Abstract
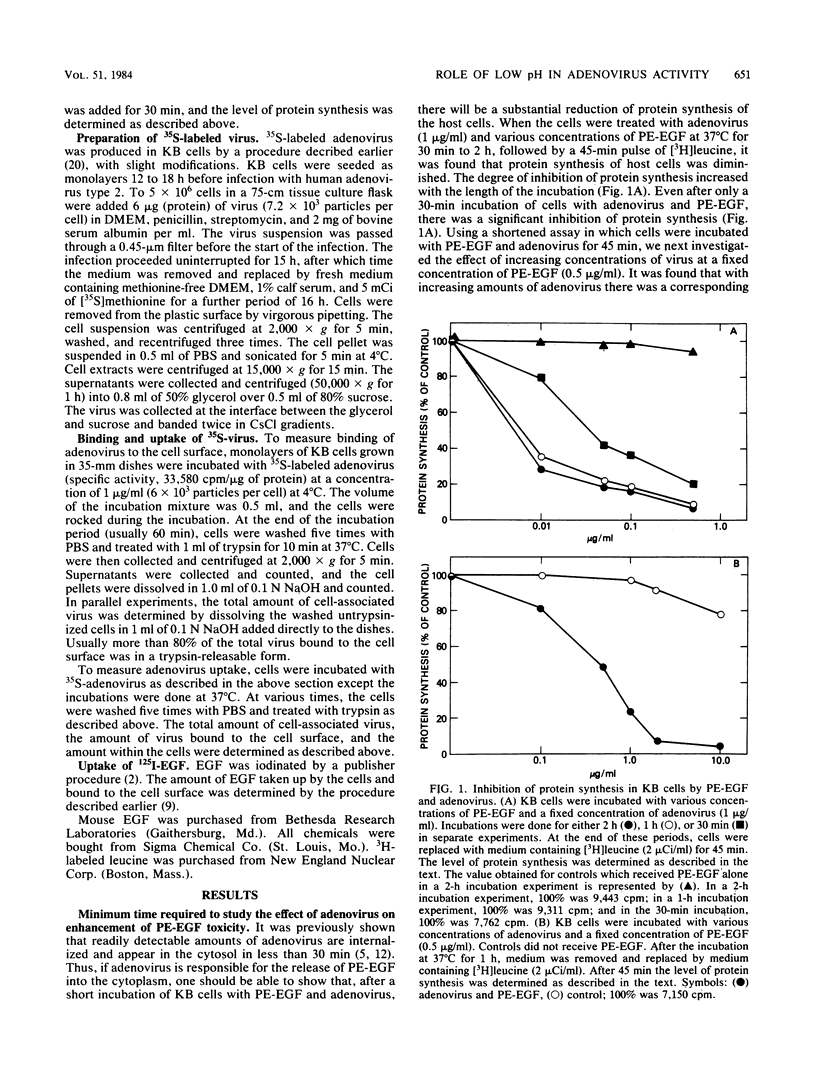
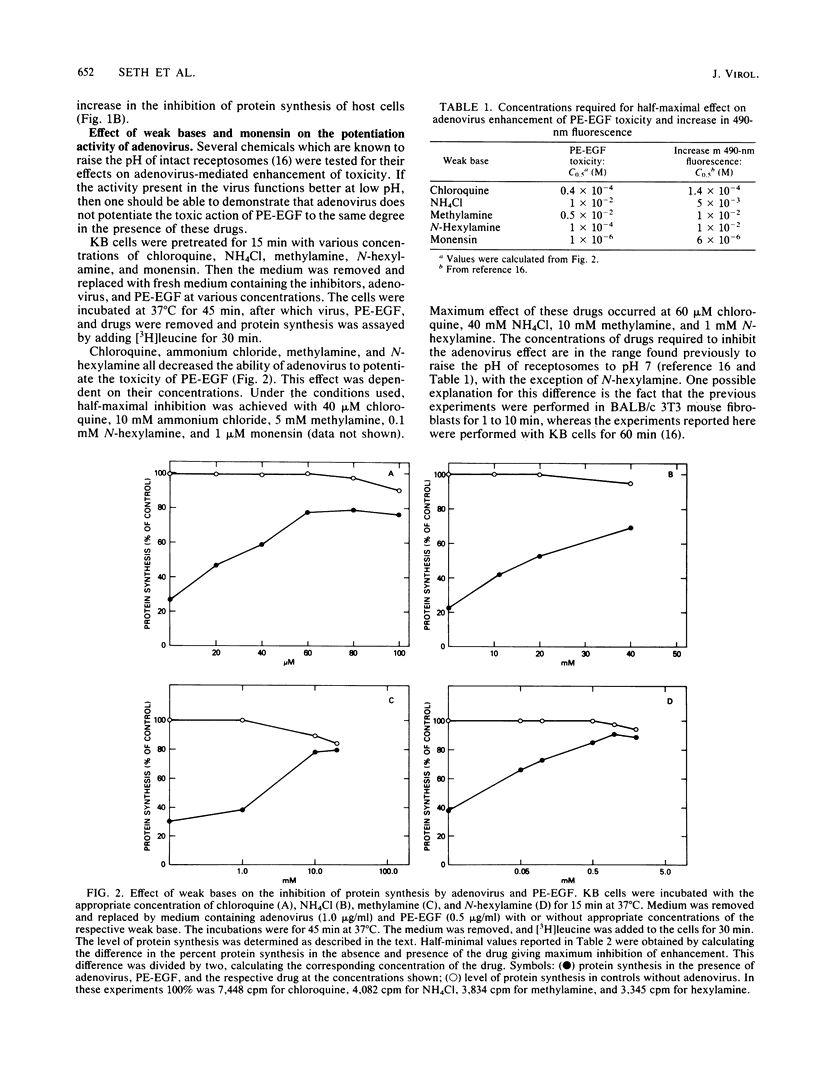
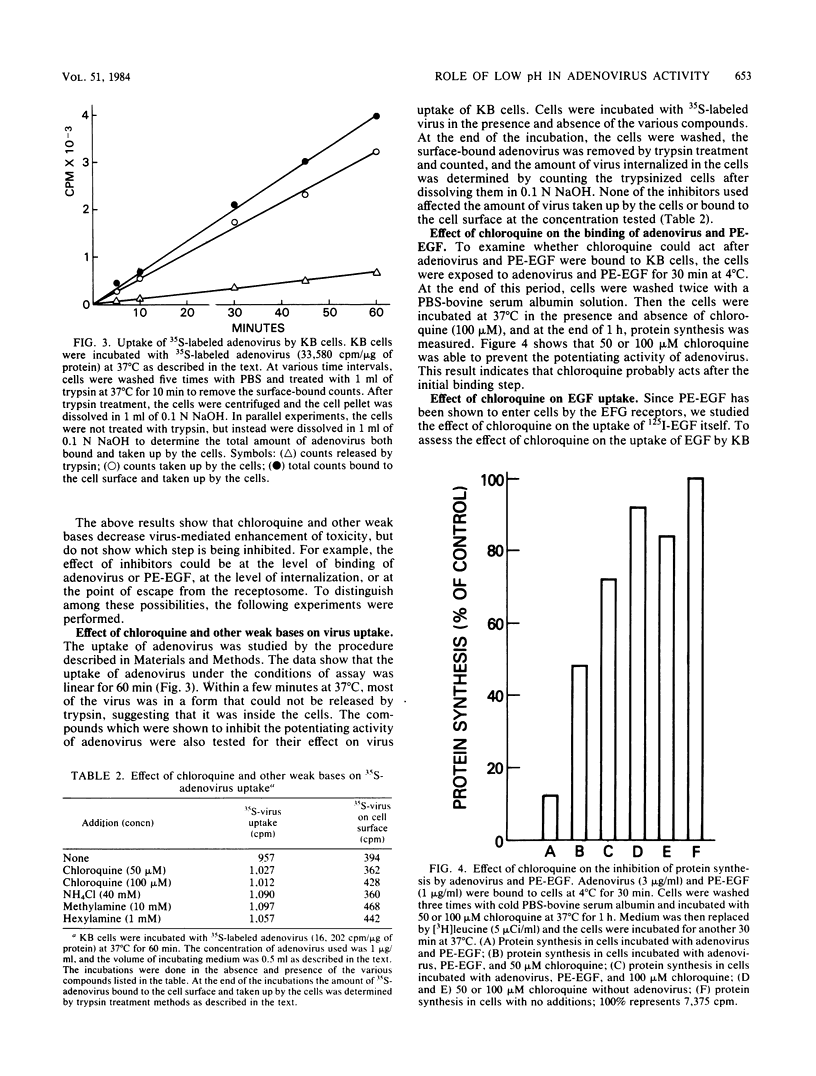
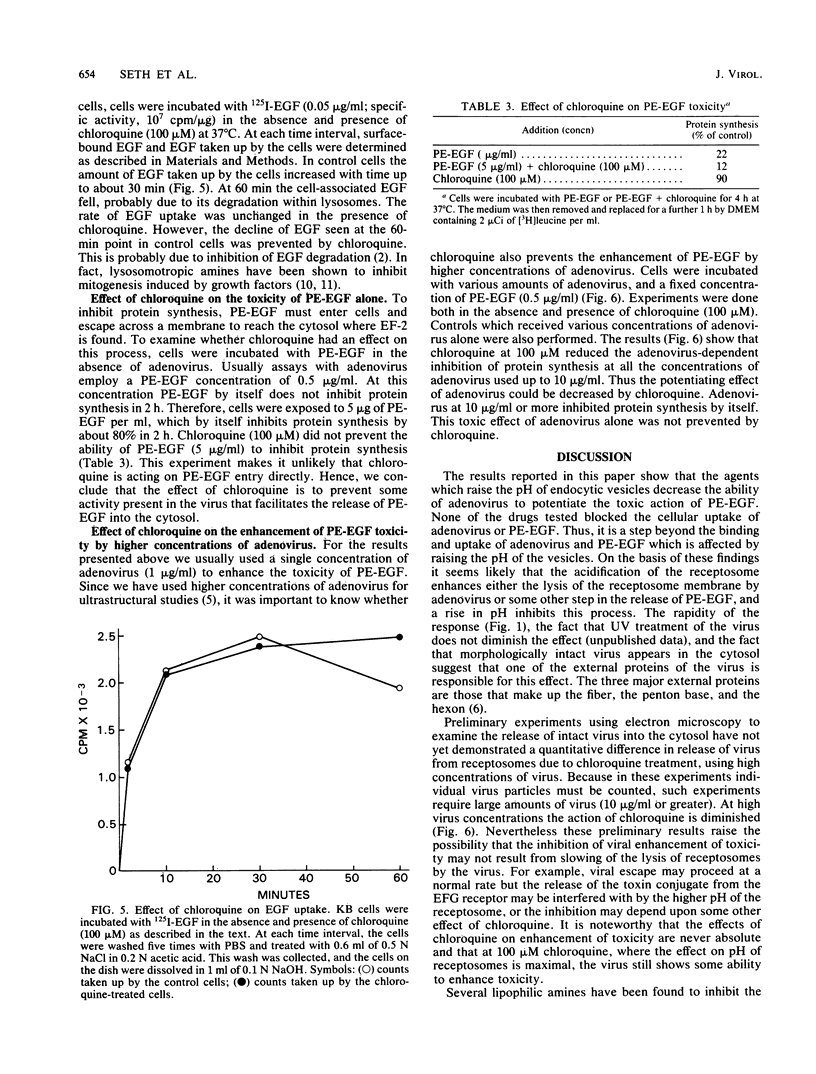
A conjugate of Pseudomonas exotoxin and epidermal growth factor (PE-EGF) inhibits proteins synthesis in KB cells, and this inhibition is increased by adenovirus. Protein synthesis inhibition is dependent on the amount of adenovirus and PE-EGF used and the time of incubation of cells with these agents. With 1 microgram of adenovirus and 0.5 micrograms of PE-EGF per ml, protein synthesis is inhibited about 80% in a 60-min experiment. Under these conditions neither adenovirus nor PE-EGF alone has any effect. In the presence of several weak bases or monensin, the enhancement of toxicity was substantially inhibited; half-maximal inhibition was achieved with 40 microM chloroquine, 10 mM ammonium chloride, 5 mM methylamine, 0.1 mM N-hexylamine and 1 microM monensin. At the concentrations employed, none of the inhibitors affected the amount of virus taken up or bound to the cell surface, and chloroquine had no effect on the amount of EGF taken up in 60 min. Chloroquine did not prevent the toxicity of the PE-EGF (5 micrograms/ml) alone. Because these compounds are known to elevate the pH in receptosomes, it seems likely that the acidification of the receptosome either enhances the lysis of the membrane by adenovirus or enhances some other step in the release of PE-EGF.