Abstract
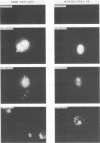
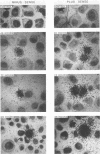
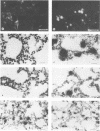
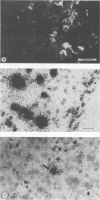
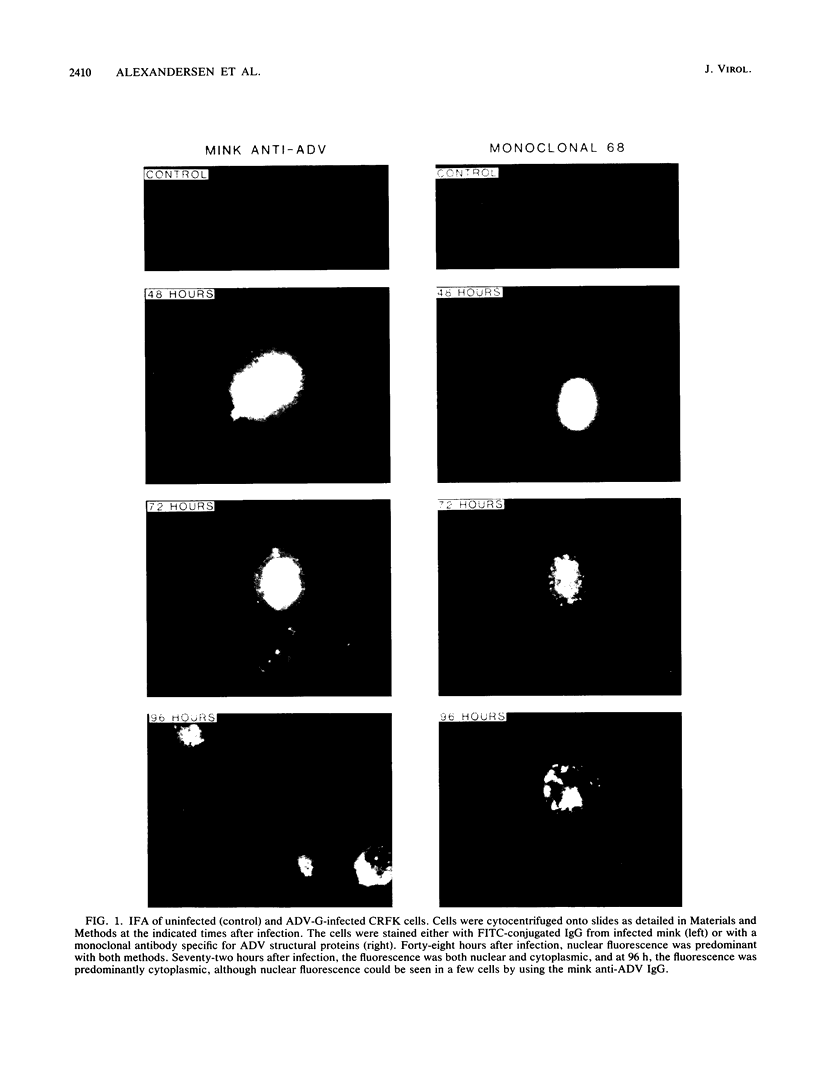
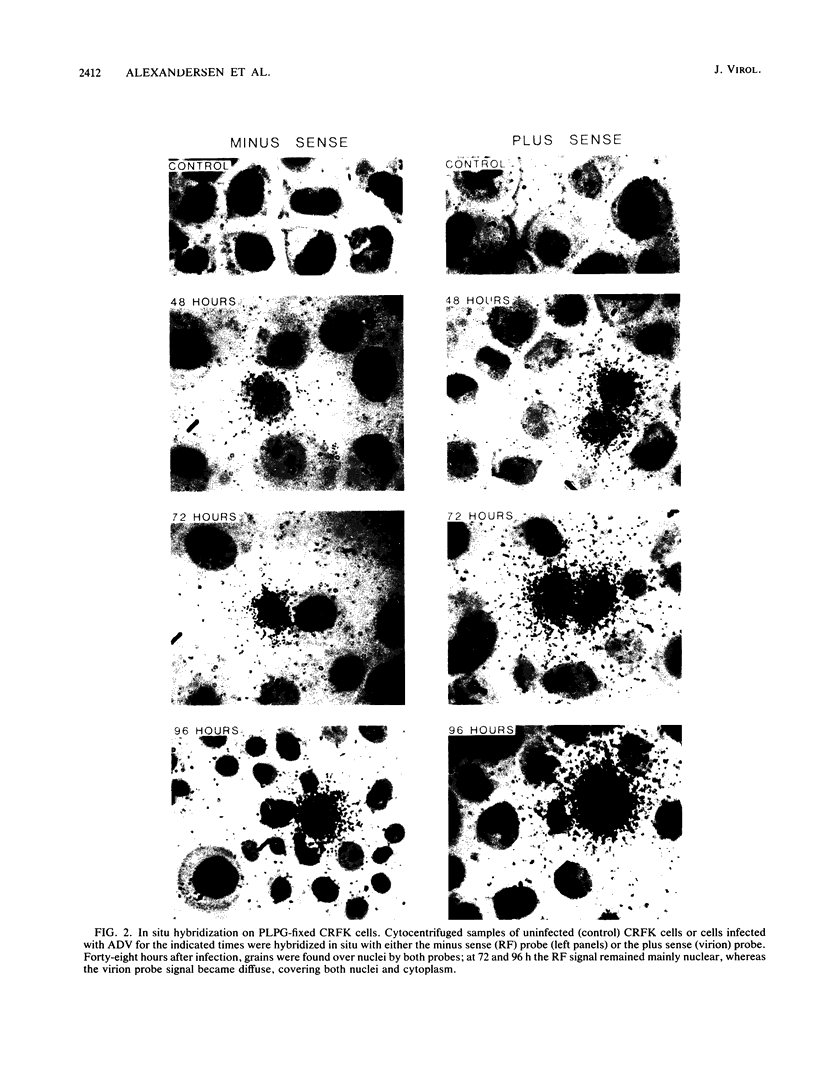
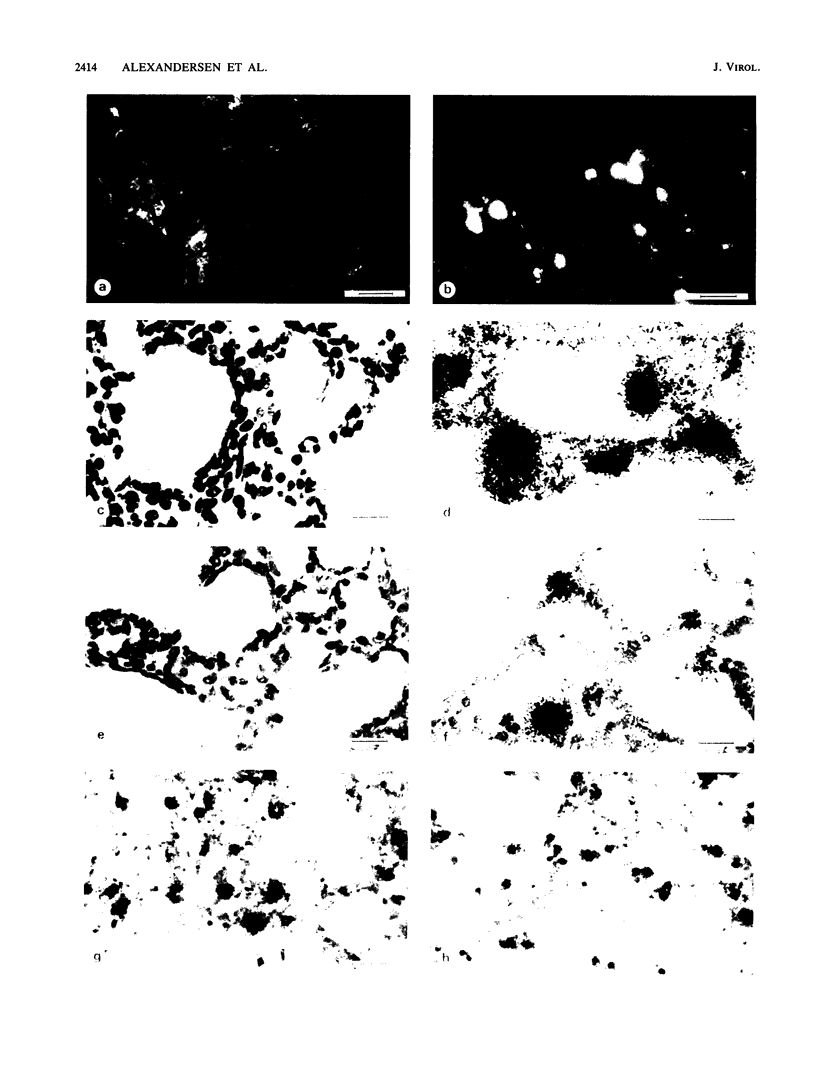
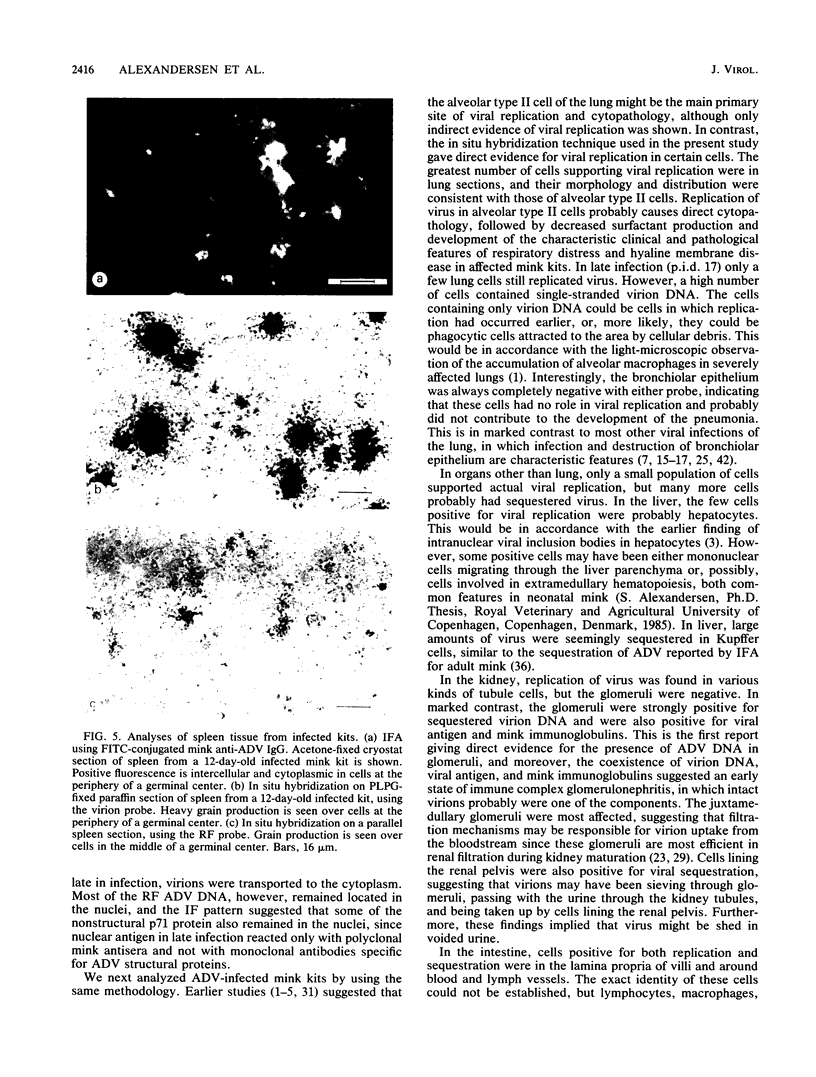
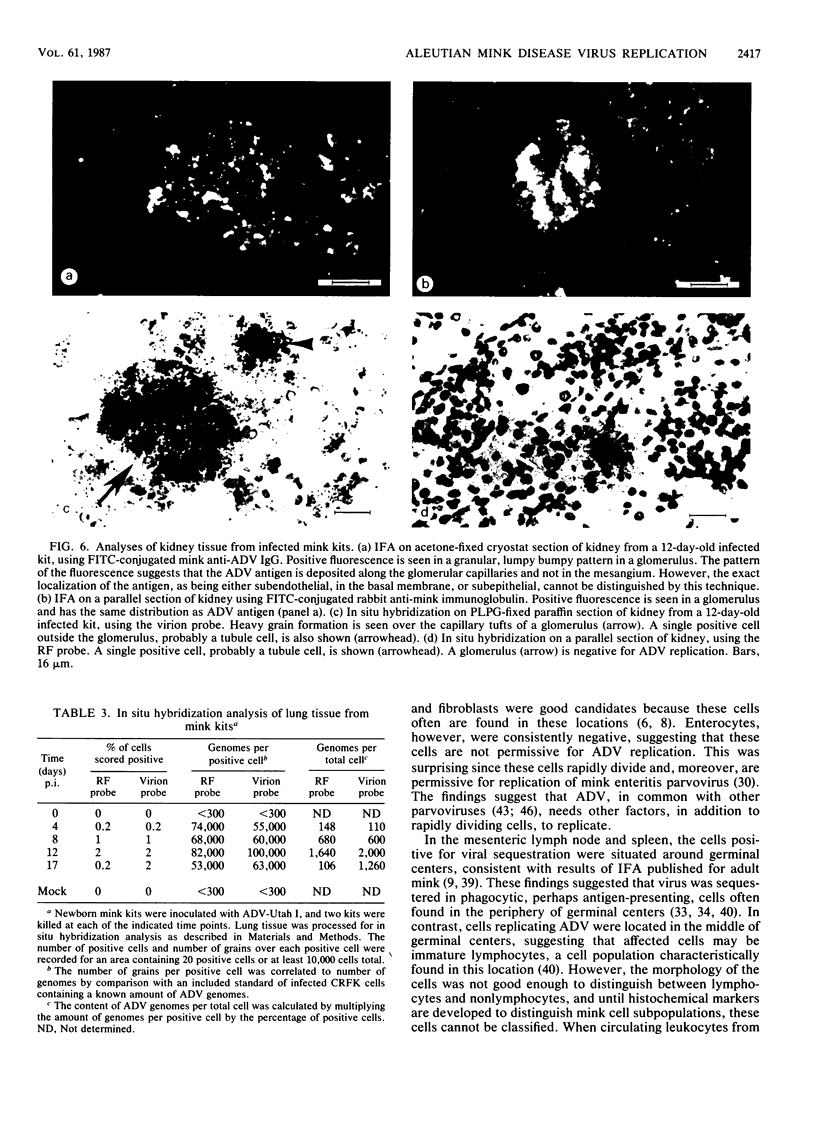
Strand-specific hybridization probes were utilized in in situ molecular hybridization specifically to localize replicative form DNA of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV). Throughout in vitro infection, duplex replicative form DNA of ADV was located in the cell nuclei. Single-stranded virion DNA and capsid proteins were present in the nuclei early in infection, but were later translocated to the cytoplasm. In neonatal mink, ADV causes acute interstitial pneumonia, and replicative forms of viral DNA were found predominantly in alveolar type II cells of the lung. Viral DNA was also found in other organs, but strand-specific probes made it possible to show that most of this DNA represented virus sequestration. In addition, glomerular immune complexes containing intact virions were detected, suggesting that ADV virions may have a role in the genesis of ADV-induced glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandersen S., Aasted B. Restricted heterogeneity of the early antibody response to Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Aug;94(4):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S. Acute interstitial pneumonia in mink kits: experimental reproduction of the disease. Vet Pathol. 