Abstract
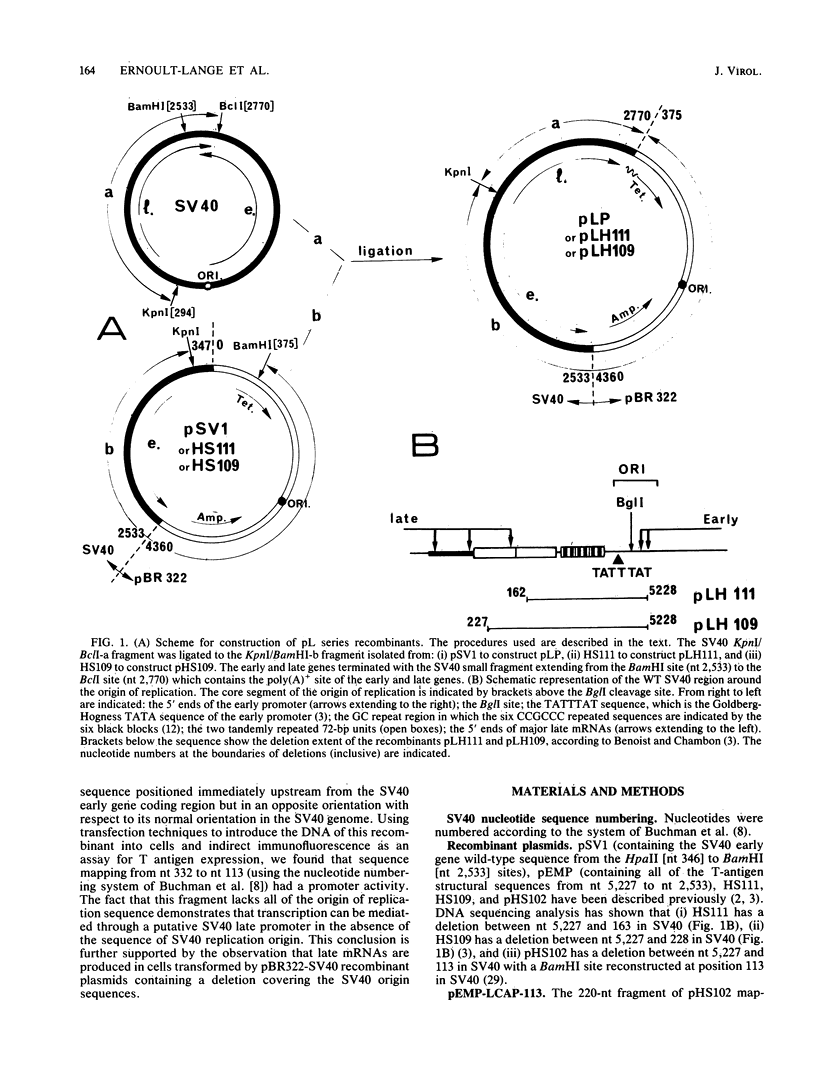
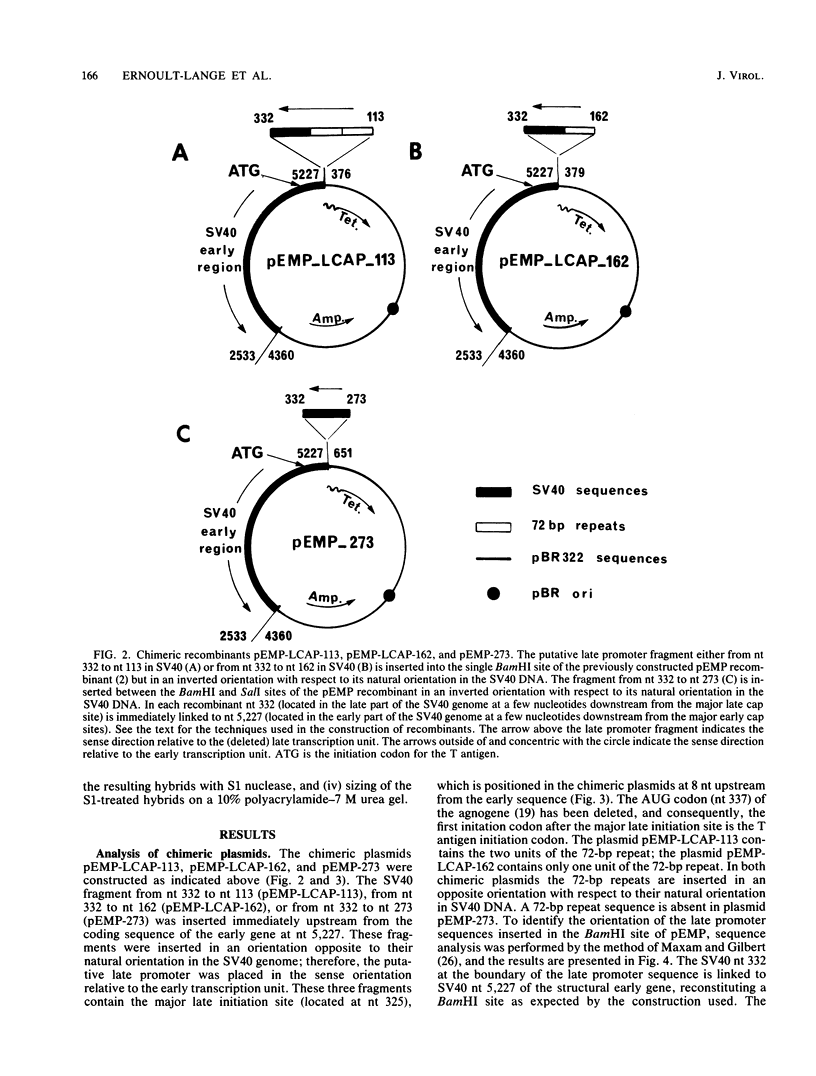
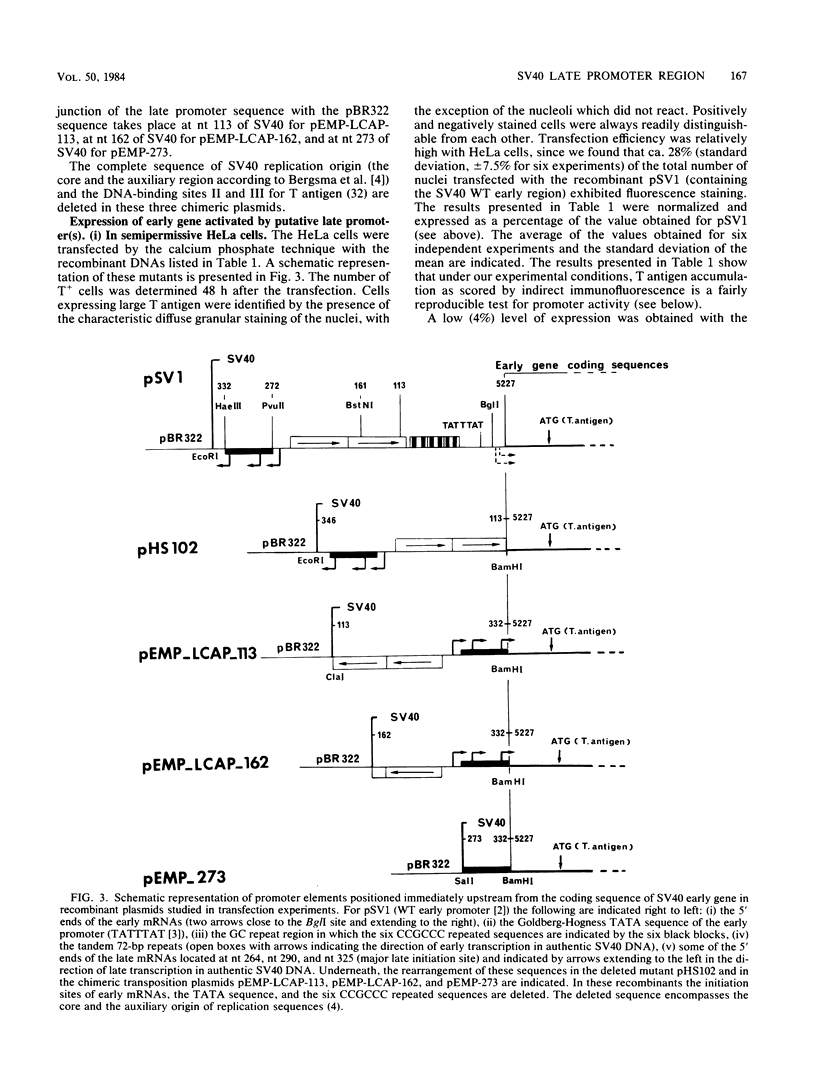
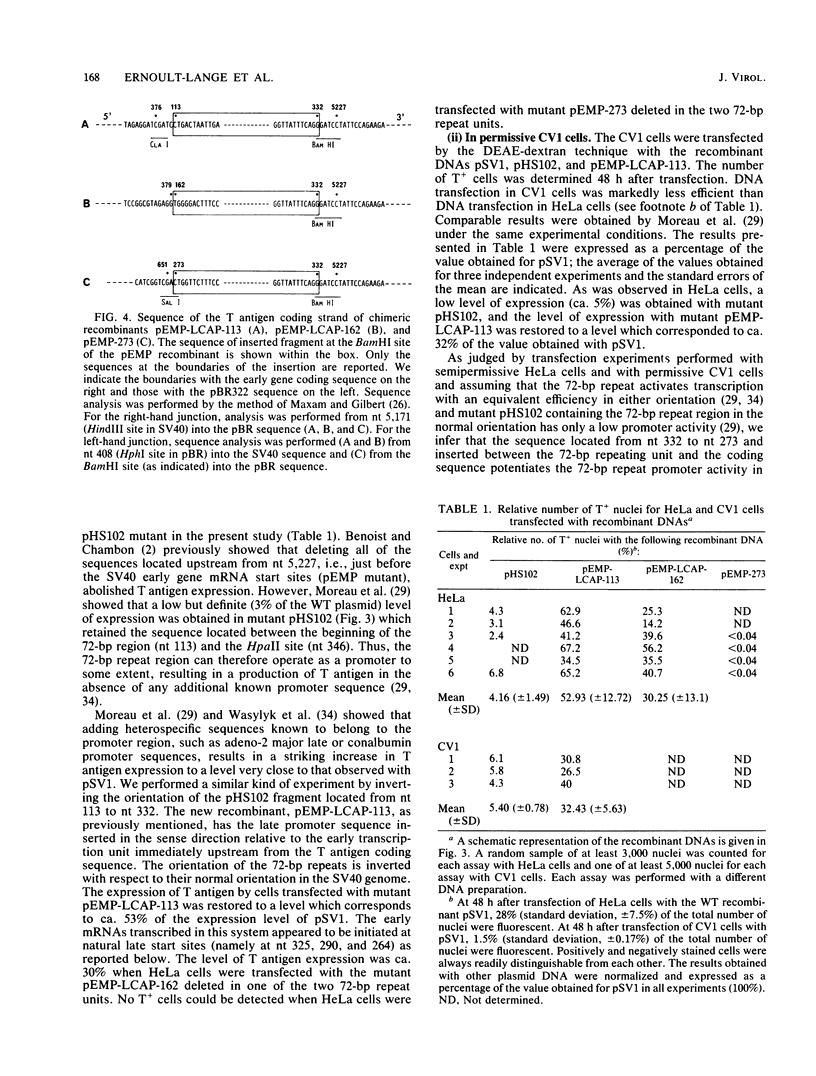
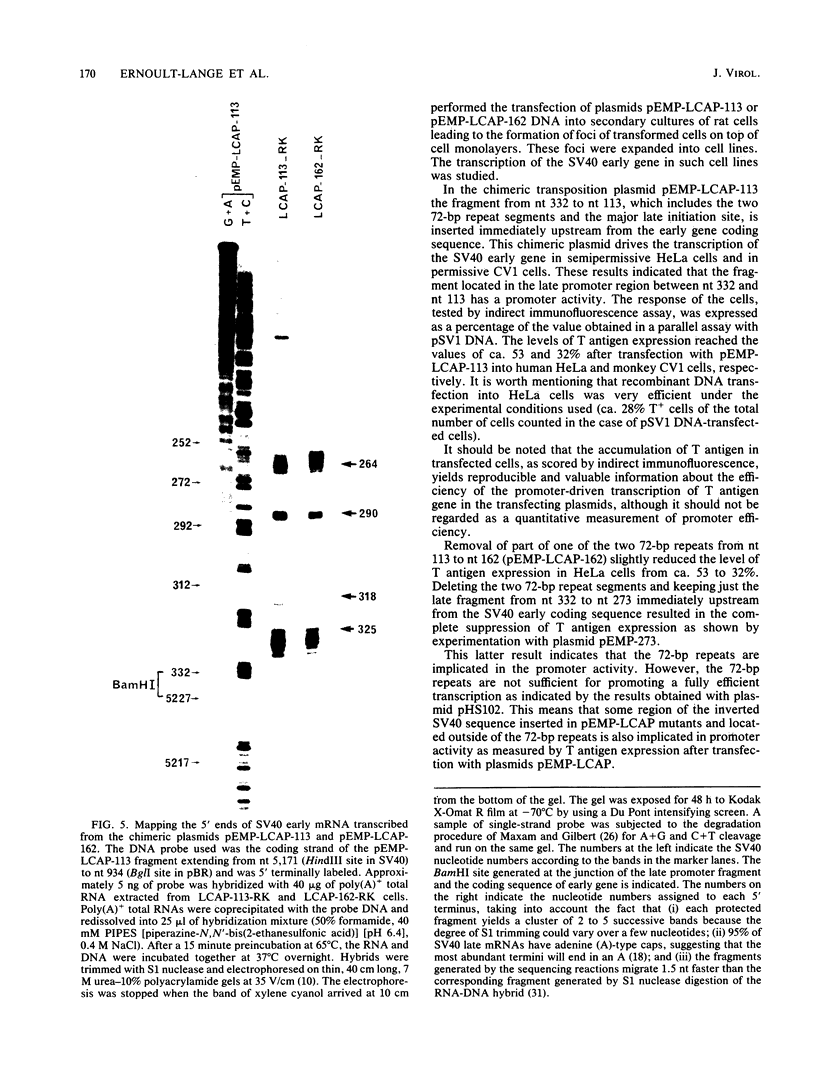
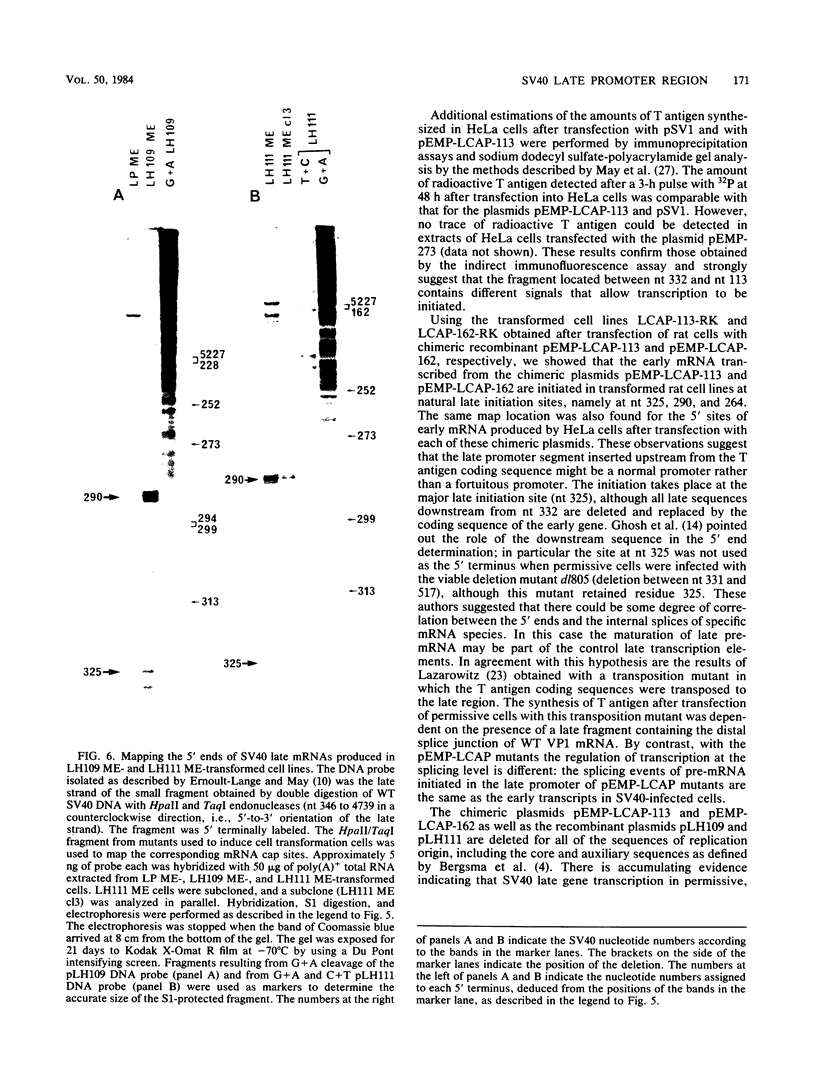
To improve our knowledge of the simian virus 40 (SV40) late promoter control region, we took advantage of the fact that T antigen can be expressed with a heterologous promoter. We constructed three chimeric plasmids (pEMP-273, pEMP-LCAP-162, and pEMP-LCAP-113) each with a putative late promoter sequence positioned immediately upstream from the SV40 early gene coding region but in an orientation opposite to its natural orientation in the SV40 genome. After transfection of the recombinant DNA into HeLa or CV1 cells, T antigen accumulation, as scored by indirect immunofluorescence, was used as a functional test for promoter activity. We found that the sequence mapping from nucleotides 332 to 273 is not sufficient for promoting transcription of SV40 early gene but does potentiate the promoter activity of the 72-base-pair repeats