Abstract
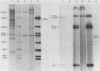
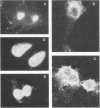
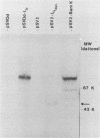
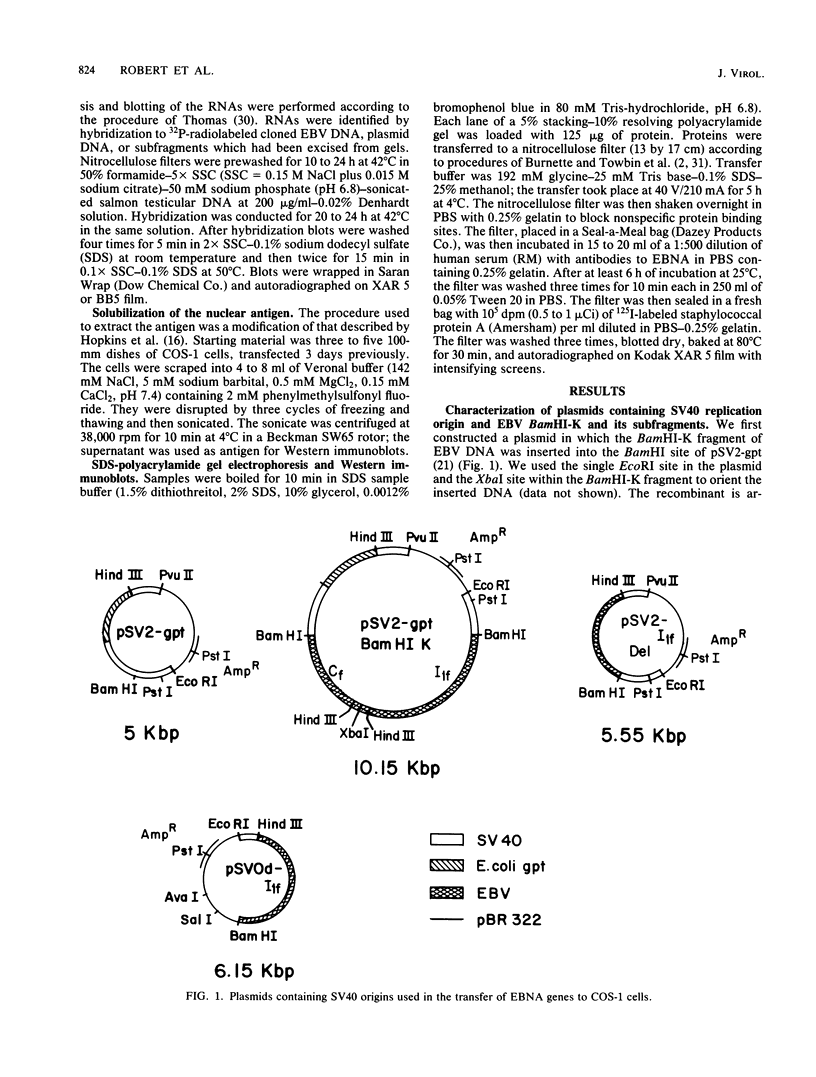
In a previous study the BamHI-K fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA was shown to induce a nuclear antigen, Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA), when cotransfected with the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene into mouse LTK- cells. We have now inserted the BamHI-K fragment and a BamHI/HindIII subfragment, I1f , into shuttle vectors containing the origin of replication of simian virus 40. These plasmids have been introduced into COS-1, which are monkey kidney cells transformed by an origin-defective simian virus 40 genome. This expression system permitted rapid characterization of antigens, mRNAs, and proteins related to EBNA. The same-sized EBNA protein (approximately 78,000) was made after transfection with BamHI-K (5.2 kilobase pairs [kbp]) or the I1f subfragment (2.9 kbp). A deletion of about 600 bp occurred when the I1f fragment was propagated on the pSV2 plasmid in Escherichia coli. The deleted fragment gave rise to a smaller protein (approximately 52,000). These data provide evidence that EBNA is encoded by the 2.9-kbp I1f and is not an induced cellular protein. Nuclear antigen and polypeptide expression occurred equally well when the Epstein-Barr virus DNA was cloned on PSV2 -gpt or pSVOd . The latter plasmid lacks sequences allowing for efficient early gene transcription as well as splicing and polyadenylation signals which are present in pSV2 . Preliminary mapping of the EBNA gene transcripts demonstrated that two mRNAs (2.9 and 2.4 kilobases [kb]) are homologous to the I1f fragment. Taken together, the data suggest that the 2.9-kbp I1f fragment contains the structural gene for EBNA synthesis. COS-1 cells will thus provide a valuable system in which to analyze functional domains of the EBNA gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Santangelo G. M. Analysis in Cos-1 cells of processing and polyadenylation signals by using derivatives of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):267–279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Miller G., Gradoville L., Heston L., Westrate M. W., Maris W., Wright J., Brandsma J., Summers W. C. Genome of a mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus contains DNA fragments previously regarded to be unique to Burkitt's lymphoma isolates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Robert M. F., Shedd D., Summers W. P., Robinson J. E., Wolak J., Stefano J. E., Miller G. Identification of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen polypeptide in mouse and monkey cells after gene transfer with a cloned 2.9-kilobase-pair subfragment of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Cell-surface expression of influenza haemagglutinin from a cloned DNA copy of the RNA gene. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):620–625. doi: 10.1038/293620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Boyd A., Stoerker J., Holliday J. Functional mapping of the Epstein-Barr virus genome: identification of sites coding for the restricted early antigen, the diffuse early antigen, and the nuclear antigen. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):188–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Wolf H., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus genes in different cell types after microinjection of viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):433–436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E. A., Summers W. P., Dowling S., Shedd D., Gradoville L., Miller G. Two Epstein-Barr viral nuclear neoantigens distinguished by gene transfer, serology, and chromosome binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7650–7653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Miller G., Henle W., Rabson M., Shedd D., Niederman J. C. Expression of Epstein-Barr viral early antigen in monolayer tissue cultures after transfection with viral DNA and DNA fragments. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Khoury G. Expression of simian virus 40-rat preproinsulin recombinants in monkey kidney cells: use of preproinsulin RNA processing signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat sequence in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is transcribed in latent and productive infections. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):311–320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.311-320.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Witmer T. J., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):734–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Grogan E., Heston L., Robinson J., Smith D. Epstein-Barr viral DNA: infectivity for human placental cells. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):452–455. doi: 10.1126/science.6259735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Wigler M., Axel R., Silverstein S. The transfer and stable integration of the HSV thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L. Identification of transcribed regions of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):8–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.8-18.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Spelsberg T. C. Partial purification of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen(s). J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3974–3982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoerker J., Parris D., Yajima Y., Glaser R. Pleiotropic expression of Epstein--Barr virus DNA in human epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5852–5855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Siminovitch L., Buchwald M. Persistence of freely replicating SV40 recombinant molecules carrying a selectable marker in permissive simian cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel R., Miller G. Major EB virus-specific cytoplasmic transcripts in a cellular clone of the HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma line during latency and after induction of viral replicative cycle by phorbol esters. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]