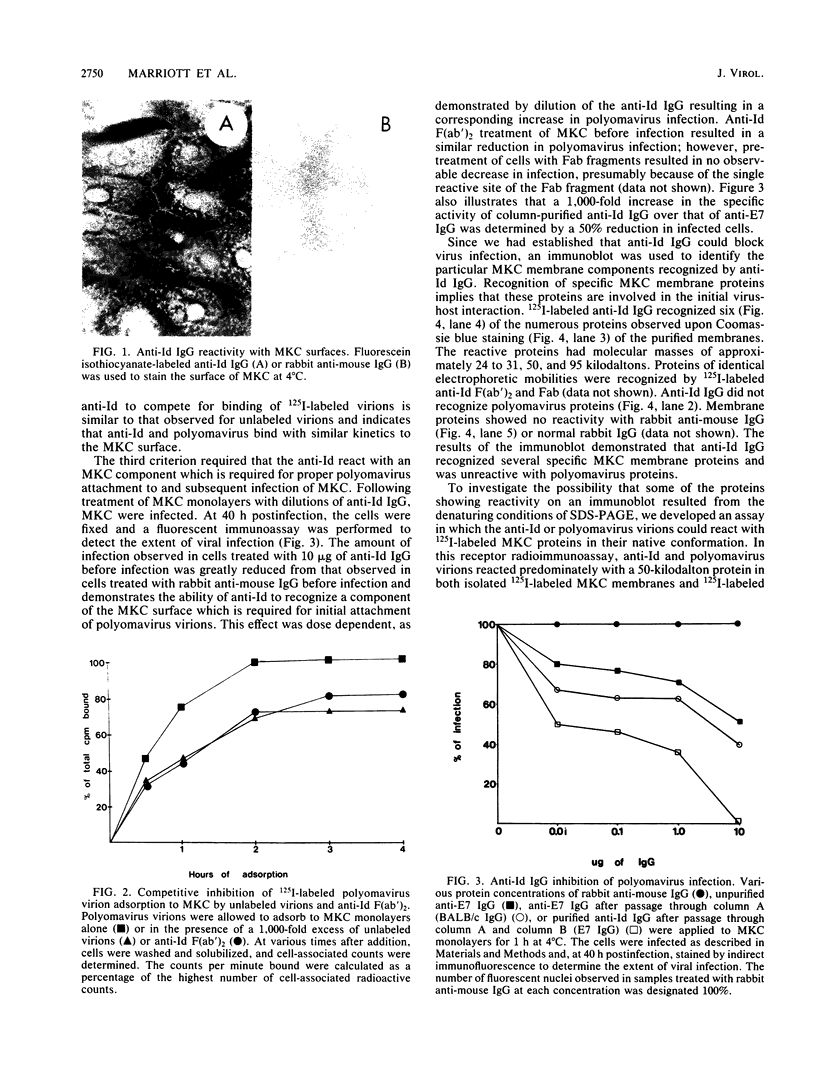
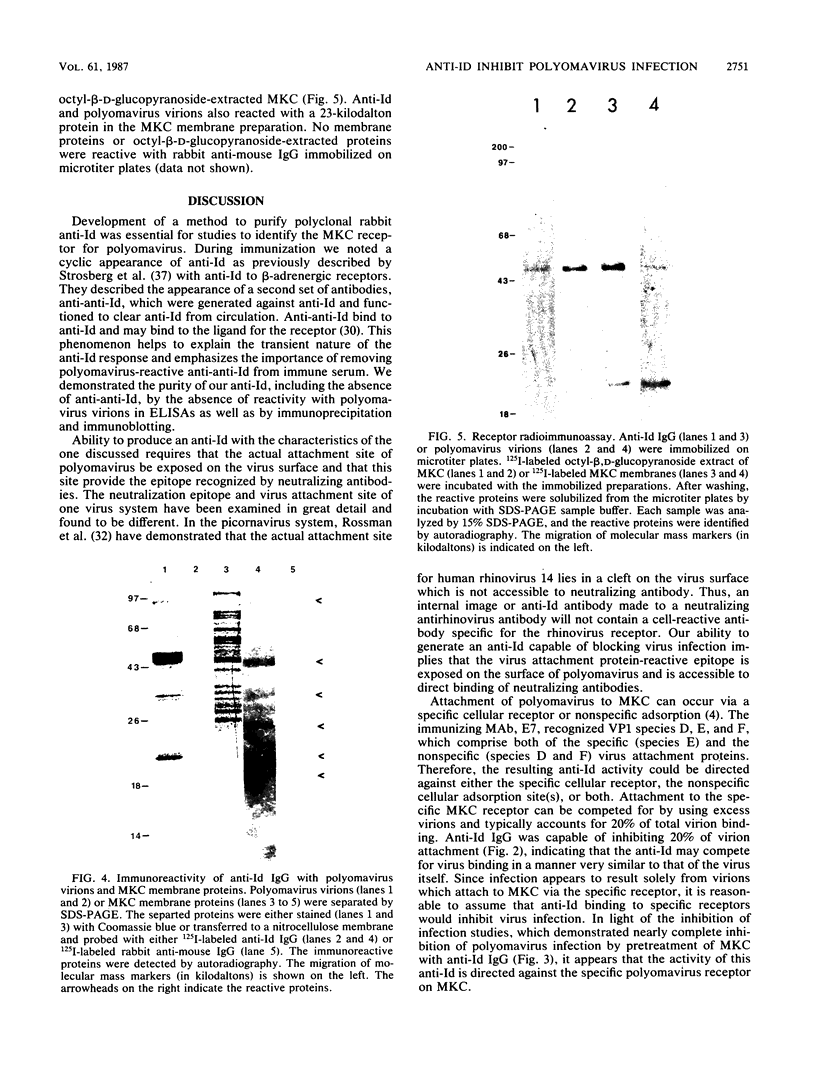
Abstract
Anti-idiotypic antibodies have been successfully used to identify and isolate the receptor for several cell ligands. To prepare an immunologic probe for identification of the polyomavirus receptor on mouse kidney cells, polyclonal antisera against antipolyomavirus antibodies were prepared in rabbits. Fab fragments of the previously characterized monoclonal antibody E7, which neutralizes polyomavirus infection, were used for immunization (S. J. Marriott and R. A. Consigli, J. Virol. 56:365-372, 1985). Sera containing the greatest anti-idiotype activity were identified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and purified by a series of affinity columns. The anti-idiotypic antibodies recognized the E7 idiotope in an ELISA, and anti-idiotype binding could be inhibited by preincubation of E7 monoclonal antibody with polyomavirus virions. When mixed with anti-idiotype immunoglobulin G (IgG), E7 was no longer capable of binding or immunoprecipitating polyomavirus virions or neutralizing polyomavirus infection. Direct immunofluorescence showed anti-idiotype IgG reactivity with a cell surface component of mouse kidney cells. Anti-idiotype F(ab')2 effectively competed with polyomavirus for binding to mouse kidney cells and displayed binding kinetics similar to those of polyomavirus. Virus infection of mouse kidney cells was blocked in a dose-dependent manner following treatment of the cells with anti-idiotype IgG. The anti-idiotype identified several proteins (95, 50, and 24 to 31 kilodaltons) in an immunoblot of mouse kidney cell membrane proteins but reacted predominantly with a single 50-kilodalton protein in a radioimmunoassay. The anti-idiotype failed to react with virus proteins in three assays, including ELISA, immunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting. The implications of this work for future identification and characterization of the polyomavirus receptor on mouse kidney cells are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Consigli R. A. Chemical cleavage of polyomavirus major structural protein VP1: identification of cleavage products and evidence that the receptor moiety resides in the carboxy-terminal region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):197–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.197-205.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Anders D. G., Trempy J., Consigli R. A. Differences in the subpopulations of the structural proteins of polyoma virions and capsids: biological functions of the multiple VP1 species. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.80-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Differential adsorption of polyoma virions and capsids to mouse kidney cells and guinea pig erythrocytes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.679-683.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Separation of neutralizing and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibody activities and specificity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):119–129. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.119-129.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Dissociation of polyoma virus by the chelation of calcium ions found associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.717-724.