Abstract
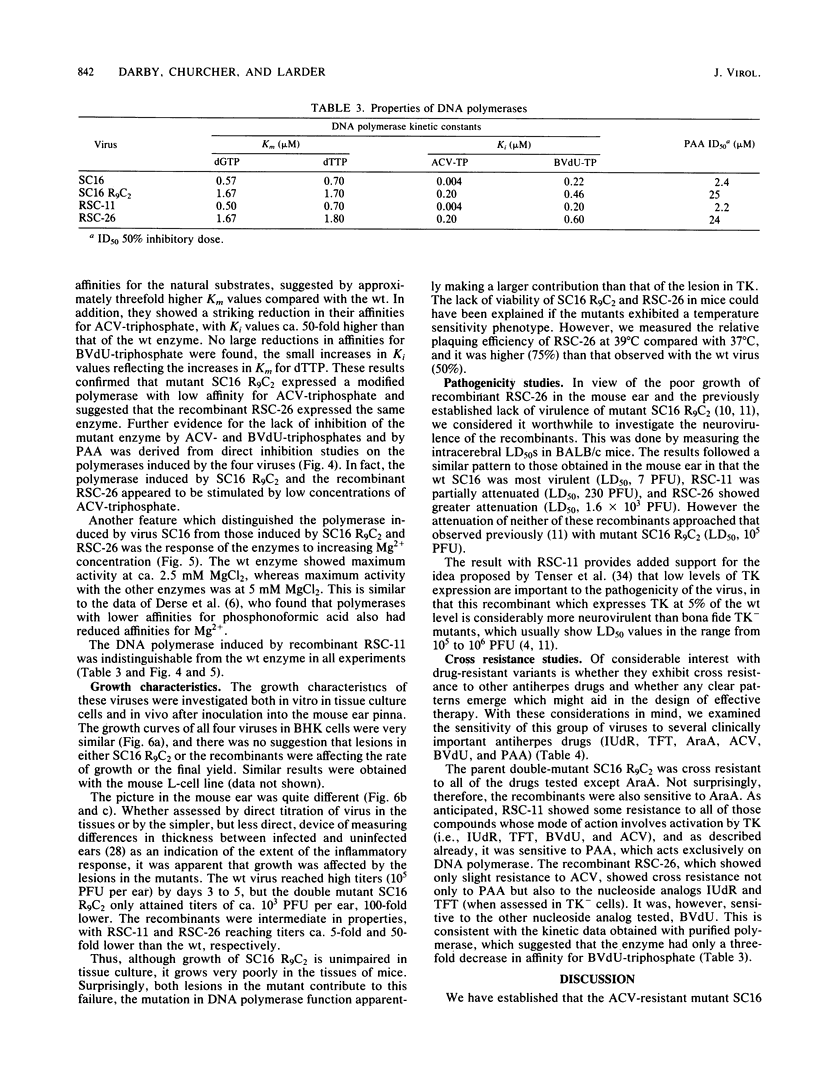
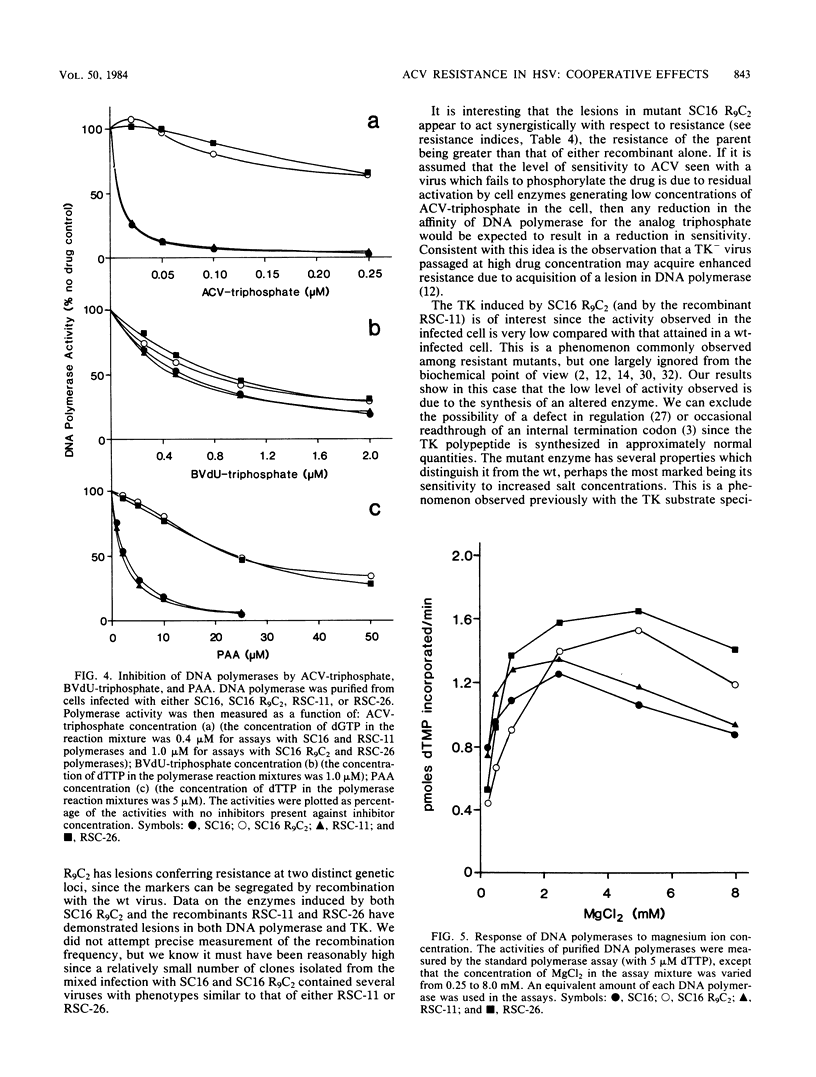
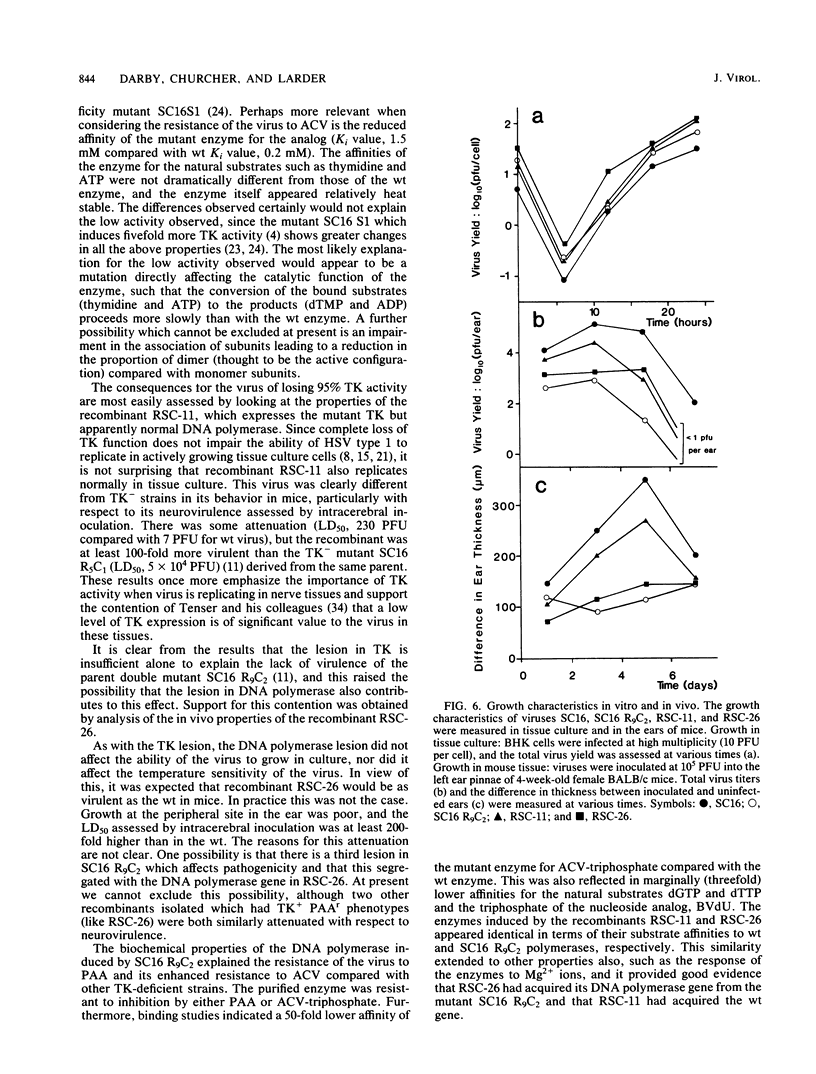
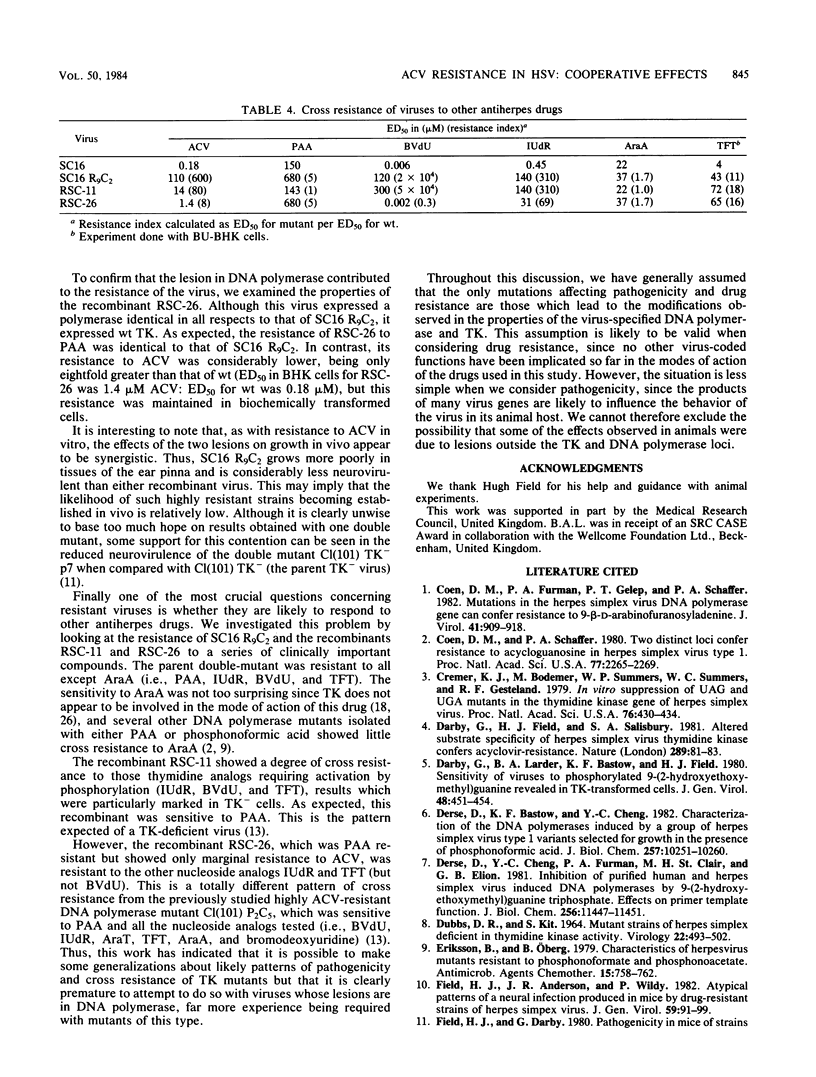
The acyclovir-resistant mutant SC16 R9C2 (H.J. Field, G. Darby, and P. Wildy , J. Gen. Virol. 49:115-124, 1980) has been shown to contain two resistance loci which segregate independently on recombination with wild-type virus. One locus is in thymidine kinase, and the other is in DNA polymerase. Both induced enzymes have altered properties, thymidine kinase showing a low affinity for acyclovir and low activity, and DNA polymerase showing a low affinity for acyclovir triphosphate. Other properties of both enzymes are described which distinguish them from their wild-type counterparts. Recombinants containing either mutant thymidine kinase ( RSC -11) or mutant DNA polymerase ( RSC -26), but not both, have been used to investigate the relative contribution of each lesion to resistance and pathogenicity. Although SC16 R9C2 and both recombinants grow as well as does wild-type virus in tissue culture, they are considerably attenuated in vivo, the greatest attenuation of virulence being seen with SC16 R9C2 and RSC -26. With respect to both acyclovir resistance and in vivo growth, the lesions appear to behave synergistically. Cross resistance studies have shown the recombinant RSC -26, which contains mutant DNA polymerase but which evidently expresses wild-type thymidine kinase, to be cross resistant to both 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine and 5-trifluoromethyl-2'-deoxyuridine but not to (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine or 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine.
