Abstract
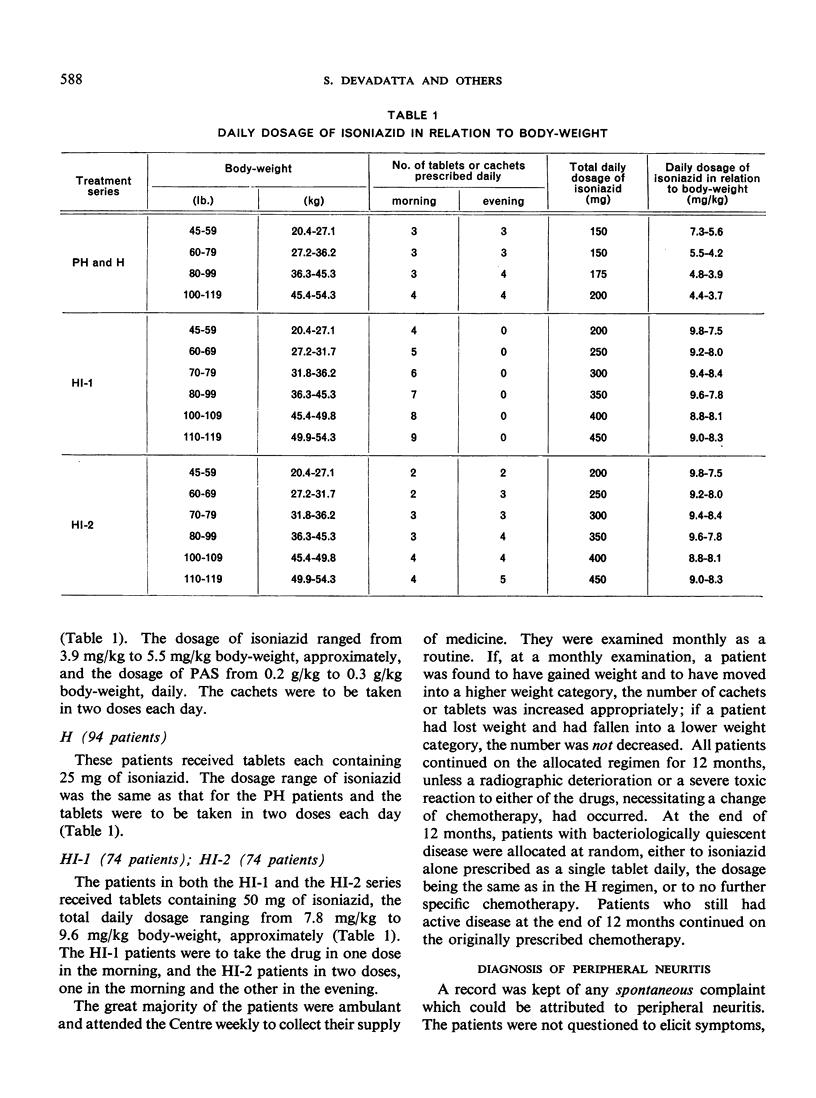
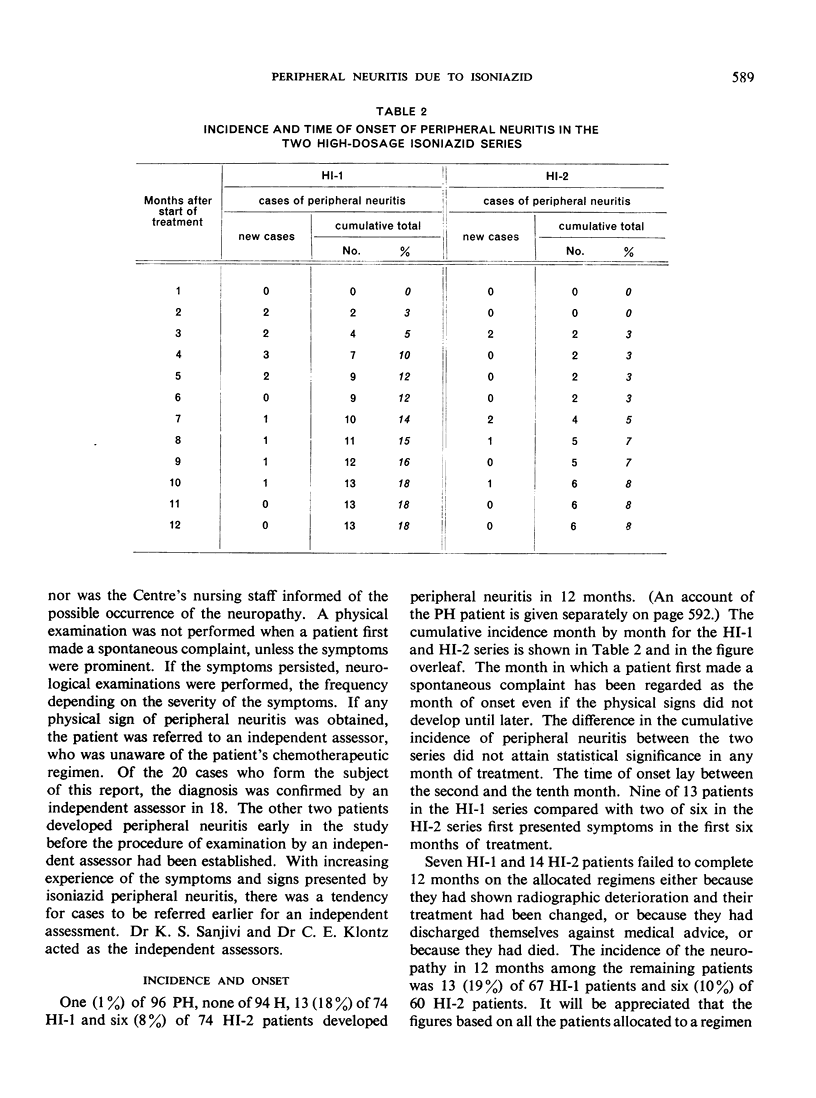
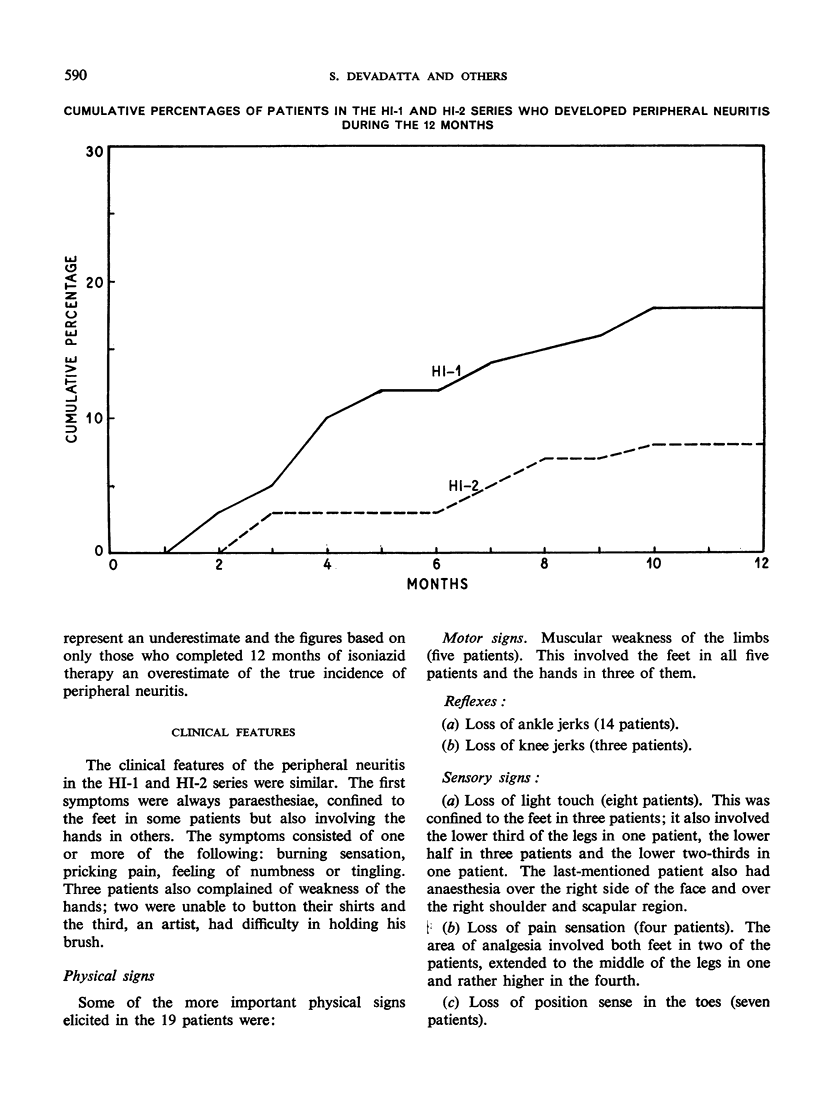
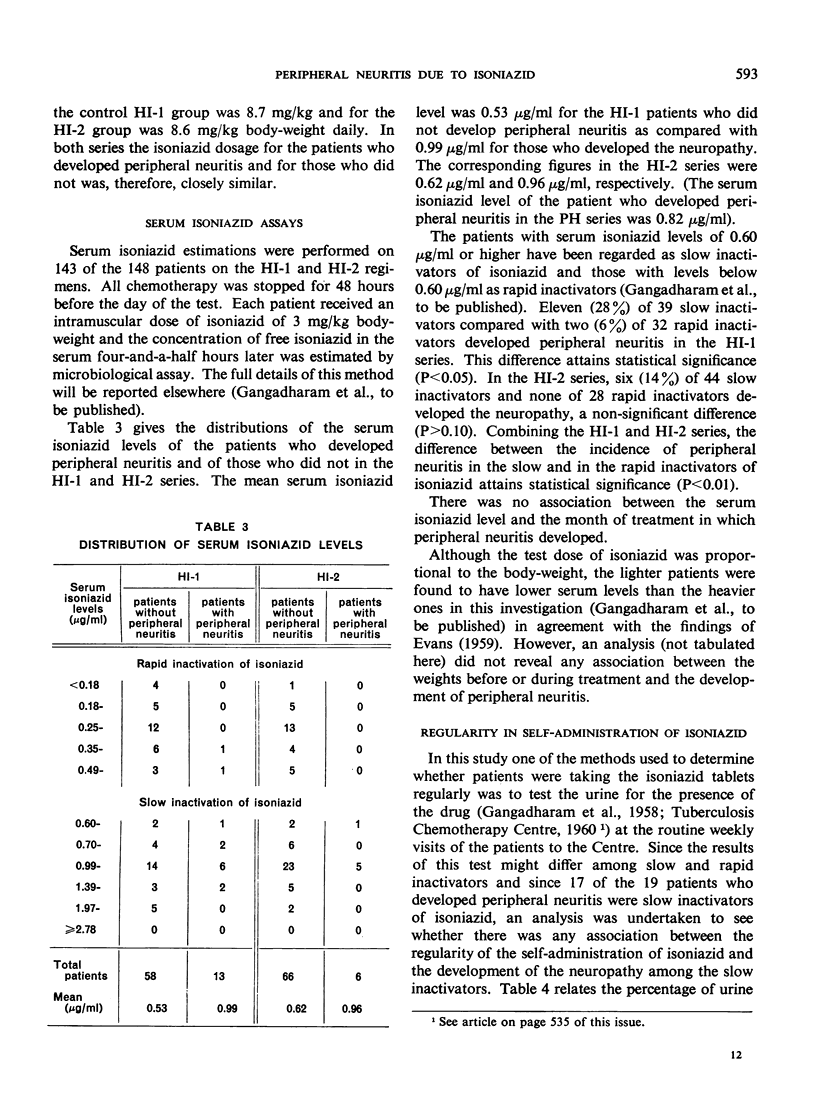
It is well known that in the treatment of tuberculosis with isoniazid the complication of peripheral neuritis may arise. This complication is normally rare when small dosages of the drug are used, but a high incidence of the neuropathy has recently been observed in East Africa in a group of malnourished tuberculous patients receiving isoniazid in comparatively low dosage (4-6 mg/kg body-weight daily). The present paper reports on 20 cases of peripheral neuritis encountered in Madras, India, among 338 poorly nourished tuberculous patients during a trial of four isoniazid regimens, two of low and two of high dosage (3.9-5.5 and 7.8-9.6 mg/kg body-weight daily, respectively). Nineteen of the 20 cases occurred in the two groups of patients receiving the high dosage and these 19 patients were found to have a higher mean serum level of free isoniazid than the patients in the same groups who did not develop the complication. The authors consider that dosages of 7.8-9.6 mg/kg body-weight daily should not be used for the mass therapy of poorly nourished patients unless steps are taken to prevent the development of peripheral neuritis. Pyridoxine has been reported to be an effective preventive, but is too expensive for use on a large scale. This study indicates, however, that administration of the cheaper vitamin B complex might give satisfactory results and warrants further investigation.