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boquet P., Duflot E. Tetanus toxin fragment forms channels in lipid vesicles at low pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7614–7618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. J., Simon M. I., Draper R. K., Montal M. Diphtheria toxin forms transmembrane channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):172–176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Padmanabhan R., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Adenovirus-induced release of epidermal growth factor and pseudomonas toxin into the cytosol of KB cells during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D., Morris R. E., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated internalization of Pseudomonas toxin by mouse fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., PINA M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. IV. Isolation, purification, and chemical analysis of adenovirus. Virology. 1963 May;20:199–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Exposure of cells to an acidic environment reverses the inhibition by methylamine of the mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Hernaez-Davis L., Cuatrecasas P. Lysosomotropic amines inhibit mitogenesis induced by growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):717–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M., Chardonnet Y., Dales S. Early events in the interaction of adenoviruses with HeLa cells. V. Polypeptides associated with the penetrating inoculum. Virology. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnell M. H., Stookey M., Draper R. K. Monensin blocks the transport of diphtheria toxin to the cell cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):57–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R. Weak bases and ionophores rapidly and reversibly raise the pH of endocytic vesicles in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):676–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Lenard J. Antihistaminics, local anesthetics, and other amines as antiviral agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3605–3609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Manhart M. D., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated entry of Pseudomonas toxin: methylamine blocks clustering step. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):806–811. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.806-811.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Lonberg-Holm K., Pettersson U. Virus-receptor interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1064–1075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1064-1075.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. The receptosome: an intermediate organelle of receptor mediated endocytosis in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