Full text
PDF
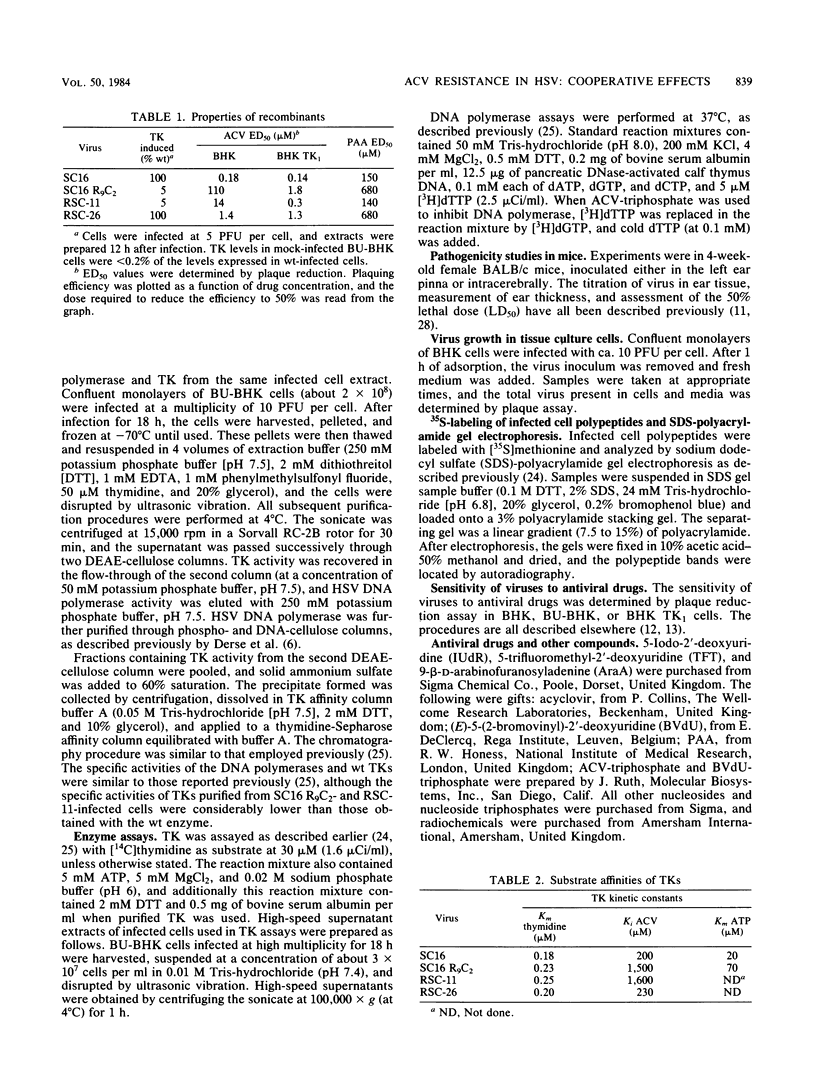
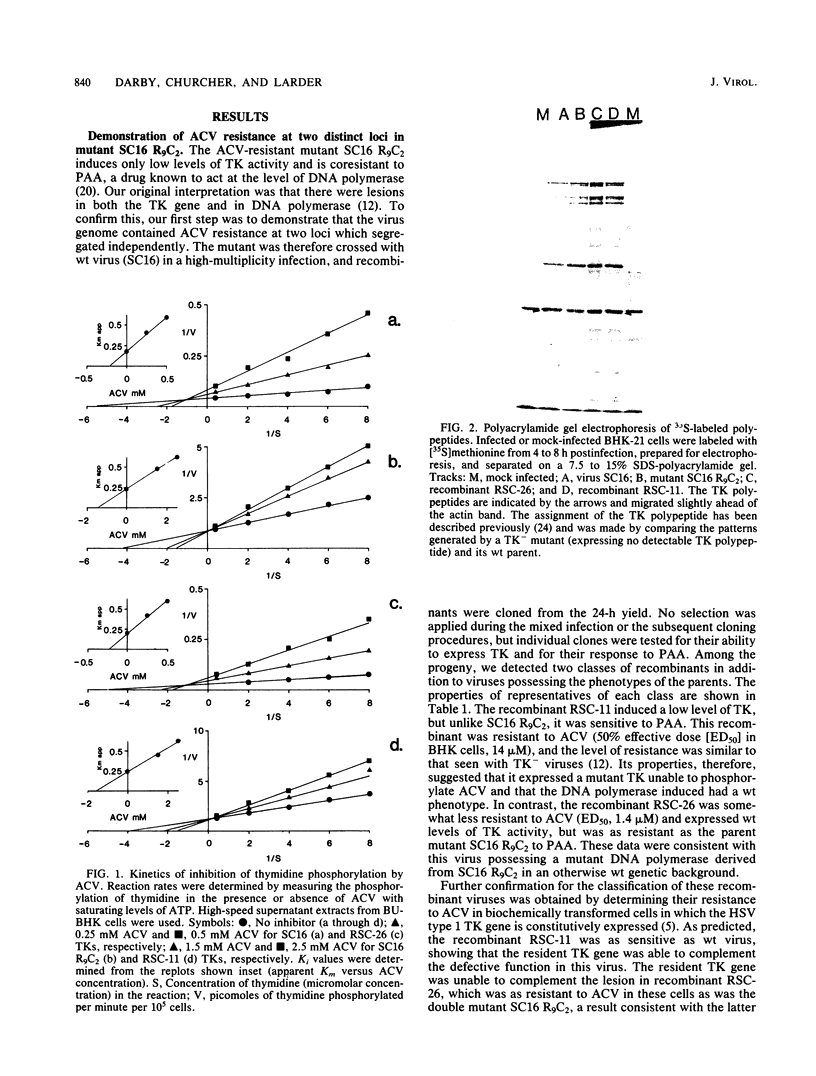
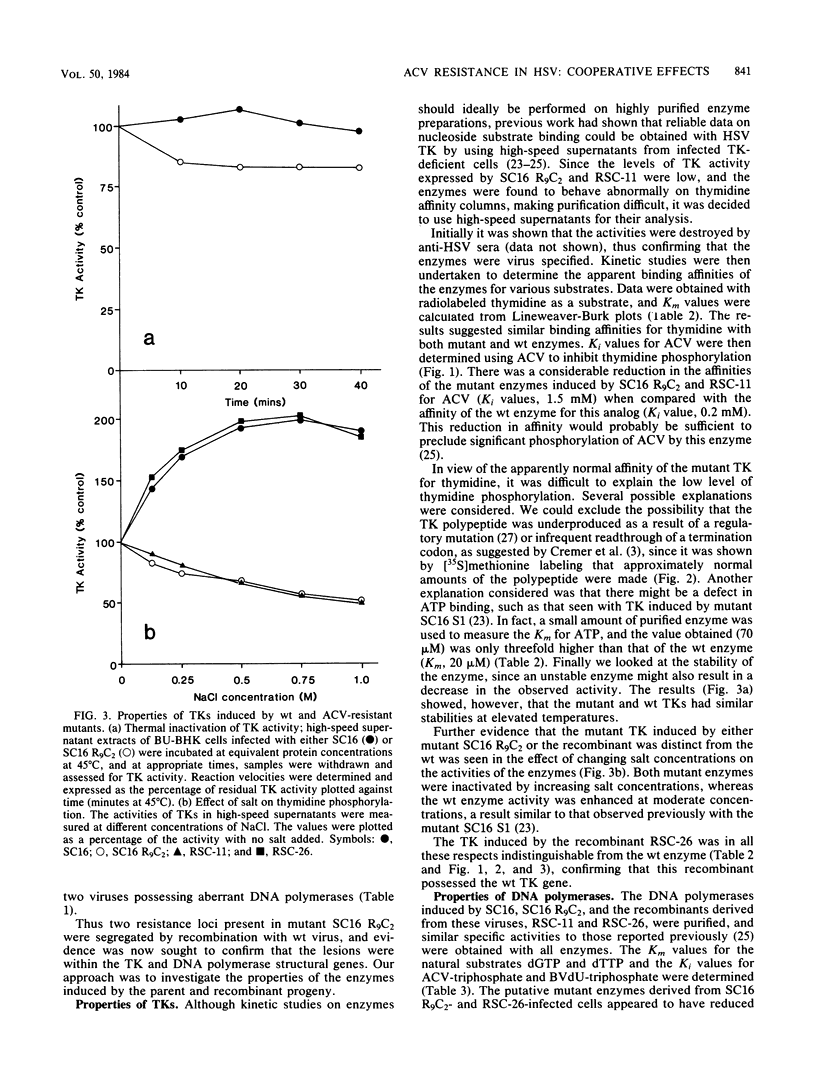

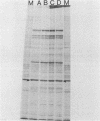
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coen D. M., Furman P. A., Gelep P. T., Schaffer P. A. Mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene can confer resistance to 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):909–918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.909-918.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Two distinct loci confer resistance to acycloguanosine in herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K. J., Bodemer M., Summers W. P., Summers W. C., Gesteland R. F. In vitro suppression of UAG and UGA mutants in the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):430–434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBBS D. R., KIT S. MUTANT STRAINS OF HERPES SIMPLEX DEFICIENT IN THYMIDINE KINASE-INDUCING ACTIVITY. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby G., Field H. J., Salisbury S. A. Altered substrate specificity of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase confers acyclovir-resistance. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):81–83. doi: 10.1038/289081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby G., Larder B. A., Bastow K. F., Field H. J. Sensitivity of viruses to phosphorylated 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine revealed in TK-transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jun;48(Pt 2):451–454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-2-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. Characterization of the DNA polymerases induced by a group of herpes simplex virus type I variants selected for growth in the presence of phosphonoformic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10251–10260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Inhibition of purified human and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. Effects on primer-template function. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11447–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Oberg B. Characteristics of herpesvirus mutants resistant to phosphonoformate and phosphonoacetate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):758–762. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Atypical patterns of neural infection produced in mice by drug-resistant strains of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):91–99. