Abstract
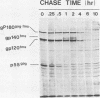
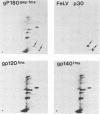
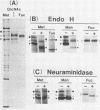
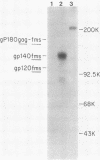
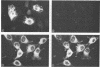
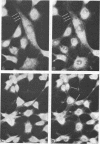
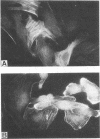
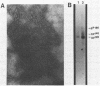
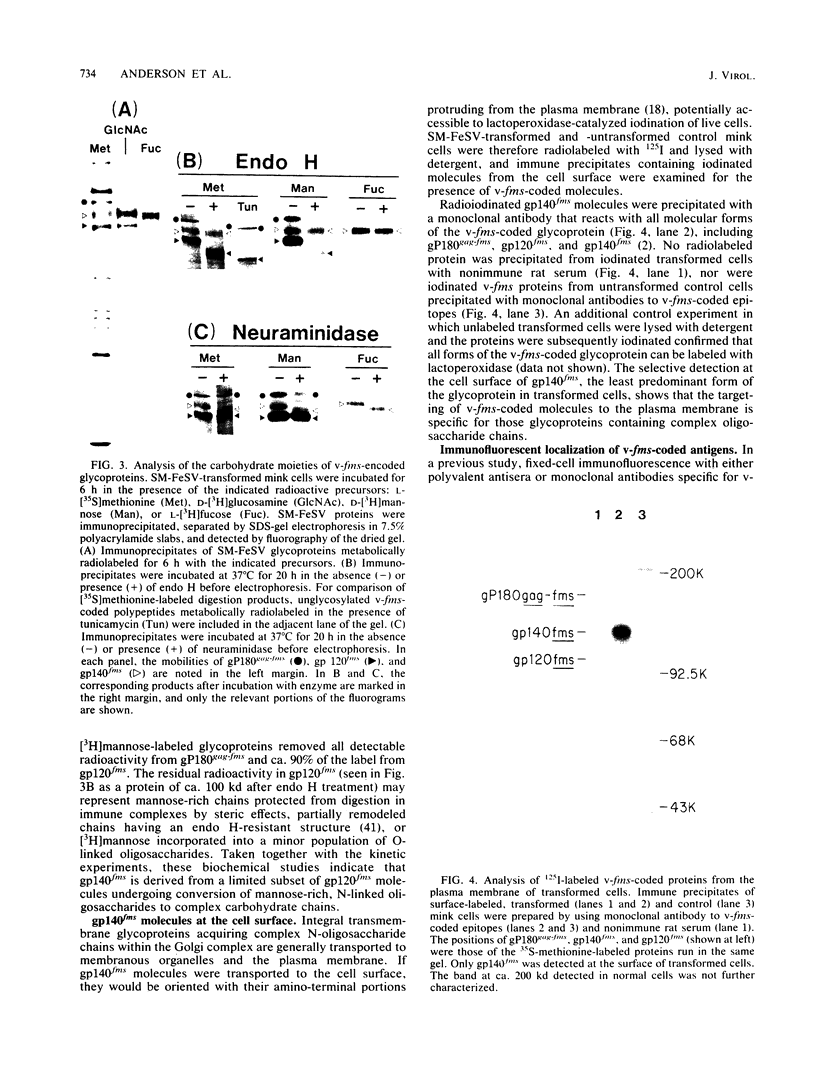
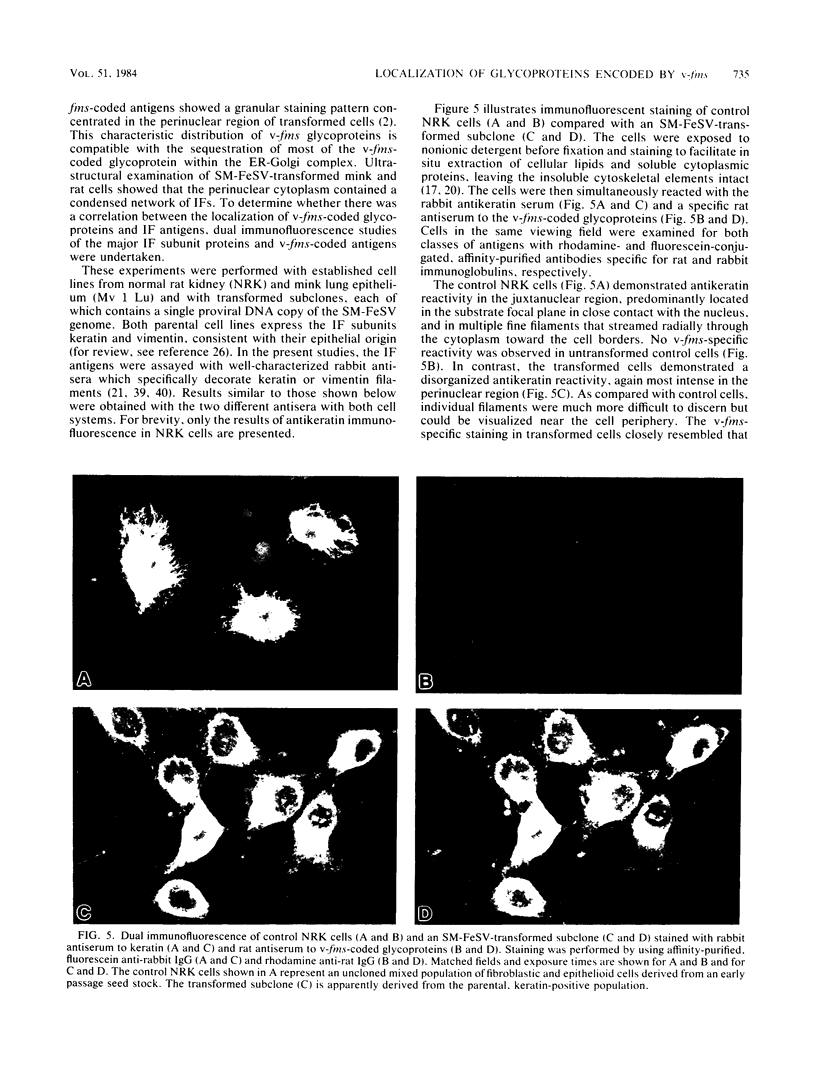
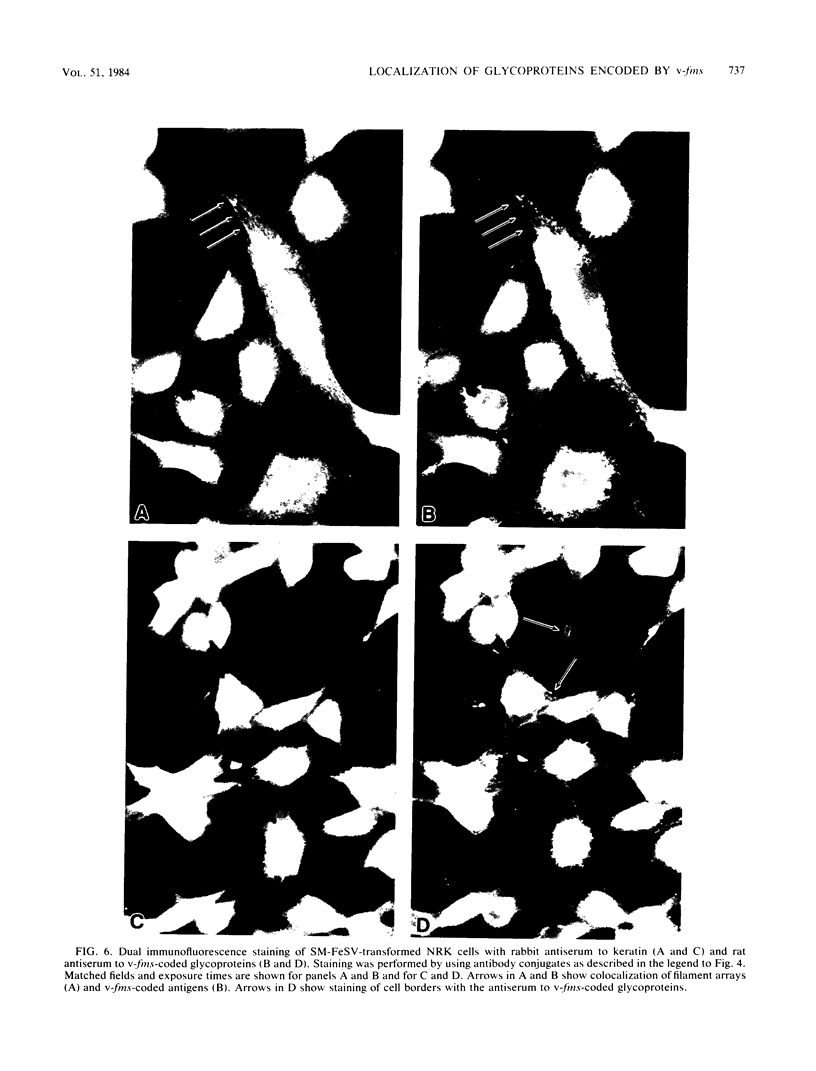
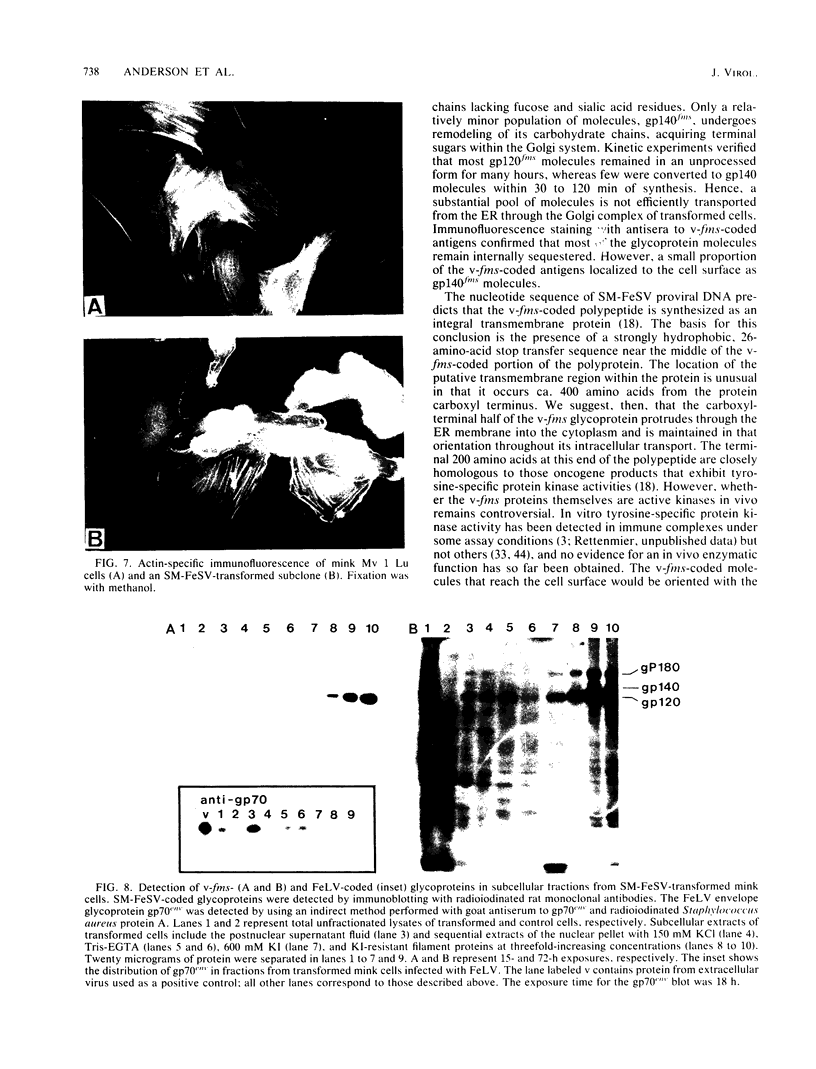
The McDonough strain of feline sarcoma virus encodes a polyprotein that is cotranslationally glycosylated and proteolytically cleaved to yield transforming glycoproteins specified by the viral oncogene v-fms. The major form of the glycoprotein (gp120fms) contains endoglycosidase H-sensitive, N-linked oligosaccharide chains lacking fucose and sialic acid, characteristic of glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Kinetic and steady-state measurements showed that most gp120fms molecules were not converted to mature forms containing complex carbohydrate moieties. Fixed-cell immunofluorescence confirmed that the majority of v-fms-coded antigens were internally sequestered in transformed cells. Dual-antibody fluorescence performed with antibodies to intermediate filaments (IFs) showed that the IFs of transformed cells were rearranged, and their distribution coincided with that of v-fms-coded antigens. No specific disruption of actin cables was observed. The v-fms gene products cofractionated with IFs isolated from virus-transformed cells and reassociated with IFs self-assembled in vitro. A minor population of v-fms-coded molecules (gp140fms) acquired endoglycosidase H-resistant, N-linked oligosaccharide chains containing fucose and sialic acid residues, characteristic of molecules processed in the Golgi complex. Some gp140fms molecules were detected at the plasma membrane and were radiolabeled by lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination of live transformed cells. We suggest that v-fms-coded molecules are translated as integral transmembrane glycoproteins, most of which are inhibited in transport through the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition protein is required for the integration of acetylcholine receptor delta subunit, a transmembrane glycoprotein, into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):501–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. J., Furth M., Wolff L., Ruscetti S. K., Sherr C. J. Monoclonal antibodies to the transformation-specific glycoprotein encoded by the feline retroviral oncogene v-fms. