Abstract
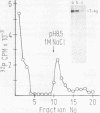
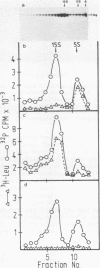
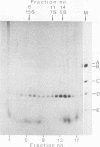
The state of phosphorylation and the relationship of various subclasses of simian virus 40 large T antigen (large T) differing in DNA-binding activity, degree of oligomerization, age, and subcellular distribution were investigated. Young large T (continuously labeled for 4 h late in infection) comprised about 20% of the total cellular large T. It was phosphorylated to a low degree and existed primarily in a monomeric form, sedimenting at 5S. More than 50% of this fraction bound to simian virus 40 DNA, preferentially to origin-containing sequences. Old large T (continuously labeled for 17 h, followed by a 4-h chase) represented the majority of the population. It was highly phosphorylated and predominantly in an oligomeric form, sedimenting at 15S to 23S. Only 10 to 20% of this fraction bound to simian virus 40 DNA. Another subclass of large T which was extracted from nuclei with 0.5 M salt resembled newly synthesized molecules in all properties tested; it was phosphorylated to a low degree, sedimented at 5S, and bound to viral DNA with high efficiency (greater than 70%). Two-dimensional phosphopeptide analysis of the individual subclasses revealed two distinct phosphorylation patterns, one characteristic for young, monomeric, and DNA-binding large T, the other for old, oligomeric, and non-DNA-binding large T. All sites previously identified in unfractionated large T (K.H. Scheidtmann et al., J. Virol. 44:116-133, 1982) were also phosphorylated in the various subclasses, but to different degrees. Peptide maps of the DNA-binding fraction, the 5S form, and the nuclear high-salt fraction showed two prominent phosphopeptides not previously characterized. Both peptides were derived from the amino-terminal region of large T, presumably involved in origin binding, and probably represent partially phosphorylated intermediates of known phosphopeptides. Our data show that the DNA-binding activity, age, and oligomerization of large T correlate with distinct states of phosphorylation. We propose that differential phosphorylation might play a role in the interaction of large T with DNA.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Reed S. I., Stark G. R. Characterization of the autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.22-27.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann E. A., Hand R. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation alter the structure of D2 hybrid T antigen. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.78-87.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler-White A. J., Humphrey G. W., Pigiet V. Association of polyoma T antigen and DNA with the nuclear matrix from lytically infected 3T6 cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry F., Harvey R., Smith A. E. Structure and biochemical functions of four simian virus 40 truncated large-T antigens. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):54–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.54-66.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Gheysen D., Knowland J., van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Evidence for the direct involvement of DNA replication origin in synthesis of late SV40 RNA. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):500–505. doi: 10.1038/300500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D. J., Tevethia M. J. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive, DNA-positive, nontransforming mutant of simian virus 40. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):605–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. A., Khoury G., Martin R. G. Phosphorylation of T-antigen and control T-antigen expression in cells transformed by wild-type and tsA mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):753–762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.753-762.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Nowak B., Burger C. Detection and characterization of multiple forms of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):92–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.92-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Westphal K. H., Brauer D., Cörlin D. Subclasses of simian virus 40 large T antigen: differential binding of two subclasses of T antigen from productively infected cells to viral and cellular DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Polyoma virus proteins: a description of the structural proteins of the virion based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and peptide analysis. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Scheller A., Barnet B., Hantzopoulos P., Oren M., Prives C. Different forms of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen varying in their affinities for DNA. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):456–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.456-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Ahrens B. SV40 early mutants that are defective for viral DNA synthesis but competent for transformation of cultured rat and simian cells. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman N., Brown M., Khoury G. Modification of SV40 T antigen by poly ADP-ribosylation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D. S., Carroll R. B. Complex of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen and 48,000-dalton host tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockmann U., Deppert W. Acylation: a new post-translational modification specific for plasma membrane-associated simian virus 40 large T-antigen. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):257–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Biochemical characterization of nuclear and cytoplasmic forms of SV40 tumor antigens encoded by parental and transport-detective mutant SV40-adenovirus 7 hybrid viruses. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):314–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Hunter T. Phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen in SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):526–532. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Hunter T., Walter G., Linke H. Evidence for simian virus 40 (SV40) coding of SV40 T-antigen and the SV40-specific proteins in HeLa cells infected with nondefective adenovirus type 2-SV40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):151–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.151-169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenarh M., Deppert W., Henning R. Mapping of a DNA-binding domain of simian virus 40 T-antigen using non-defective adenovirus 2--simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenarh M., Henning R. Self-assembly of simian virus 40 large T antigen oligomers by divalent cations. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):531–538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.531-538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenarh M., Henning R. Simian virus 40 T-antigen phosphorylation is variable. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 19;114(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80870-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison B., Kress M., Khoury G., Jay G. Simian virus 40 tumor antigen: isolation of the origin-specific DNA-binding domain. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):106–114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.106-114.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Williams R. C., Tjian R. Oligomeric structure of a simian virus 40 T antigen in free form and bound to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. The molecular basis of DNA-protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):718–723. doi: 10.1038/298718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Winocour E., Prives C. Differential affinities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico-DiLauro M., Martin R. G., Livingston D. M. Interaction of Simian Virus 40 chromatin with Simian Virus 40 T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):451–460. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.451-460.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Barnet B., Scheller A., Khoury G., Jay G. Discrete regions of simian virus 40 large T antigen are required for nonspecific and viral origin-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):73–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.73-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Beck Y., Gidoni D., Oren M., Shure H. DNA binding and sedimentation properties of SV40 T antigens synthesized in vivo and in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):123–130. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Renart J., Crawford L. V., Stark G. R. Specific association of simian virus 40 tumor antigen with simian virus 40 chromatin. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.78-87.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Kaiser A., Carbone A., Walter G. Phosphorylation of threonine in the proline-rich carboxy-terminal region of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.59-69.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Weil R., Frank G., Zuber H. Amino acid sequence analysis of fragments generated by partial proteolysis from large simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5627–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa M., Sugano S., Yamaguchi N. Association of simian virus 40 T antigen with replicating nucleoprotein complexes of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):320–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.320-330.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. B., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of dephosphorylated A protein to SV40 DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Galanti N., Jonak G. J., McKercher S., Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Baserga R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis and activation of rRNA genes by mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Different structural systems of the nucleus are targets for SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. Mutant of simian virus 40 large T-antigen that is defective for viral DNA synthesis, but competent for transformation of cultured rat cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):854–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.854-864.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B., Shaw S. B., Wilson V. G. Alternative interactions of the SV40 A protein with DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Wilson V. G., Ryder K. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of protein bound to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.151-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Collins J. K. Modification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):647–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.647-657.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Regulation of viral transcription and DNA replication by the SV40 large T antigen. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:5–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A., Clark R. Catalytic properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):103–111. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Metabolic turnover of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):442–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.442-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Flory P. J., Jr Phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):165–169. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Scheidtmann K. H., Carbone A., Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Antibodies specific for the carboxy- and amino-terminal regions of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5197–5200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson E., Revel M., Winocour E. Inhibition of simian virus 40 replication by interferon treatment late in the lytic cycle. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Improved localization of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):315–331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.315-331.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]