Abstract
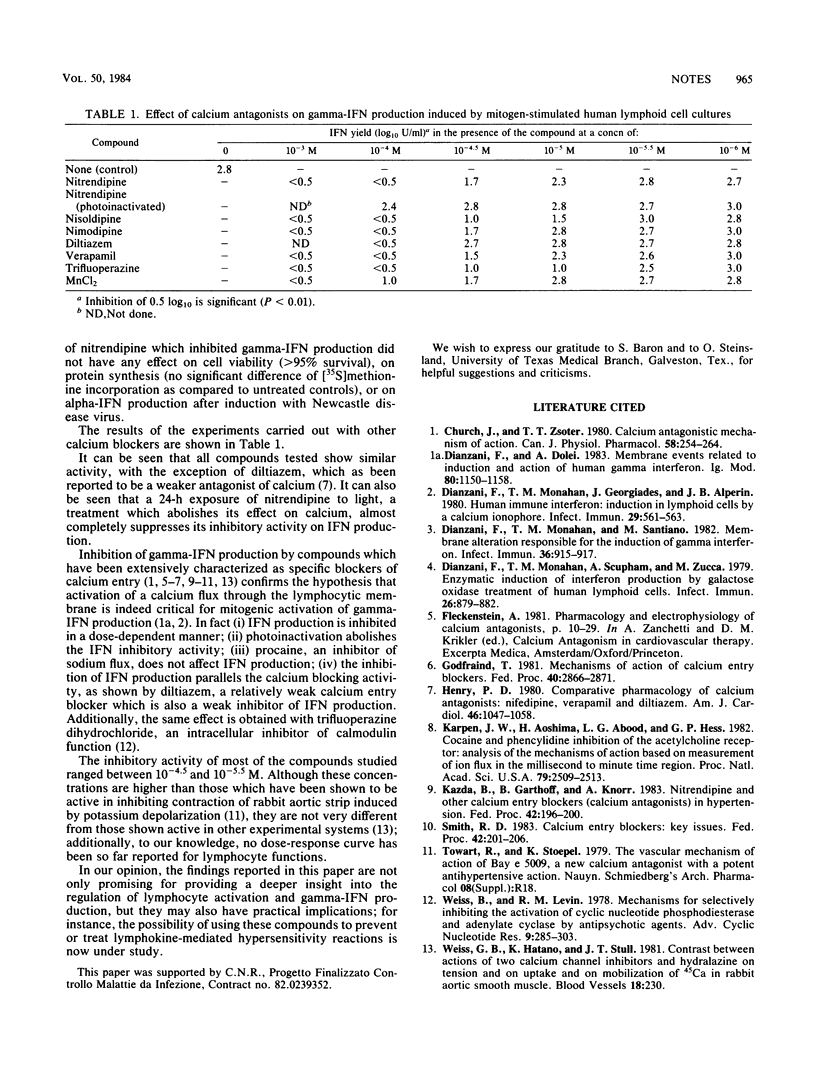
Mitogen-induced gamma interferon production by human lymphoid cell cultures was studied in the presence of calcium entry blockers. A dose-dependent inhibition was found in the presence of drug concentrations down to 10(-5) M. This finding shows that calcium flow through lymphocyte membranes after oxidation of membrane-bound galactose residues is also critical for triggering interferon production.
Full text
PDF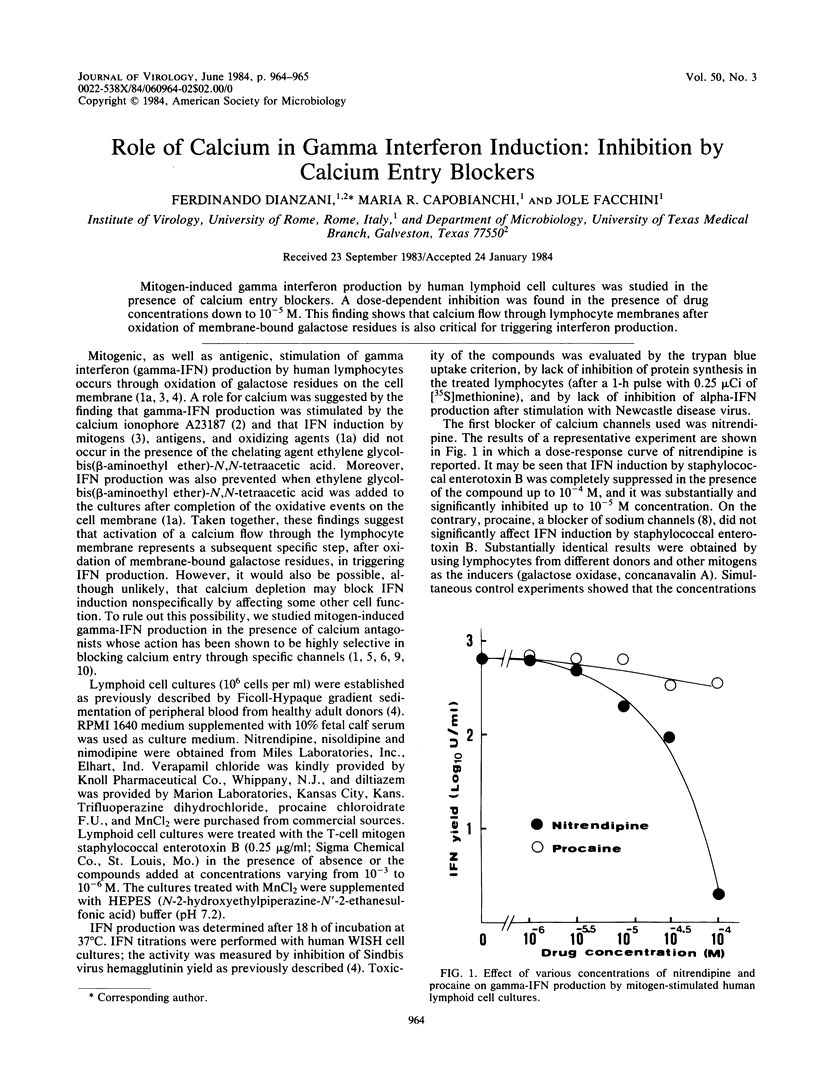
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Church J., Zsotér T. T. Calcium antagonistic drugs. Mechanism of action. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;58(3):254–264. doi: 10.1139/y80-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Monahan T. M., Georgiades J., Alperin J. B. Human immune interferon: induction in lymphoid cells by a calcium ionophore. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):561–563. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.561-563.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Monahan T. M., Santiano M. Membrane alteration responsible for the induction of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):915–917. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.915-917.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Monahan T. M., Scupham A., Zucca M. Enzymatic induction of interferon production by galactose oxidase treatment of human lymphoid cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):879–882. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.879-882.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T. Mechanisms of action of calcium entry blockers. Fed Proc. 1981 Dec;40(14):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. D. Comparative pharmacology of calcium antagonists: nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem. Am J Cardiol. 1980 Dec 1;46(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(80)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen J. W., Aoshima H., Abood L. G., Hess G. P. Cocaine and phencyclidine inhibition of the acetylcholine receptor: analysis of the mechanisms of action based on measurements of ion flux in the millisecond-to-minute time region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2509–2513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazda S., Garthoff B., Knorr A. Nitrendipine and other calcium entry blockers (calcium antagonists) in hypertension. Fed Proc. 1983 Feb;42(2):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D. Calcium entry blockers: key issues. Fed Proc. 1983 Feb;42(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Levin R. M. Mechanism for selectively inhibiting the activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and adenylate cyclase by antipsychotic agents. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:285–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


