Abstract
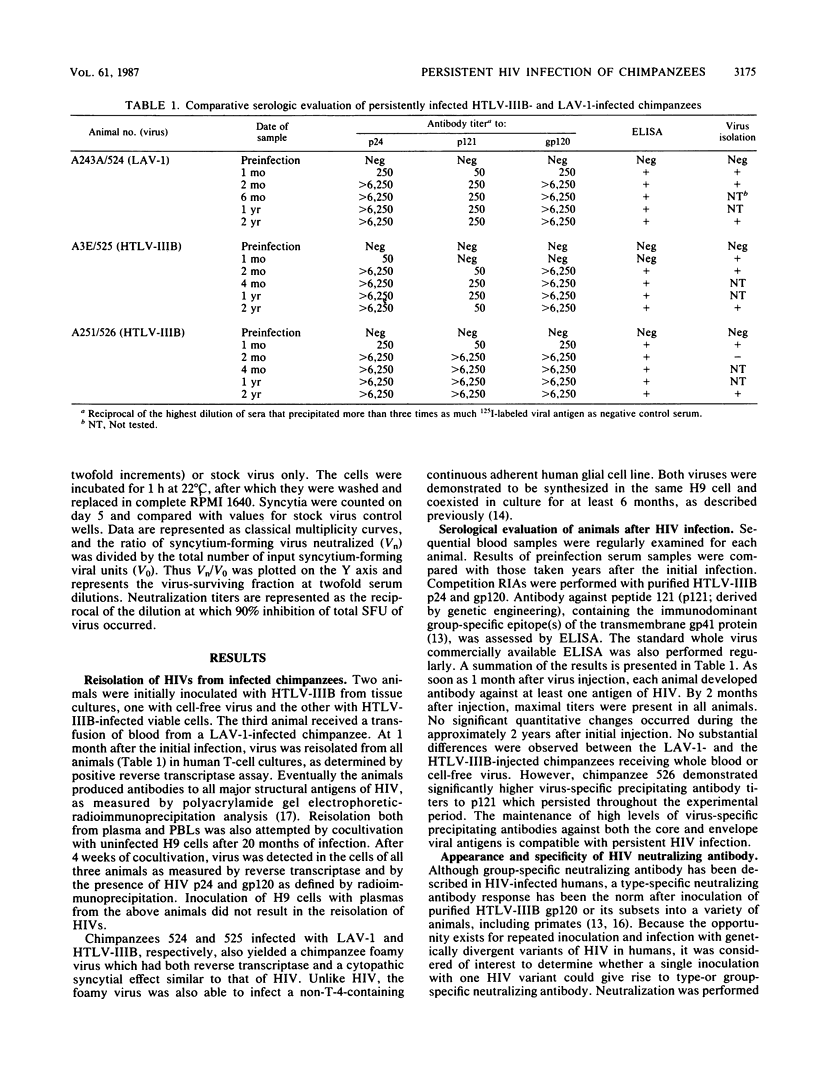
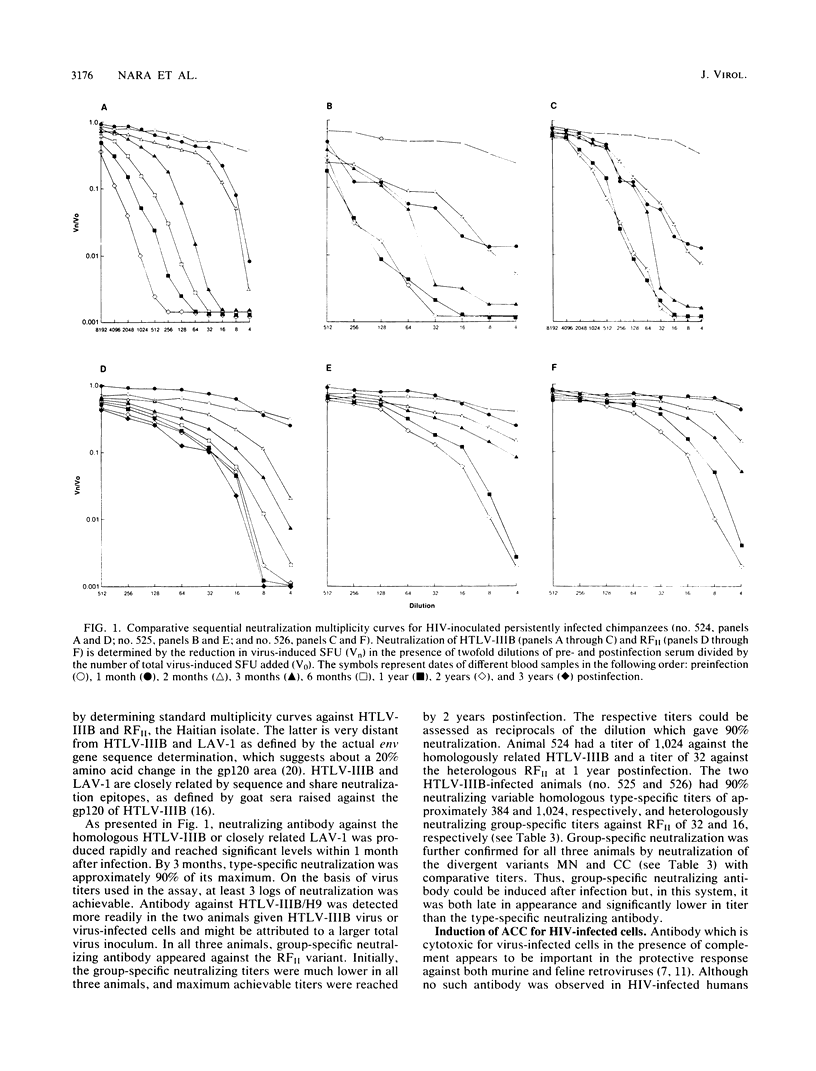
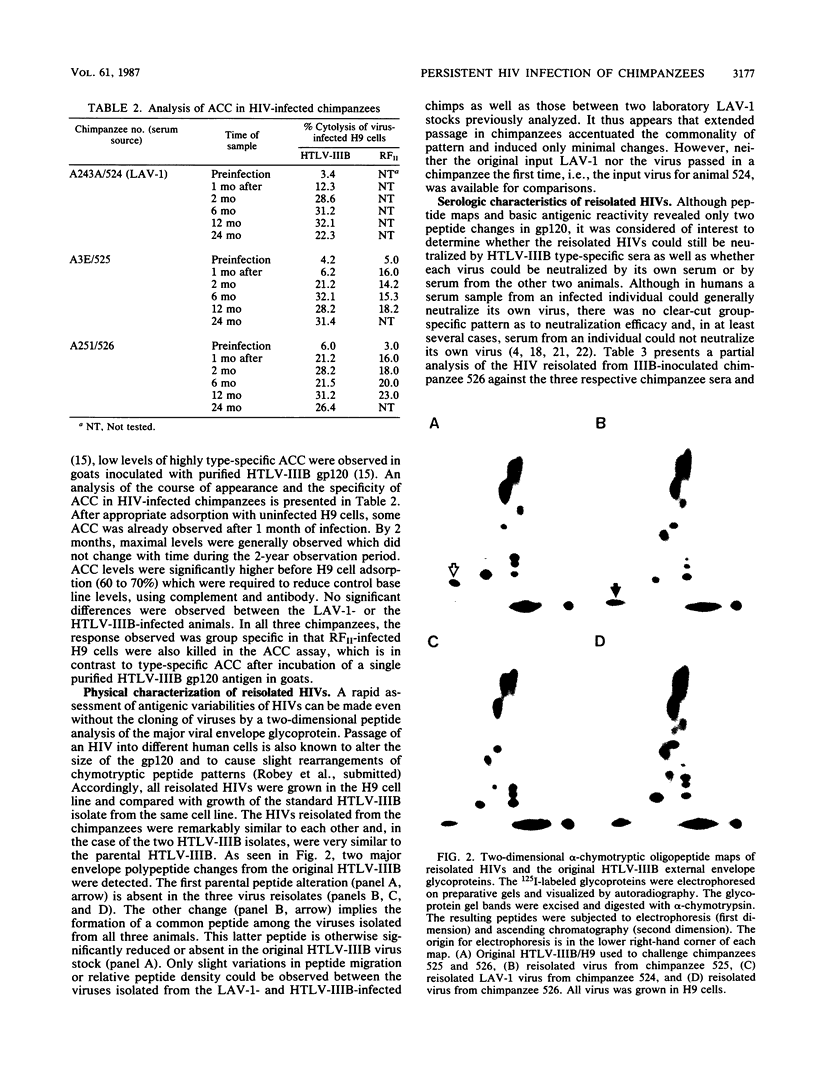
Persistent infection by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) in the chimpanzee may be valuable for immunopathologic and potential vaccine evaluation. Two HIV strains, the tissue culture-derived human T-cell lymphotropic virus type IIIB (HTLV-IIIB) and in vivo serially passaged lymphadenopathy-associated virus type 1 (LAV-1), were injected intravenously into chimpanzees. Two animals received HTLV-IIIB as either virus-infected H9 cells or cell-free virus. A third animal received chimpanzee-passaged LAV-1. Evaluation of their sera for virus-specific serologic changes, including neutralizations, was done during a 2-year period. During this period all animals had persistently high titers of antibodies to viral core and envelope antigens. All three animals developed a progressively increasing type-specific neutralizing LAV-1 versus HTLV-IIIB antibody titer during the 2-year observation period which broadened in specificity to include HTLV-HIRF, HTLV-IIIMN, and HTLV-IIICC after 6 to 12 months. The antibody titers against both viruses were still increasing by 2 years after experimental virus inoculation. Sera from all animals were capable of neutralizing both homologously and heterologously reisolated virus from chimpanzees. A slightly more rapid type-specific neutralizing response was noted for the animal receiving HTLV-IIIB-infected cells compared with that for cell-free HTLV-IIIB. Sera from all persistently infected chimpanzees were capable of mediating group-specific antibody-mediated complement-dependent cytolysis of HIV-infected cells derived from all isolates tested. Viruses reisolated from all three animals at 20 months after inoculation revealed very similar peptide maps of their respective envelope gp120s, as determined by two-dimensional chymotrypsin oligopeptide analysis. One peptide, however, from the original HTLV-IIIB-inoculated virus was deleted in viruses from all three animals, and in addition, we noted the appearance of a new or modified peptide which was common to LAV-1 as well as to HTLV-IIIB reisolated from infected chimpanzees. It thus appears that a group-specific neutralizing antibody response as well as a group-specific cytotoxic response can develop in chimpanzees after an inoculation of a single HIV variant. This finding suggests that a common, less immunodominant determinant(s) is present on a single HIV strain which could induce group-specific antibodies during viral