1986 Sep;23(5):579–588. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Hau J. Rocket line immunoelectrophoresis: an improved assay for simultaneous quantification of a mink parvovirus (Aleutian disease virus) antigen and antibody. J Virol Methods. 1985 Feb;10(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Uttenthal-Jensen A., Aasted B. Demonstration of non-degraded Aleutian disease virus (ADV) proteins in lung tissue from experimentally infected mink kits. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;87(1-2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01310549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A. The histopathology of experimental pneumonia in pigs produced by Aujeszky's disease virus. Res Vet Sci. 1973 Mar;14(2):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo: demonstration of Aleutian disease virus DNA in tissues of infected mink. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Characterization of Aleutian disease virus as a parvovirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.836-843.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Bloom M., Hadlow W., Race R. Purification and ultrastructure of Aleutian disease virus of mink. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):456–457. doi: 10.1038/254456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ingram D. G. Antigen and antibody in Aleutian disease in mink. I. Precipitation reaction by agar-gel electrophoresis. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):555–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Fabricant C. G., Nelson-Rees W. A. Development, characterization, and viral susceptibility of a feline (Felis catus) renal cell line (CRFK). In Vitro. 1973 Nov-Dec;9(3):176–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02618435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutlip R. C., Lehmkuhl H. D. Experimentally induced parainfluenza type 3 virus infection in young lambs: pathologic response. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Dec;43(12):2101–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Molineaux S., Clements J. E., Ghotbi Z. Slow, persistent replication of lentiviruses: role of tissue macrophages and macrophage precursors in bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7086–7090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSON J. B., GORHAM J. R., LEADER R. W., WAGNER B. M. Experimental hypergammaglobulinemia in mink. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:357–364. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow W. J., Race R. E., Kennedy R. C. Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1016-1023.