in initiating the transcription at natural late cap sites. Considering that both plasmids pEMP-LCAP-162 and pEMP-LCAP-113 lack all of the sequence of the SV40 replication origin, we conclude that SV40 transcription can be mediated through a putative late promoter in the absence of the sequence for the SV40 replication origin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. Deletions covering the putative promoter region of early mRNAs of simian virus 40 do not abolish T-antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Gheysen D., Knowland J., van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Evidence for the direct involvement of DNA replication origin in synthesis of late SV40 RNA. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):500–505. doi: 10.1038/300500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May E. Evidence of transcription from the late region of the integrated simian virus 40 genome in transformed cells: location of the 5' ends of late transcripts in cells abortively infected and in cells transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):756–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.756-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Manley J. L., Prives C. L. Methylation of simian virus 40 Hpa II site affects late, but not early, viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Piatak M., Mertz J. E., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P. Altered utilization of splice sites and 5' termini in late RNAs produced by leader region mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):610–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.610-624.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., van Heuverswyn H., Gheysen D., Fiers W. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of late mRNA induced by a viable simian virus 40 deletion mutant. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.484-493.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Sharp P. A. Expression of early and late simian virus 40 transcripts in the absence of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):592–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.592-597.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Sharp P. A. Sequences controlling in vitro transcription of SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2293–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., May E. Regulation of early and late simian virus 40 transcription: overproduction of early viral RNA in the absence of a functional T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.167-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange M., May E., May P. Ability of nonpermissive mouse cells to express a simian virus 40 late function(s). J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):940–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.940-951.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G. Simian virus 40 mutant with transposed T-antigen and VP1 genes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1025–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1025-1037.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Khoury G., Vande Woude G., Gruss P. Activation of SV40 genome by 72-base pair tandem repeats of Moloney sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):568–572. doi: 10.1038/295568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Lasne C., Prives C., Borde J., May P. Study of the functional activities concomitantly retained by the 115,000 Mr super T antigen, an evolutionary variant of simian virus 40 large T antigen expressed in transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):901–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.901-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Stephens D. L., Mertz J. E. Kinetics of accumulation and processing of simian virus 40 RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1581–1594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Subramanian K. N., Roy P., Weissman S. M. Late messenger RNA production by viable simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the leader region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):589–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. T antigen binding and the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]