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Leick V. Rapid equilibrium isopycnic CsC1 gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;179(1):136–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland W. L., Wassermann N. H., Sarangarajan R., Penn A. S., Erlanger B. F. Monoclonal antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor by a normally functioning auto-anti-idiotypic mechanism. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):56–57. doi: 10.1038/305056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Co M. S., Gaulton G. N., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Isolation and biochemical characterization of the mammalian reovirus type 3 cell-surface receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1494–1498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY B. E., ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., STEWART S. E., HUEBNER R. J. Hemagglutination with the SE polyoma virus. Virology. 1958 Aug;6(1):290–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R. Anti-hormone anti-idiotypes are probes for receptor structure and function. Immunol Lett. 1985;9(4):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Briones-Urbina R., Islam M. N. Anti-idiotypic antibodies as probes for hormone-receptor interaction. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1255–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H., Cahan L. D., Paulson J. C. Polyoma virus recognizes specific sialyligosaccharide receptors on host cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Bourgaux P. Decapsidation of polyoma virus: identification of subviral species. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Co M. S., Royer H. D., Greene M. I. Anti-idiotypic antibodies as probes of cell surface receptors. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Nov;65(1):5–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00226015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith G. R., Consigli R. A. Cross-linking of a polyomavirus attachment protein to its mouse kidney cell receptor. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.773-781.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Rockson S. G., Haber E. An antiidiotypic antibody that recognizes the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1147–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI110550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. N., Pepper B. M., Briones-Urbina R., Farid N. R. Biological activity of anti-thyrotropin anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jan;13(1):57–63. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Rosner M. R. Characterization of murine-specific leukemia virus receptor from L cells. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):900–908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.900-908.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman R. S., Noseworthy J. H., Nepom J. T., Finberg R., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Cell receptors for the mammalian reovirus. II. Monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody blocks viral binding to cells. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2539–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Dreesman G. R. Production and characterization of anti-idiotype reagents for the analysis of viral antigen systems. J Virol Methods. 1983 Aug;7(2):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Consigli R. A. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.365-372.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
