Abstract
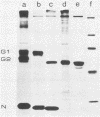
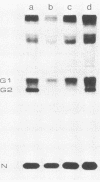
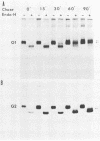
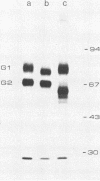
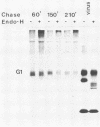
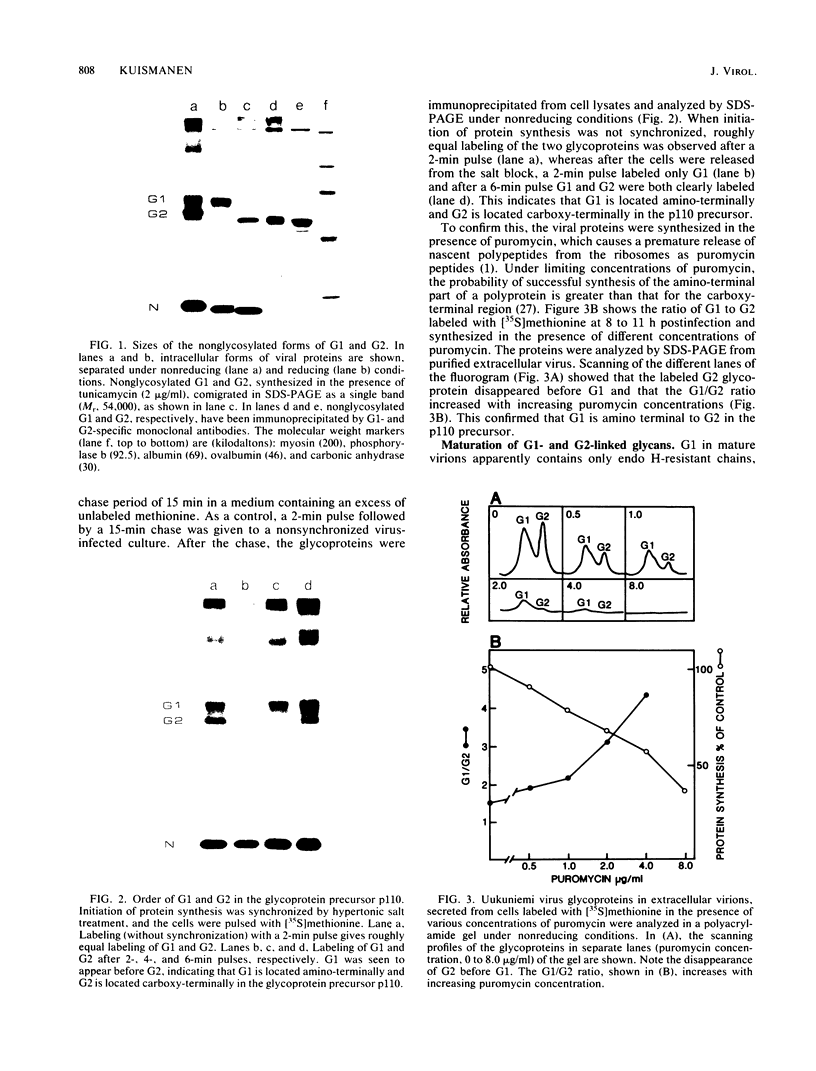
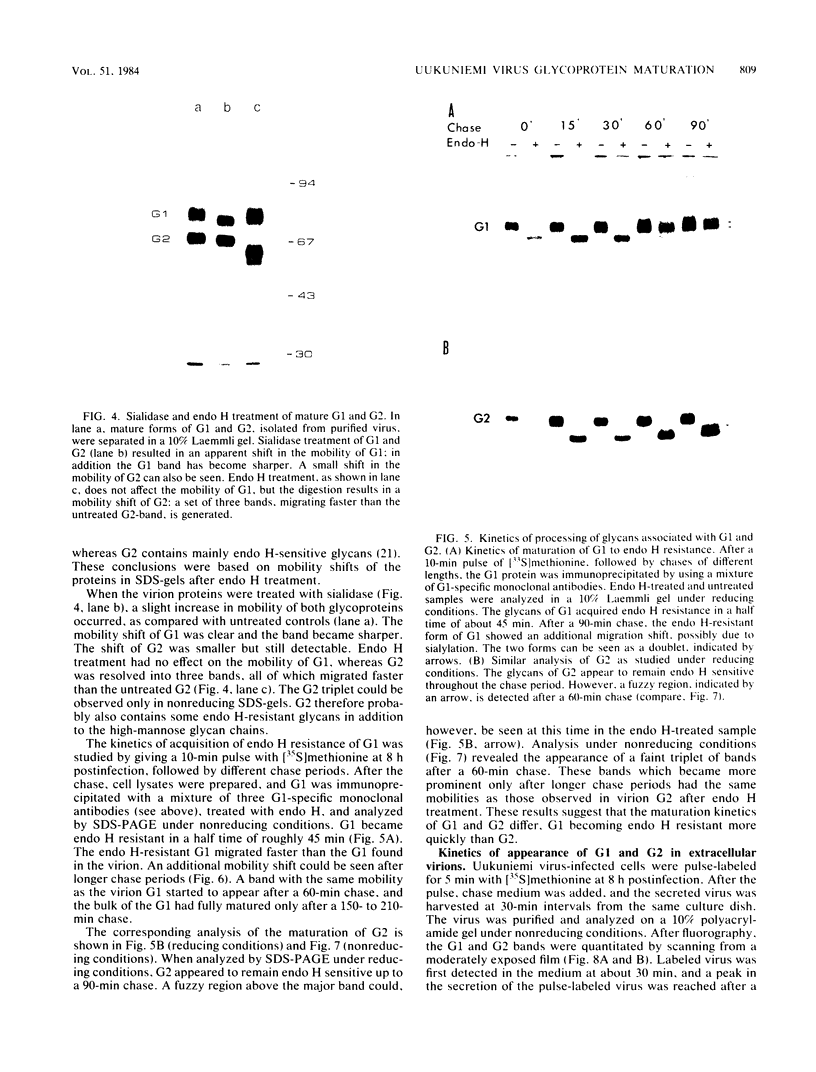
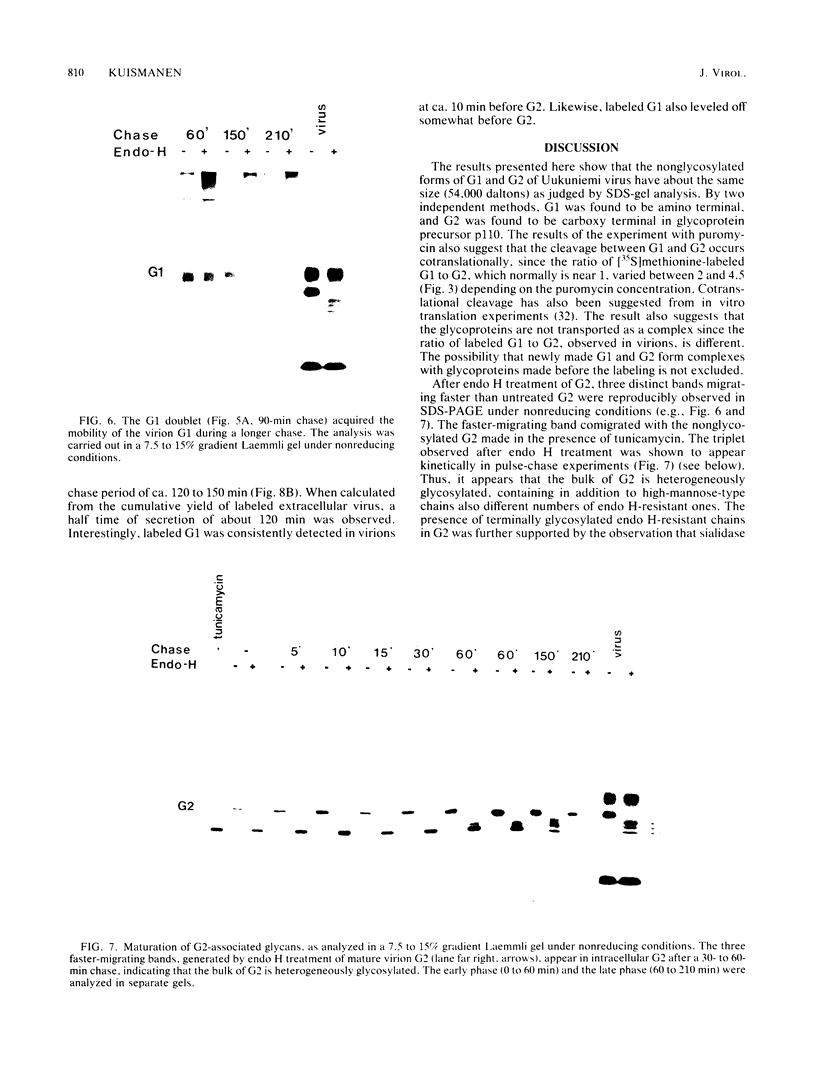
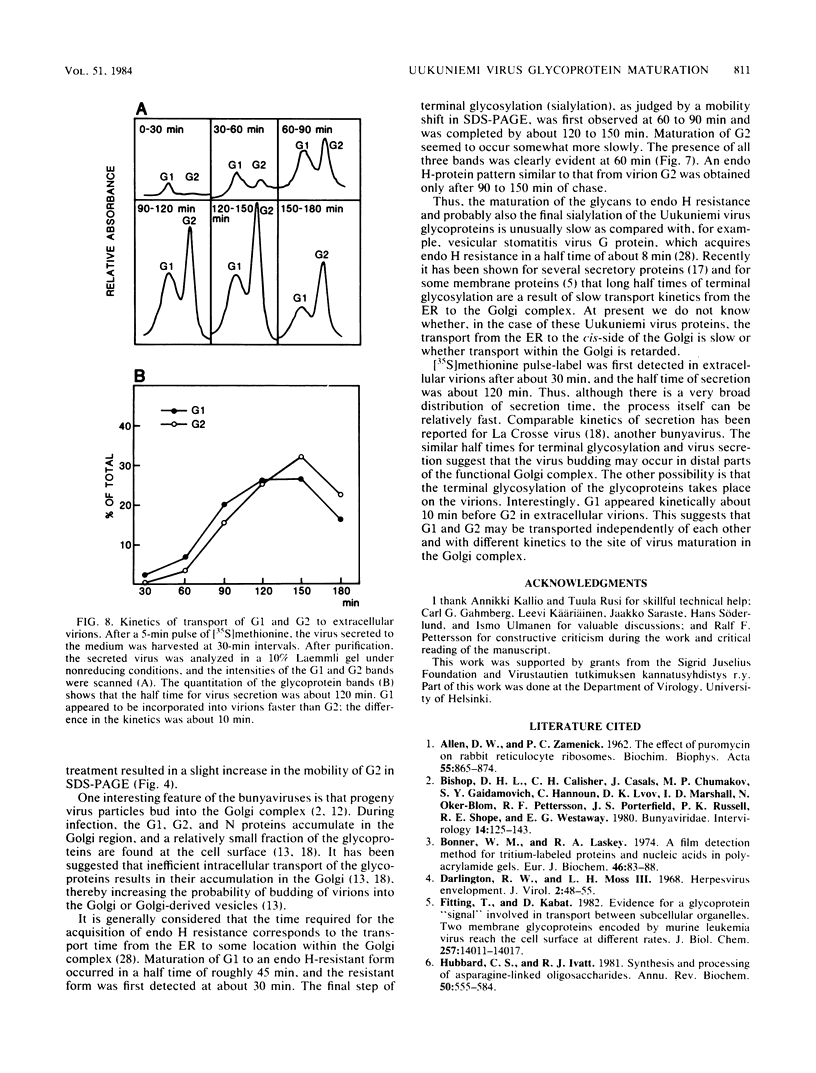
Uukuniemi virus, which matures specifically in the Golgi complex, contains two species of envelope glycoproteins, G1 (Mr, 70,000) and G2 (Mr, 65,000). These are translated as a polyprotein, p110, from an mRNA which is complementary to the medium-sized segment of the virion RNAs. By synchronized initiation of protein synthesis and pulse-labeling, it was shown that glycoprotein G1 is amino terminal in precursor protein p110. Apparently, the nonglycosylated forms of these proteins (Mr, 54,000 to 57,000), synthesized in the presence of tunicamycin, comigrate in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, because a similar-sized protein could be isolated by immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies directed against either G1 or G2. The G1 protein, which in the virion contains exclusively endoglycosidase H (endo H)-resistant glycans, was converted to the endo H-resistant form in a half time of about 45 min. The G2 protein, which in the virion has a heterogeneous glycosylation pattern as revealed by endo H digestion, attained this partial endo H resistance only after 90 to 150 min of chase. The transport time of Uukuniemi virus glycoproteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex was considerably longer than that for alpha and rhabdovirus glycoproteins. Determination of the transport time of G1 and G2 to extracellular virions revealed that G1 is incorporated into mature virions