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Darby G., Wildy P. Isolation and characterization of acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):115–124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Neden J. Isolation of bromovinyldeoxyuridine-resistant strains of herpes simplex virus and successful chemotherapy of mice infected with one such strain by using acyclovir. Antiviral Res. 1982 Oct;2(5):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(82)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Wildy P. The pathogenicity of thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of herpes simplex virus in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):267–277. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H., McMillan A., Darby G. The sensitivity of acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus to other antiviral drugs. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):281–285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Coen D. M., St Clair M. H., Schaffer P. A. Acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 express altered DNA polymerase or reduced acyclovir phosphorylating activities. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):936–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.936-941.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Field H. J., Blyth W. A. Acute and recurrent infection with herpes simplex virus in the mouse: a model for studying latency and recurrent disease. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):341–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Gentry G. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Induction of both thymidine and deoxycytidine kinase activity by herpes viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):465–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., DeStefano E. Pathogenesis of experimental skin infections induced by drug-resistant herpes simplex virus mutants. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):693–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.693-701.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Cheng Y. C., Darby G. Characterization of abnormal thymidine kinases induced by drug-resistant strains of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):523–532. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G. Properties of a novel thymidine kinase induced by an acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):649–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.649-658.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Derse D., Cheng Y. C., Darby G. Properties of purified enzymes induced by pathogenic drug-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus. Evidence for virus variants expressing normal DNA polymerase and altered thymidine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2027–2033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B., Klenow H., Hansen K. Some properties of partially purified mammalian adenosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):350–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Field H. J., Quartey-Papafio R. Cell-mediated immunity in herpes simplex virus-infected mice: induction, characterization and antiviral effects of delayed type hypersensitivity. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jun;48(Pt 2):351–357. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Khan A. Resistance of peripheral autonomic neurons to in vivo productive infection by herpes simplex virus mutants deficient in thymidine kinase activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):571–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.571-580.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnipper L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine: role of viral thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2270–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Poirier R. H., Lynd F. T. In vitro and in vivo resistance of herpes simplex virus to 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine (acycloguanosine). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):144–150. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Wagner M., Summers W. C. Possible peptide chain termination mutants in thymide kinase gene of a mammalian virus, herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4081–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Dunstan M. E. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase expression in infection of the trigeminal ganglion. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Ressel S., Dunstan M. E. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase expression in trigeminal ganglion infection: correlation of enzyme activity with ganglion virus titer and evidence of in vivo complementation. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):328–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90638-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]