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. A., Evan A. P. Maturation of the glomerular visceral epithelium and capillary endothelium in the puppy kidney. Anat Rec. 1979 Jan;193(1):1–21. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karstad L., Pridham T. J. Aleutian Disease of Mink: I. Evidence of its Viral Etiology. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1962 May;26(5):97–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimsey P. B., Engers H. D., Hirt B., Jongeneel C. V. Pathogenicity of fibroblast- and lymphocyte-specific variants of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):8–13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.8-13.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S., Alexandersen S., Lund E., Have P., Hansen M. Acute interstitial pneumonitis caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1984 Sep;92(5):391–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb04419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. J., 3rd, NOSSAL G. J. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. VI. THE PHAGOCYTIC RETICULUM OF LYMPH NODE FOLLICLES. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1075–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Ada G. L., Austin C. M., Pye J. Antigens in immunity. 8. Localization of 125-I-labelled antigens in the secondary response. Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):349–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Aleutian disease of mink. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:261–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. 3. Immune complex arteritis. Am J Pathol. 1973 May;71(2):331–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Chesebro B., Bloom M. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. Monoclonal antibodies against Aleutian disease virus distinguish virus strains and differentiate sites of virus replication from sites of viral antigen sequestration. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):285–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck J. A., Koestner A., Kasza L. The lesions of porcine adenoviral infection in germfree and pathogen-free pigs. Pathol Vet. 1967;4(6):537–552. doi: 10.1177/030098586700400603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George J. A., Cranz D. L., Zicker S. C., Etchison J. R., Dungworth D. L., Plopper C. G. An immunohistochemical characterization of rhesus monkey respiratory secretions using monoclonal antibodies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):556–563. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN G. W., HELMBOLDT C. F. Aleutian disease of mink. I. Experimental transmission of the disease. Am J Vet Res. 1962 Nov;23:1280–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]