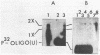
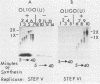
Abstract
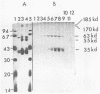
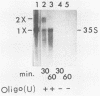
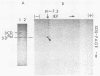
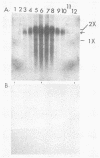
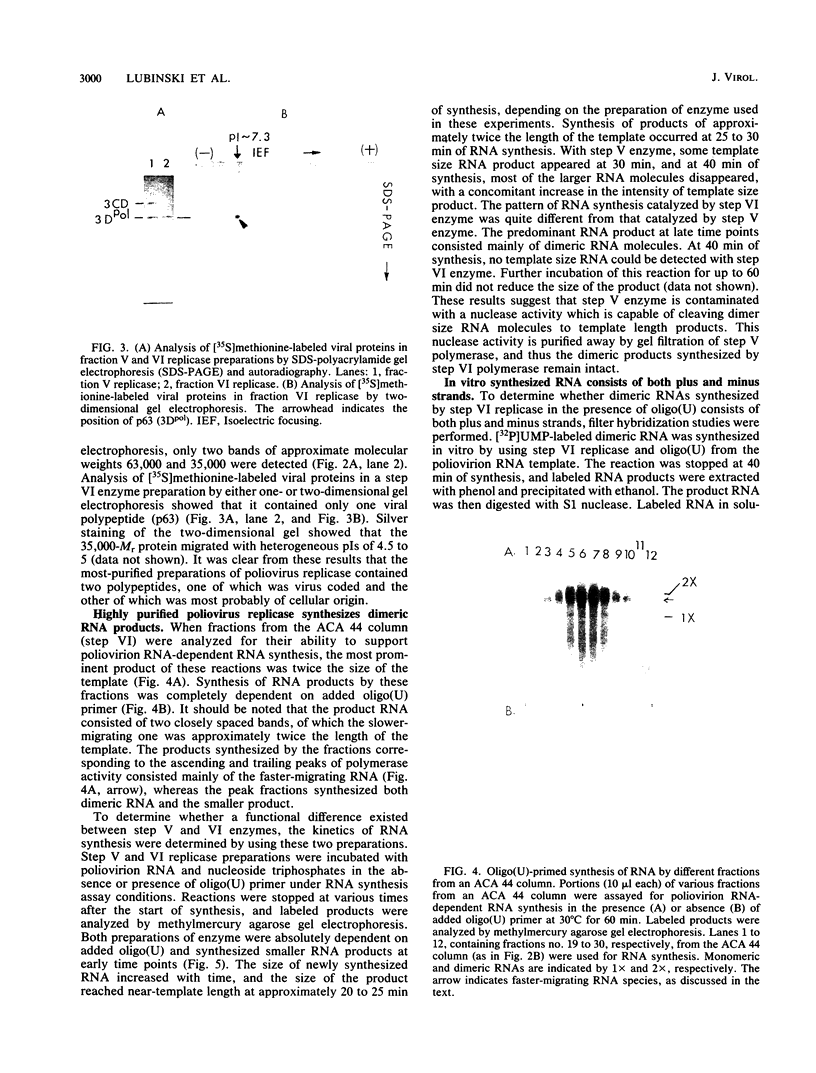
Poliovirus-specific RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (replicase, 3Dpol) was purified from HeLa cells infected with poliovirus. The purified enzyme preparation contained two proteins of apparent molecular weights 63,000 and 35,000. The 63,000-Mr polypeptide was virus-specific RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and the 35,000-Mr polypeptide was of host origin. Both polypeptides copurified through five column chromatographic steps. The purified enzyme preparation catalyzed synthesis of covalently linked dimeric RNA products from a poliovirion RNA template. This reaction was absolutely dependent on added oligo(U) primer, and the dimeric product appeared to be made of both plus- and minus-strand RNA molecules. Experiments with 5' [32P]oligo(U) primer and all four unlabeled nucleotides suggest that the viral replicase elongates the primer, copying the poliovirion RNA template (plus strand), and the newly synthesized minus strand snaps back on itself to generate a template-primer structure which is elongated by the replicase to form covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules. Kinetic studies showed that a partially purified preparation of poliovirus replicase contains a nuclease which can cleave the covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules, generating template-length RNA products.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. C., Baltimore D. Purification of a terminal uridylyltransferase that acts as host factor in the in vitro poliovirus replicase reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):221–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A. Purification of host factor required for in vitro transcription of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey T. D., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Host factor-induced template modification during synthesis of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):802–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.802-811.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey T. D., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Synthesis of plus- and minus-strand RNA from poliovirion RNA template in vitro. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.790-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Lubinski J., Dasgupta A., Racaniello V. R. In vitro synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8424–8428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski J. M., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Dasgupta A. Mechanism of in vitro synthesis of covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules by the poliovirus replicase. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.459-467.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Gibbons G. F., Dasgupta A. The host protein required for in vitro replication of poliovirus is a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Hocko J., Navab M., Dasgupta A. ATP is required for initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis in vitro: demonstration of tyrosine-phosphate linkage between in vitro-synthesized RNA and genome-linked protein. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):515–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.515-523.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senkevich T. G., Cumakov I. M., Lipskaya G. Y., Agol V. I. Palindrome-like dimers of double-stranded RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Rickles R. J., Flanegan J. B. Genome-length copies of poliovirion RNA are synthesized in vitro by the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4610–4617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. C., Tuschall D. M., Flanegan J. B. Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and host cell protein synthesize product RNA twice the size of poliovirion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.256-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]