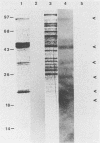
- Marriott S. J., Griffith G. R., Consigli R. A. Octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside extracts polyomavirus receptor moieties from the surfaces of mouse kidney cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.375-382.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Center M. S., Consigli R. A. Origin of the polyoma virus-associated endonuclease. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.127-131.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Consigli R. A. Immunological reactivity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1113-1120.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisonoff A., Lamoyi E. Implications of the presence of an internal image of the antigen in anti-idiotypic antibodies: possible application to vaccine production. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Dec;21(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noseworthy J. H., Fields B. N., Dichter M. A., Sobotka C., Pizer E., Perry L. L., Nepom J. T., Greene M. I. Cell receptors for the mammalian reovirus. I. Syngeneic monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody identifies a cell surface receptor for reovirus. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2533–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffar-Deshayes L., Choppin J., Lévy J. P. Lymphoid cell surface receptor for Moloney leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein gp71. II. Isolation of the receptor. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2352–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Couraud P. O., Andre C., Vray B., Strosberg A. D. Anti-alprenolol anti-idiotypic antibodies bind to beta-adrenergic receptors and modulate catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sege K., Peterson P. A. Use of anti-idiotypic antibodies as cell-surface receptor probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Consigli R. A. Transient inhibition of polyoma virus synthesis by Sendai virus (parainfluenza I). I. Demonstration and nature of the inhibition by inactivated virus. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1091-1097.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G. S., Dailey M. O., Gallatin W. M., McGrath M. S., Weissman I. L., Pillemer E. A. Isolation of molecules recognized by monoclonal antibodies and antisera: the solid phase immunoisolation technique. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Lloyd C. W., Rees D. A. Rapid isolation of plasma membranes in high yield from cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):187–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann N. H., Penn A. S., Freimuth P. I., Treptow N., Wentzel S., Cleveland W. L., Erlanger B. F. Anti-idiotypic route to anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies and experimental myasthenia gravis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4810–4814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston V. D., Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Isolation and characterization of polyoma uncoating intermediates from the nuclei of infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1173–1181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1173-1181.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]