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMSON C., IKARD S., TCHERTKOFF I., YILMAZ R. Large dose isoniazid regimen for pulmonary tuberculosis; effect of glutamic acid; management of drug toxicity with pyridoxine. Sea View Hosp Bull. 1956 Jul;16(2):62–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIEHL J. P., NIMITZ H. J. Studies on the use of high dose of isoniazid. I. Toxicity studies. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Sep;70(3):430–441. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIEHL J. P., SKLAVEM J. H. Toxicity of isoniazid. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Aug;68(2):296–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIEHL J. P., VILTER R. W. Effect of isoniazid on vitamin B6 metabolism; its possible significance in producing isoniazid neuritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Mar;85(3):389–392. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON G. J., ROBERTS G. B., TYRRELL W. F. The relationship of neuropathy to the treatment of tuberculosis with isoniazid. Scott Med J. 1956 Nov;1(11):350–354. doi: 10.1177/003693305600101102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMMON G. C., BURGE F. W., KING G. Neural toxicity in tuberculous patients treated with isoniazid (isonicotinic acid hydrazide). AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Jul;70(1):64–69. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320310070005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGADHARAM P. R., MITCHISON D. A., SUBBAIAH T. V., SHORT E. I. [The detection of isoniazid in urine]. Tubercle. 1958 Aug;39(4):191–200. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(58)80067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES H. B., BIEHL J. P., JONES A. P., SCHMIDT L. H. Metabolism of isoniazid in man as related to the occurrence of peripheral neuritis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Aug;70(2):266–273. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES W. A., JONES G. P. Peripheral neuropathy due to isoniazid; report of two cases. Lancet. 1953 May 30;1(6770):1073–1074. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ S., GRUVER R., SMITH B., McCORMICK G. Peripheral neuritis due to hydrazide derivatives. Dis Chest. 1954 Sep;26(3):264–267. doi: 10.1378/chest.26.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNT F. W., JENKINS B. E., FEREBEE S. H. Control study of comparative efficacy of isoniazid, streptomycin-isoniazid, and streptomycin; para-aminosalicylic acid in pulmonary tuberculosis therapy. IV. Report on forty-week observations on 583 patients with streptomycin susceptible infections. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Aug;68(2):264–269. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OESTREICHER R., DRESSLER S. H., MIDDLEBROOK G. Peripheral neuritis in tuberculous patients treated with isoniazid. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Sep;70(3):504–508. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.3.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILTER R. W., MUELLER J. F., GLAZER H. S., JARROLD T., ABRAHAM J., THOMPSON C., HAWKINS V. R. The effect of vitamin B6 deficiency induced by desoxypyridoxine in human beings. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Sep;42(3):335–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDORN W. S., ERVIN F. Schizophreniclike psychotic reactions with administration of isoniazid. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Sep;72(3):321–324. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02330030055005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD M. M. Central nervous system complications during I.N.H. treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Br J Tuberc Dis Chest. 1955 Jan;49(1):20–29. doi: 10.1016/s0366-0869(55)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