infection and replication. The identification of this group-specific epitope and the induction of analogous immunity may be relevant to vaccine development against human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Eichberg J. W., Masur H., Saxinger W. C., Gallo R., Macher A. M., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Transmission of HTLV-III infection from human plasma to chimpanzees: an animal model for AIDS. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):549–552. doi: 10.1126/science.6093251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin F., McLane M. F., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Groopman J. E., Essex M. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1094–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.2986291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Klatzmann D., Montagnier L. Deficient LAV1 neutralising capacity of sera from patients with AIDS or related syndromes. Lancet. 1985 Apr 13;1(8433):879–880. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Genetic variation in AIDS viruses. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Dunlop N. M., Schwarz H., Ihle J. N., Weinhold K., Bolognesi D. P., Schafer W. XVIII. Effective treatment of AKR leukemia with antibody to gp7 1 eliminates the neonatal burst of ecotropic AKR virus producing cells. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):68–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Sch5AAFER W., Bolognesi D. P. Neutralization of homologous and heterologous oncornaviruses by antisera against the p15(E) and gp71 polypeptides of Friend murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):169–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. P., Feorino P. M., Broderson J. R., McClure H. M., Getchell J. P., McGrath C. R., Swenson B., McDougal J. S., Palmer E. L., Harrison A. K. Infection of chimpanzees with lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1276–1277. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92824-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Swenson R. B., McGrath C. R., Brodie A., Getchell J. P., Jensen F. C., Anderson D. C., Broderson J. R., Francis D. P. Persistent infection of chimpanzees with human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus: a potential model for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.116-124.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C., Amyx H. