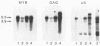Abstract
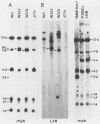
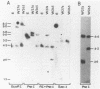
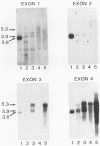
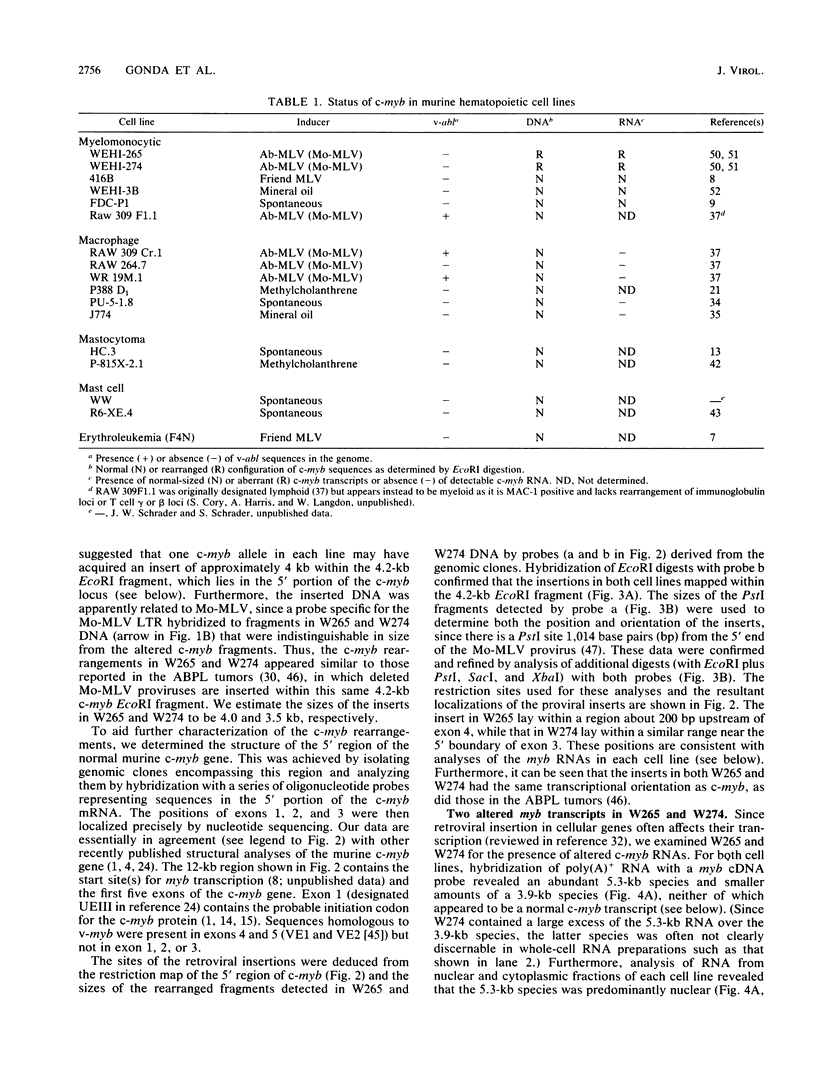
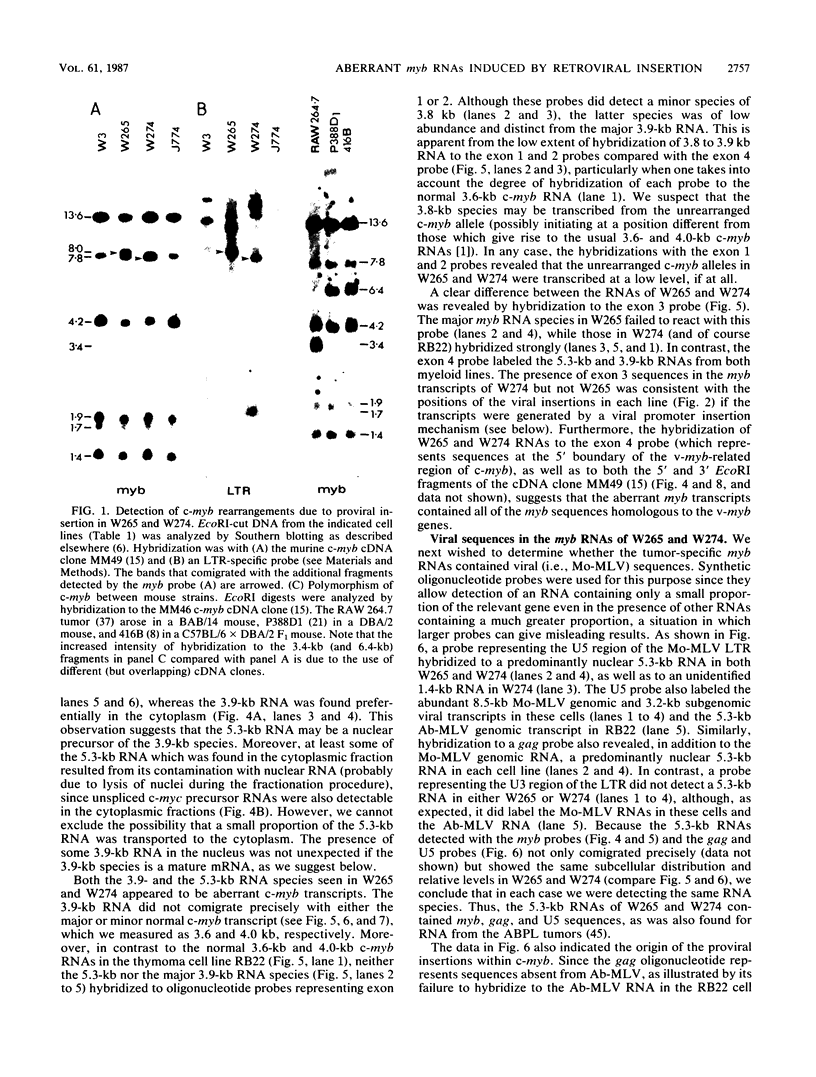
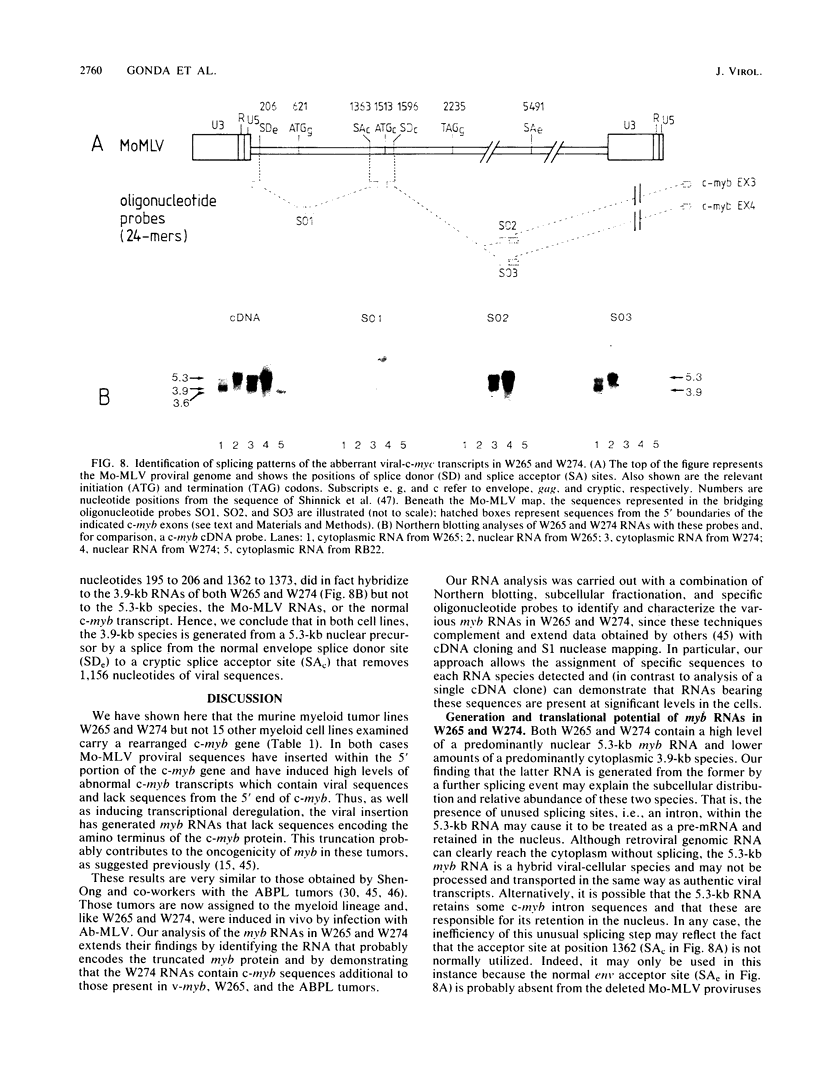
Two murine monocytic leukemia cell lines, WEHI-265 and WEHI-274, were found to carry a rearranged c-myb gene. The rearrangements are due to insertion of a deleted Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MLV) provirus in the 5' region of the c-myb gene and thus are similar to rearrangements in the ABPL tumors (G. L. C. Shen-Ong, M. Potter, J. F. Mushinski, S. Lavu, and E. P. Reddy, Science 226:1077-1080, 1984). In each cell line, the retroviral insertion has induced high levels of two aberrant RNA species, which, as in the ABPL tumors (G. L. C. Shen-Ong, H. C. Morse, M. Potter, and J. F. Mushinski, Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:380-392, 1986), contain both viral (Mo-MLV) and cellular (myb) sequences. Both species lack the sequences encoding the amino terminus of the c-myb protein and thus could encode a protein which, like the v-myb gene products (and the predicted ABPL myb proteins), is truncated at the amino terminus. We have found that the larger (5.3 kilobase [kb]) and more abundant of the tumor-specific myb RNAs was predominantly nuclear, while the smaller species (3.9 kb) was cytoplasmic. Furthermore, our data imply that the 3.9-kb RNA was derived from the 5.3-kb RNA by an additional splice which utilized a cryptic splice acceptor site within the viral gag sequences. On the basis of subcellular distribution and predicted translational potential, we conclude that the 3.9-kb RNA is probably the mRNA which encodes a truncated myb protein. We also show that, due to different insertion points in W265 and W274, the W274 myb RNAs contained sequences from a c-myb exon upstream of the exons represented in the W265 (and ABPL) RNAs. The significance of our findings with regard to transformation by myb in these tumors is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender T. P., Kuehl W. M. Murine myb protooncogene mRNA: cDNA sequence and evidence for 5' heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Graf T. Myeloblasts transformed by the avian acute leukemia virus E26 are hormone-dependent for growth and for the expression of a putative myb-containing protein, p135 E26. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1069–1073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle S., Sheiness D. Structural organization of the mouse proto-myb gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):688–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D. Thymocyte subsets transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):390–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Gerondakis S., Adams J. M. Interchromosomal recombination of the cellular oncogene c-myc with the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is a reciprocal exchange. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):697–703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Scott D., Teich N. M. Isolation and characterisation of a bipotential haematopoietic cell line. