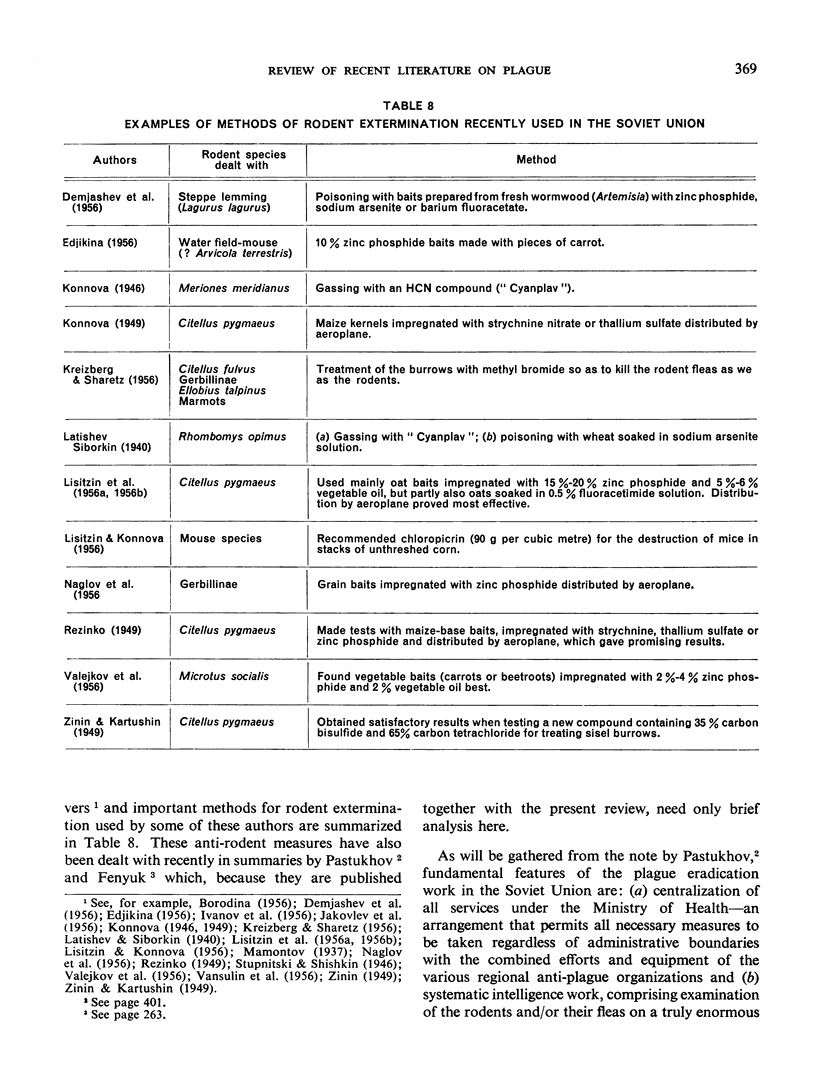
- SEMENOVA E. L., KARTASHEVA A. L., ABRAMOVA G. F., LOPATUKHINA L. G. O sravnitel'noi lechebnoi effektivnosti bakteriomitsina, biomitsina, streptomitsina i gammaglobulina pri chume; v eksperimente. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1957 Mar;28(3):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHISHKIN A. K. Rostovskii-na-Donu nauchno-issledovatel'skii protivochumnyi institut Ministerstva zdravookhraneniia SSSR. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1957 Sep;28(9):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN S. J., HIGUCHI K., MEYERS E. Production of protective antigens by Pasteurella pestis in a synthetic medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 May;86(1):112–114. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN S. J. The isolation of fractions from Pasteurella pestis for use in a hemagglutination test. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. N., EDDY G. W. Techniques for rearing and handling body lice, Oriental rat fleas, and cat fleas. Bull World Health Organ. 1954;10(1):127–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., KEPPIE J., STANLEY J. L. A method for collecting bacteria and their products from infections in experimental animals, with special reference to Bacillus anthracis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Oct;34(5):471–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. N., MCCAMISH J., SEELY J., COOKE G. M. The development of pneumonic plague in mice and the effect of paralysis of respiratory cilia upon the course of infection. J Infect Dis. 1957 May-Jun;100(3):215–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/100.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIVACK M. L., FOSTER L., LARSON A., CHEN T. H., BAKER E. E., MEYER K. F. The immune response of the guinea pig to the antigens of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1958 Feb;80(2):132–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIVACK M. L., KARLER A. Purification of the toxin of Pasteurella pestis by continuous-flow paper electrophoresis. J Immunol. 1958 Jun;80(6):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRIKANTAN T. N., AGARWALA S. C., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Studies in the enzyme make-up of Pasteurella pestis. III. Oxidative metabolism of virulent and avirulent strains. Indian J Med Res. 1957 Apr;45(2):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRIKANTAN T. N., AGARWALA S. C., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Studies in the enzyme make-up of Pasteurella pestis. V. Dehydrogenase activity of virulent and avirulent strains. Indian J Med Res. 1957 Oct;45(4):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK H. E. Five new fleas of the genus Thrassis jordan, 1929 (Ceratophyllidae: Siphonaptera), a genus of known importance in plague transmission. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):332–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK H. E., KARTMAN L. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. VI. The laboratory culture of Xenopsylla vexabilis hawaiiensis Jordan, 1932. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1957 Jul;6(4):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINIGER F. Fortschritte der Rattenbekämpfung. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1953;160(1-5):300–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINIGER F., KNOTHE H. Die hygienische Bedeutung der Nagetiere in Schleswig-Holstein. Arztl Wochensch. 1951 Dec 14;6(50):1189–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWELLENGREBEL N. H. Researches on ectoparasites of man in the vicinity of Marrakech (Morocco). Doc Med Geogr Trop. 1953 Jun;5(2):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL E., CHEN T. H. Two simple tests for the differentiation of plague and pseudo tuberculosis bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):103–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.103-104.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARELA G., VAZQUEZ A. Hallazgo de la peste selvatica en la República Mexicana; infección natural del Cynomys mexicanus (perros llaneros) con Pasteurella pestis. Rev Inst Salubr Enferm Trop. 1954 Dec;14(4):219–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASILENKO V. S., TINKER I. S., SHIRANOVICH P. I. Bor'ba s blokhami krys v usloviiakh krupnykh gorodov kak mera profilaktiki chumy. I. Med Parazitol (Mosk) 1958 Jul-Aug;27(4):464–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN J., WALZ U., REEDAL J. S., AJL S. J. Studies on plague. II. Immunological properties of purified Pasteurella pestis toxin. J Bacteriol. 1955 Aug;70(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.2.170-176.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORSFOLD J. T. An outbreak of plague at Chitokoloki, Balovale. Cent Afr J Med. 1955 May;1(3):116–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


