Abstract
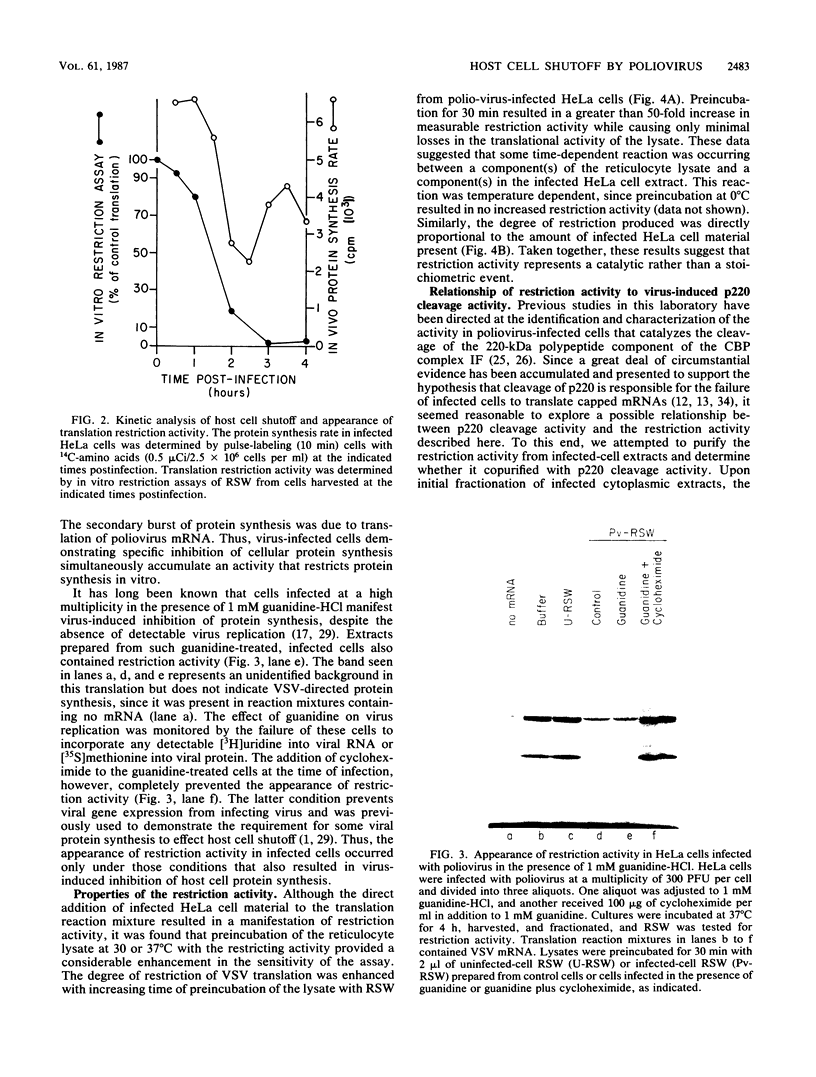
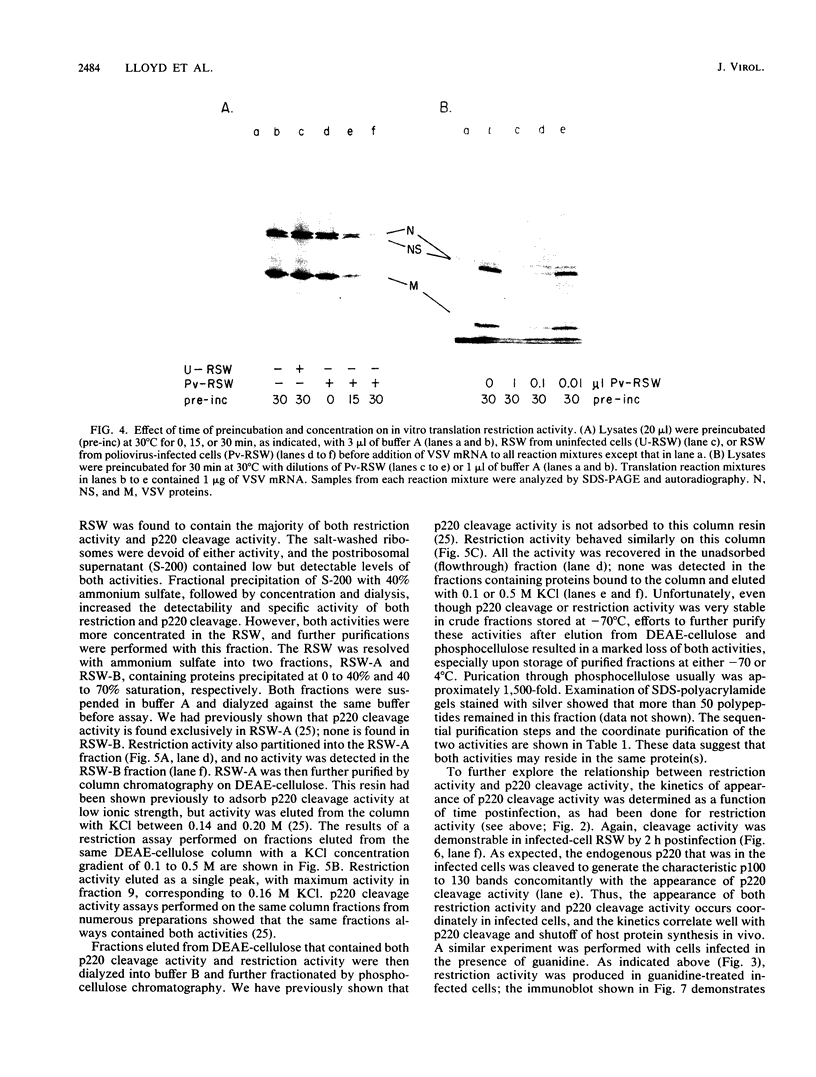
Poliovirus infection of HeLa cells results in a rapid inhibition of host protein synthesis by a mechanism that does not affect the translation of poliovirus RNA. It has been suggested that this virus-induced translational control results from inactivation of the cap-binding protein complex, and it has been shown that the 220-kilodalton component(s) (p220) of the cap-binding protein complex is cleaved in infected HeLa cells to form antigenically related polypeptides of 100 to 130 kilodaltons. We have previously described an activity in infected cells that specifically restricts translation of capped mRNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Here, we describe further refinements and characterization of restriction assay. We determined that the assay is a good in vitro model for study of host cell shutoff by several criteria: (i) translation was inhibited in both instances at the step involving mRNA binding to ribosomes; (ii) translation of capped mRNA was specifically inhibited, whereas translation of poliovirus RNA was not; (iii) restriction activity appeared in infected cells with kinetics which parallel host cell shutoff; and (iv) restriction activity, like the specific inhibition of host translation, appeared in cells infected in the presence of guanidine-HCl. The restricting activity was partially purified from poliovirus-infected cells and was compared with the virus-induced p220 cleavage activity. Both activities copurified through numerous cell fractionation and biochemical fractionation procedures. However, specific restriction of capped mRNA translation in reticulocyte lysates occurred without complete cleavage of the endogenous p220.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgert K., Koschel K., Täuber H., Wecker E. Effect of inactivation by hydroxylamine on early functions of poliovirus. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.1-6.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Initiation factor preparations from poliovirus-infected cells restrict translation in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E. Specificity of initiation factor preparations from poliovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):573–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.573-575.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B., Ehrenfeld E. Two-dimensional gel analyses of the 24-kDa cap binding protein from poliovirus-infected and uninfected HeLa cells. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):497–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Etchison D., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis eukaryotic initiation factors 4A and 4B are not altered by poliovirus infection of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7236–7239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Manis S. Inhibition of 80S initiation complex formation by infection with poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):441–445. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Milburn S., Hershey J. W. Demonstration in vitro that eucaryotic initiation factor 3 is active but that a cap-binding protein complex is inactive in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.832-837.