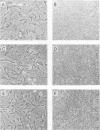
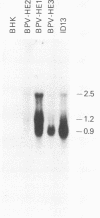
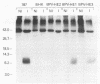
Abstract
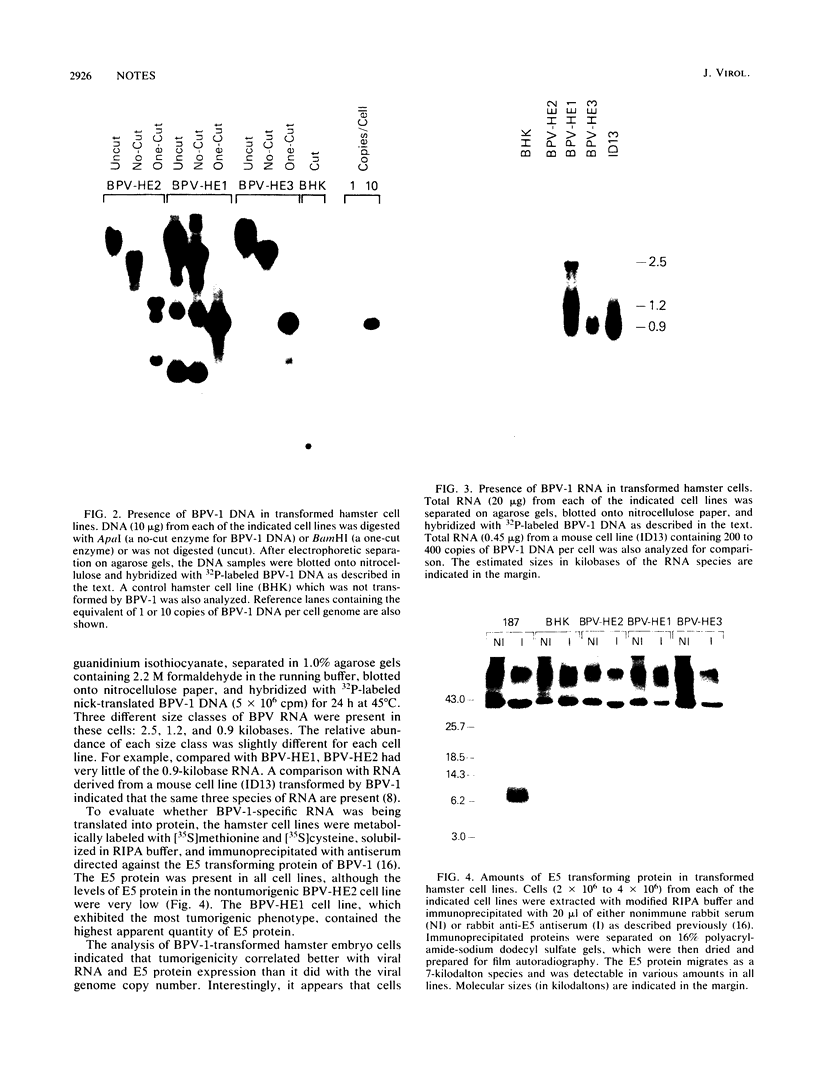
Three independent cell lines were established from primary cultures of LSH hamster embryo cells infected with bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1). Although these cell lines differed in their in vitro saturation densities, none was capable of colony formation in soft agar. Interestingly, two cell lines (BPV-HE1 and BPV-HE3) were tumorigenic in nude mice, syngeneic hamsters, and allogeneic hamsters, whereas BPV-HE2 was not. All three cell lines contained similar numbers of the BPV-1 genome (approximately 50 to 200 copies per cell). However, the nontumorigenic BPV-HE2 cell line contained very low levels of BPV-specific RNA and only small amounts of the BPV-1 E5 transforming protein. The efficiency and rate of tumor formation by BPV-HE1 and BPV-HE3 correlated directly with the apparent amount of viral E5 protein. This analysis suggests that there is a threshold level of BPV protein synthesis required for tumorigenicity, there is a continuum of tumorigenic phenotypes which may depend upon the level of BPV protein expression, and BPV-transformed hamster cells can withstand allogeneic transplantation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2996134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Fisher P. B. Characterization of Fischer rat embryo (CREF) cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus type 1. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):180–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Guralski D., Schiller J. T. Translation of open reading frame E5 of bovine papillomavirus is required for its transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMANN J. C., LEVY J. P., LASNERET J., THOMAS M., BOIRON M., BERNARD J. INDUCTION DE FIBROMES SOUS-CUTAN'ES CHEZ LE HAMSTER DOR'E PAR INOCULATION D'EXTRAITS ACELLULAIRES DE PAPILLOMES BOVINS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Oct 14;257:2328–2331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisoni M., Meneguzzi G., de Lapeyrière O., Binétruy B., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F. The transformed phenotype in culture and tumorigenicity of Fischer rat fibroblast cells (FR3T3) transformed with bovine papilloma virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groff D. E., Lancaster W. D. Genetic analysis of the 3' early region transformation and replication functions of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. A., Engel L., Lowy D. R., Howley P. M. Virus-specific transcription in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):22–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaureguiberry G., Favre M., Orth G. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome in hamster sarcoma cells in vivo and in vitro: variation in the level of transcription. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):1199–1204. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Olson C. Animal papillomaviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):191–207. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.191-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Cook J. L. A new role for DNA virus early proteins in viral carcinogenesis. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):15–20. doi: 10.1126/science.3843807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meischke H. R. In vitro transformation by bovine papilloma virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):473–487. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Localization and analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 transforming functions. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):377–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.377-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Vousden K. H., Lowy D. R. E5 open reading frame of bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes a transforming gene. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.1-6.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade-Glass M., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small, hydrophobic polypeptide. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.3014660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS M., BOIRON M., TANZER J., LEVY J. P., BERNARD J. IN VITRO TRANSFORMATION OF MICE CELLS BY BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1964 May 16;202:709–710. doi: 10.1038/202709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Spalholz B. A., Rabson M. S., Howley P. M. Dissociation of transforming and trans-activation functions for bovine papillomavirus type 1. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):575–577. doi: 10.1038/318575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]