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):696–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.696-702.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Lauver A. V., Devare S. G. Biochemical and immunological characterization of polyproteins coded for by the McDonough, Gardner-Arnstein, and Snyder-Theilen strains of feline sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):196–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.196-207.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Lauver A. V. Gene products of McDonough feline sarcoma virus have an in vitro-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates tyrosine residues: lack of detection of this enzymatic activity in vivo. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.812-821.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Abulafia R. Association of glycoconjugates with the cytoskeletal framework. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):684–692. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner L., Fedele L. A., Garon C. F., Anderson S. J., Sherr C. J. McDonough feline sarcoma virus: characterization of the molecularly cloned provirus and its feline oncogene (v-fms). J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):489–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.489-500.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I. Temperature-sensitive changes in surface modulating assemblies of fibroblasts transformed by mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Gilbert J. H., Porzig K. J., Scolnick E. M., Aaronson S. A. Nature and distribution of feline sarcoma virus nucleotide sequences. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.821-827.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Structural associations of synemin and vimentin filaments in avian erythrocytes revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Synemin: a new high molecular weight protein associated with desmin and vimentin filaments in muscle. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Gobet M., Sherr C. J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the feline retroviral oncogene v-fms shows unexpected homology with oncogenes encoding tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Ramsay G. M., Savin K., Kitchener G., Graf T., Beug H. Identification and characterization of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB gene product as a membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Wang K., Singer S. J. Intracellular distributions of mechanochemical proteins in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huu Duc-Nguyen, Rosenblum E. N., Zeigel R. F. Persistent infection of a rat kidney cell line with Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1133-1140.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata A. Use of endo- and exoglycosidases for structural studies of glycoconjugates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific messenger RNAs in permissive cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8015–8022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Katz F. N., Lodish H. F., Blobel G. A signal sequence for the insertion of a transmembrane glycoprotein. Similarities to the signals of secretory proteins in primary structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8667–8670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Levy B. T. Highly purified pp60src induces the actin transformation in microinjected cells and phosphorylates selected cytoskeletal proteins in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):102–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Michael A. F. Retardation of fading and enhancement of intensity of immunofluorescence by p-phenylenediamine. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jun;31(6):840–842. doi: 10.1177/31.6.6341464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Sealy L., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB locus is a glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Karess R. E., Anderson S. M., Hanafusa H. Tryptic peptide analysis of avian oncovirus gag and pol gene products. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):102–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.102-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Van de Ven W. J., Blomberg J., Stephenson J. R. Differences in mechanisms of transformation by independent feline sarcoma virus isolates. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1084-1089.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Turek L. P., Sherr C. J. Three independent isolates of feline sarcoma virus code for three distinct gag-x polyproteins. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.259-264.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Ball E. H., Geiger B., Chen W. T. Immunolabeling studies of cytoskeletal association in cultured cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):303–316. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Immunofluorescent staining of keratin fibers in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Keratin filaments of cultured human epidermal cells. Formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds during terminal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Kobata A. The substrate specificities of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases CII and H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven W. J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Nalewaik R. P., Stephenson J. R. Characterization of a 170,000-dalton polyprotein encoded by the McDonough strain of feline sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.165-175.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F., Kelloff G. J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Hill R. W., Stephenson J. R. Monoclonal antibodies specific to transforming polyproteins encoded by independent isolates of feline sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):896–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.896-904.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Changes in microfilament organization and surface topogrophy upon transformation of chick embryo fibroblasts with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost C. S., Hedgpeth J., Lingappa V. R. A stop transfer sequence confers predictable transmembrane orientation to a previously secreted protein in cell-free systems. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]