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. INHIBITION OF HOST CELL MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS BY HIGH MULTIPLICITIES OF POLIOVIRUS UNDER CONDITIONS PREVENTING VIRUS SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:574–581. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Etchison D., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Association of cap-binding protein with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 in initiation factor preparations from uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):200–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.200-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Control of protein synthesis in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. I. mRNA discrimination by crude initiation factors. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):510–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.510-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Ehrenfeld E. The effect of poliovirus infection on the translation in vitro of VSV messenger ribonucleoprotein particles. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):415–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Goldstein E., Penman S. Poliovirus-induced inhibition of polypeptide initiation in vitro on native polyribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1834–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Dodds J. T., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Betsch D. F., Weith H. L., Thach R. E. Influence of 5' proximal secondary structure on the translational efficiency of eukaryotic mRNAs and on their interaction with initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13979–13989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Edery I., Hanecak R., Wimmer E., Sonenberg N. Poliovirus protease 3C (P3-7c) does not cleave P220 of the eucaryotic mRNA cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):489–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.489-493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Edery I., Sonenberg N. Isolation and structural characterization of cap-binding proteins from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):515–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.515-524.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz R., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in HeLa cells. 3. Inhibition during poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):661–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.661-668.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus protease does not mediate cleavage of the 220,000-Da component of the cap binding protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2723–2727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E., Ehrenfeld E. Cleavage of the cap binding protein complex polypeptide p220 is not effected by the second poliovirus protease 2A. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Emmert A. Modulation of the expression of poliovirus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Guertin D., Lee K. A. Capped mRNAs with reduced secondary structure can function in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1633–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Rose J. K., Leong K., Bergmann J. E., Gordon J., Baltimore D. Purification of a factor that restores translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA in extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]