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):471–474. doi: 10.1038/277471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozier C., Walbaum S., Leprince D., Stehelin D. EcoRI RFLP linked to the human myb gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1928–1928. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Pragnell I. B., Kluge N., Gaedicke G., Steinheider G., Ostertag W. Induction of endogenous and of spleen focus-forming viruses during dimethylsulfoxide-induced differentiation of mouse erythroleukemia cells transformed by spleen focus-forming virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1863–1867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duprey S. P., Boettiger D. Developmental regulation of c-myb in normal myeloid progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6937–6941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURTH J., HAGEN P., HIRSCH E. I. Transplantable mastocytoma in the mouse containing histamine, heparin, 5-hydroxytryptamine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Aug-Sep;95(4):824–828. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Bishop J. M. Structure of the protein encoded by the chicken proto-oncogene c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3677–3684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Weizsaecker F., Grieser S., Coll J., Stehelin D., Patschinsky T., Bister K., Bechade C., Calothy G., Leutz A. v-mil induces autocrine growth and enhanced tumorigenicity in v-myc-transformed avian macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Frykberg L., Brady C., Stanley I., Beug H., Vennström B., Graf T. v-erbA cooperates with sarcoma oncogenes in leukemic cell transformation. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Handwerger B. S., Wunderlich J. R. Identification of macrophage-like characteristics in a cultured murine tumor line. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):894–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Cellular oncogenes and multistep carcinogenesis. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.6356358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Structural organization and nucleotide sequence of mouse c-myb oncogene: activation in ABPL tumors is due to viral integration in an intron which results in the deletion of the 5' coding sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5309–5320. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C. Leukemic transformation with avian myeloblastosis virus: present status. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;71:79–101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66193-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushinski J. F., Potter M., Bauer S. R., Reddy E. P. DNA rearrangement and altered RNA expression of the c-myb oncogene in mouse plasmacytoid lymphosarcomas. Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):795–798. doi: 10.1126/science.6687762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Moore M. A., Nilsson K. Lysozyme synthesis by established human and murine histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1528–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Cleveland J. L., Fredrickson T. N., Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Jansen H. W., Patschinsky T., Bister K. Rapid induction of hemopoietic neoplasms in newborn mice by a raf(mil)/myc recombinant murine retrovirus. