Abstract
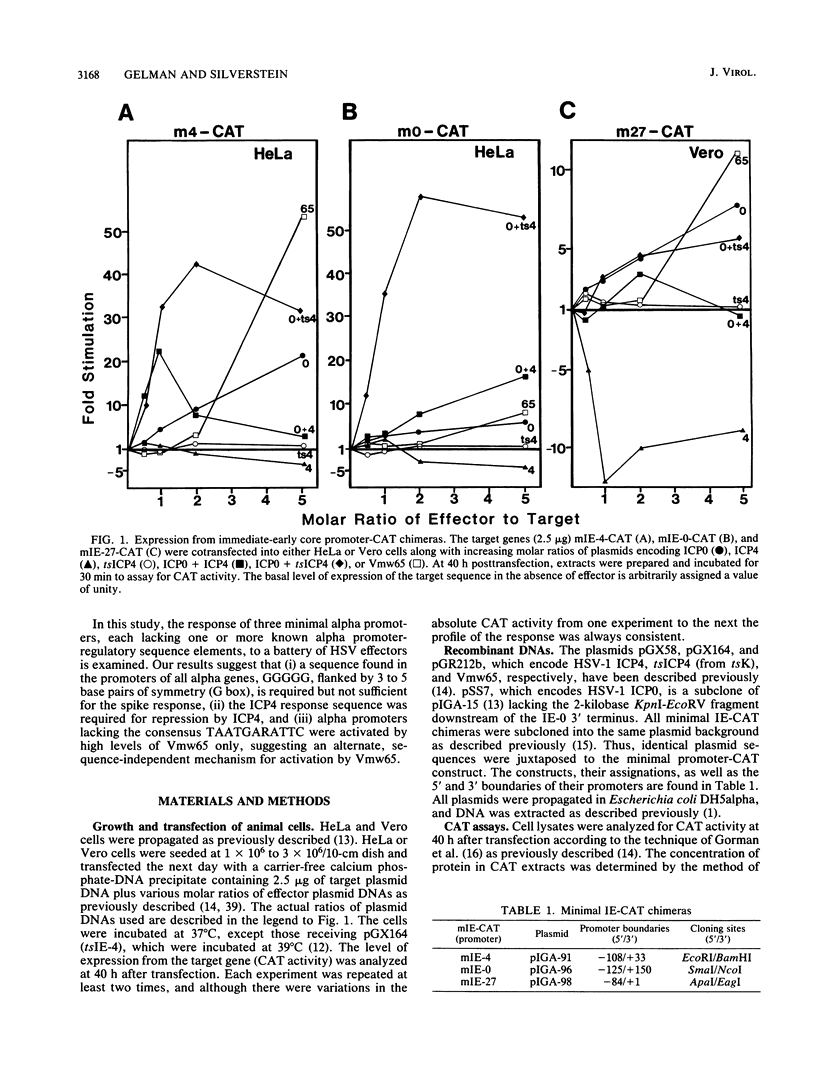
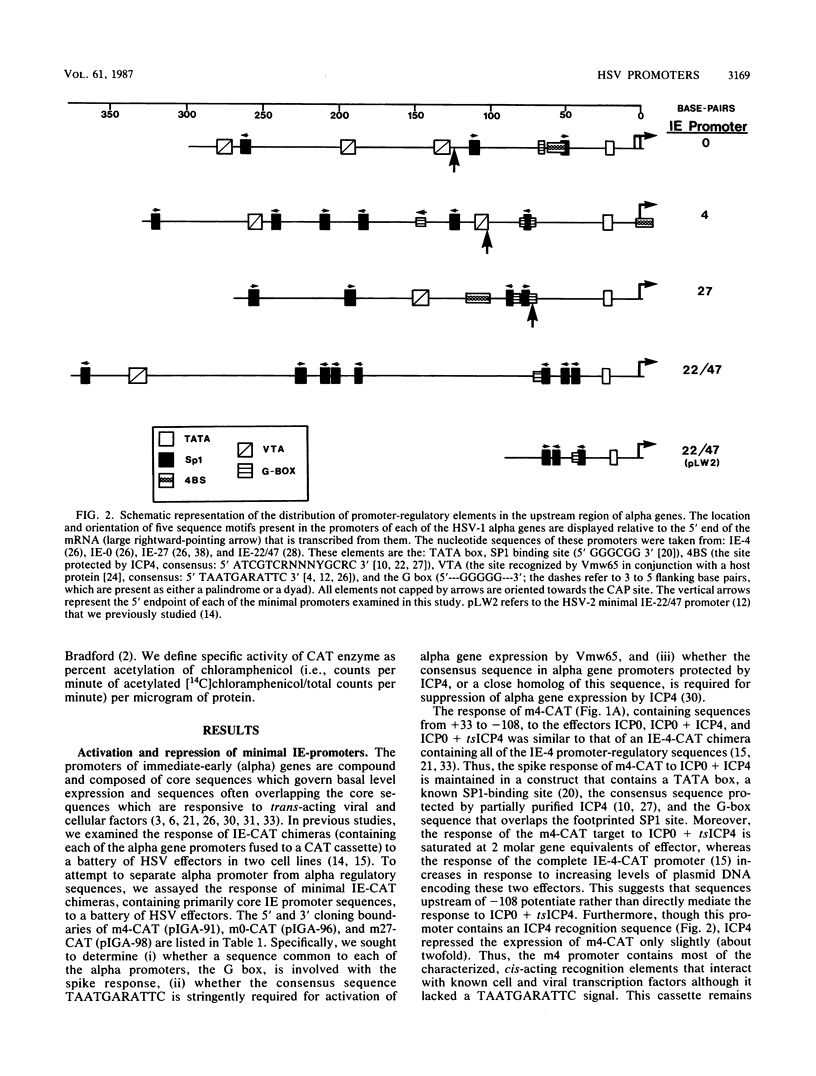
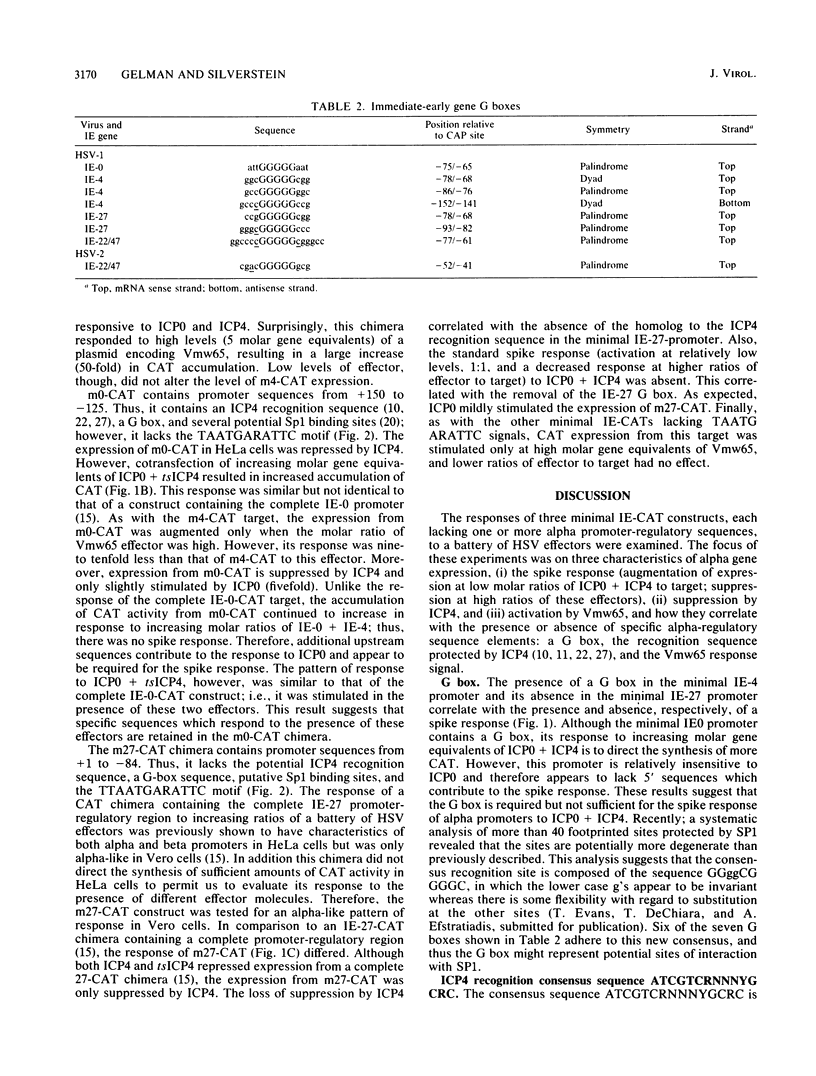
The immediate-early promoters of herpes simplex virus give rise to the first series of transcripts after infection. These promoters are composed of compound sequence elements that govern basal level and regulated transcription. The response of three core (truncated) promoters from the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE-4, IE-0, and IE-27 genes to a battery of virus-encoded trans-acting proteins was examined in a short-term transient expression assay system. The results of this study reveal (i) a role for a sequence, 5'---GGGGG---3', flanked by 3 to 5 base pairs of symmetry (the G box), which is present in the upstream region of all immediate-early gene promoters, (ii) a requirement for the consensus sequence protected by ICP4 for autoregulation by this immediate-early gene product, and (iii) an alternative, sequence-independent mechanism for the augmentation of alpha gene expression by the virion-associated transcriptional activator Vmw65, now designated as TIF.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Preston C. M. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene 3: DNA sequences required for enhancer-like activity and response to trans-activation by a virion polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):929–943. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Devi-Rao G., Thompson R. L., Wagner E. K. Virus-induced modification of the host cell is required for expression of the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene controlled by a late herpes simplex virus promoter (VP5). J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):19–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.19-30.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding properties of a herpes simplex virus immediate early protein. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1084–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1084-1087.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney D. F., McLauchlan J., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. A modular system for the assay of transcription regulatory signals: the sequence TAATGARAT is required for herpes simplex virus immediate early gene activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7847–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Co-ordinate regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression is mediated by the functional interaction of two immediate early gene products. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters are responsive to virus and cell trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2286–2296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2286-2296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Evidence for translational regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 gD expression. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.389-394.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Sp1 binds to promoter sequences and activates herpes simplex virus 'immediate-early' gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):179–182. doi: 10.1038/317179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Host cell proteins bind to the cis-acting site required for virion-mediated induction of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T. Binding of the herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene product ICP4 to its own transcription start site. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.858-865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Tannahill D. Effects of orientation and position on the activity of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene far-upstream region. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S., Engelhardt D. L. Alterations in the protein synthetic apparatus of cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Rixon F. J., Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Immediate-early mRNA-2 of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 is unspliced: conserved sequences around the 5' and 3' termini correspond to transcription regulatory signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6271–6287. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