about 10 min faster than G2, suggesting that G1 and G2 are transported with different kinetics to the site of virus maturation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN D. W., ZAMECNIK P. C. The effect of puromycin on rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:865–874. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90899-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Calisher C. H., Casals J., Chumakov M. P., Gaidamovich S. Y., Hannoun C., Lvov D. K., Marshall I. D., Oker-Blom N., Pettersson R. F. Bunyaviridae. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):125–143. doi: 10.1159/000149174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitting T., Kabat D. Evidence for a glycoprotein "signal" involved in transport between subcellular organelles. Two membrane glycoproteins encoded by murine leukemia virus reach the cell surface at different rates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R. Cotranslational and posttranslational processing of viral glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Localization of two cellular forms of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1121–1127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1121-1127.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Reitman M. L., Varki A., Goldberg D., Gabel C. A. Steps in the phosphorylation of the high mannose oligosaccharides of lysosomal enzymes. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;(92):138–156. doi: 10.1002/9780470720745.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Bång B., Hurme M., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus maturation: immunofluorescence microscopy with monoclonal glycoprotein-specific antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):137–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.137-146.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Hedman K., Saraste J., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus maturation: accumulation of virus particles and viral antigens in the Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1444–1458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Structure and replication of alpha-viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:15–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Käriäinen L. Sequential translation of nonstructural proteins in cells infected with a Semliki Forest virus mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Braell W. A., Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J., Zilberstein A. Synthesis and assembly of membrane and organelle proteins. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1981;12:247–307. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364373-5.50016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N., Snider M., Strous G. J. Hepatoma secretory proteins migrate from rough endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi at characteristic rates. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):80–83. doi: 10.1038/304080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff D. H., Lenard J. A membrane glycoprotein that accumulates intracellularly: cellular processing of the large glycoprotein of LaCrosse virus. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massalski A., Coulter-Mackie M., Dales S. Assembly of mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:111–118. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Whitfield S. G. Bunyaviridae: morphologic and morphogenetic similarities of Bunyamwera serologic supergroup viruses and several other arthropod-borne viruses. Intervirology. 1973;1(4):297–316. doi: 10.1159/000148858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Kuismanen E., Pettersson R. F. Monosaccharide sequence of protein-bound glycans of Uukuniemi virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.390-400.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Hewlett M. J., Baltimore D., Coffin J. M. The genome of Uukuniemi virus consists of three unique RNA segments. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R., Käriäinen L. The ribonucleic acids of Uukuniemi virus, a noncubical tick-borne arbovirus. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):608–619. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R., Käriäinen L., von Bonsdorff C. H., Oker-Blom N. Structural components of Uukuniemi virus, a noncubical tick-borne arbovirus. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acid binding: a new kind of posttranslational modification of membrane proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;102:101–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68906-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H. The post-translational processing of Semliki forest virus structural polypeptides in puromycin treated cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):56–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Arima K., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Seppälä P., Pettersson R. F. In vitro translation of Uukuniemi virus-specific RNAs: identification of a nonstructural protein and a precursor to the membrane glycoproteins. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.72-79.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W. The role of the Golgi complex in sulfate metabolism. J Cell Biol. 1973 Apr;57(1):175–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]