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):23–33. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.23-33.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Baird S., Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosson D., Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence of chicken c-myb complementary DNA and implications for myb oncogene activation. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):604–606. doi: 10.1038/319604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K. E., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S., Baluda M. A., Perbal B., Chirikjian J. G., Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence of the transforming gene of avian myeloblastosis virus. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.6283631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER R., DAY M., FISCHER G. A. Culture of neoplastic mast cells and their synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine in vitro. Cancer Res. 1959 Jan;19(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Crapper R. M. Autogenous production of a hemopoietic growth factor, persisting-cell-stimulating factor, as a mechanism for transformation of bone marrow-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6892–6896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Stanton L. W., Riley S. C., Marcu K. B., Witte O. N. Synergism of v-myc and v-Ha-ras in the in vitro neoplastic progression of murine lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3221–3231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Potter M., Mushinski J. F., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Activation of the c-myb locus by viral insertional mutagenesis in plasmacytoid lymphosarcomas. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1077–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.6093260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. Abelson murine leukemia virus: molecular cloning of infectious integrated proviral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Marshall C. J. Three different activated ras genes in mouse tumours; evidence for oncogene activation during progression of a mouse lymphoma. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):913–917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Moore M. A., Metcalf D. A transplantable myelomonocytic leukemia in BALB-c mice: cytology, karyotype, and muramidase content. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):963–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Ihle J. N., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Truncation of the c-myb gene by a retroviral integration in an interleukin 3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Gallo R. C., Arya S. K., Eva A., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A., Aaronson S. A., Wong-Staal F. Differential expression of the amv gene in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]