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Asher D. M., Rodgers-Johnson P., Epstein L. G., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C., Maluish A., Arthur L. O. Infection of chimpanzees by human T-lymphotropic retroviruses in brain and other tissues from AIDS patients. Lancet. 1985 Jan 5;1(8419):55–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. K., Essex M., Gardner M. B., Hardy W. D., Jr Natural feline leukemia virus infection and the immune response of cats of different ages. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):823–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. J., Langlois A. J., Robey W. G., Chang N. T., Gallo R. C., Fischinger P. J., Bolognesi D. P. Restricted neutralization of divergent human T-lymphotropic virus type III isolates by antibodies to the major envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9709–9713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Asher D. M., Yanagihara R., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Fischinger P. J. Simultaneous isolation of simian foamy virus and HTLV-III/LAV from chimpanzee lymphocytes following HTLV-III or LAV inoculation. Arch Virol. 1987;92(1-2):183–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01310072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Matthews T. J., Langlois A., Copeland T. D., Lerche N. W., Oroszlan S., Bolognesi D. P., Gilden R. V., Fischinger P. J. Prospect for prevention of human immunodeficiency virus infection: purified 120-kDa envelope glycoprotein induces neutralizing antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7023–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey W. G., Safai B., Oroszlan S., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Gallo R. C., Fischinger P. J. Characterization of envelope and core structural gene products of HTLV-III with sera from AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.2984774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safai B., Sarngadharan M. G., Groopman J. E., Arnett K., Popovic M., Sliski A., Schüpbach J., Gallo R. C. Seroepidemiological studies of human T-lymphotropic retrovirus type III in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet. 1984 Jun 30;1(8392):1438–1440. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91933-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H., Ihle J. N., Wecker E., Fischinger P. J., Thiel H. J., Bolognesi D. P., Schäfer W. Properties of mouse leukemia viruses. XVII. Factors required for successful treatment of spontaneous AKR leukemia by antibodies against gp71. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):568–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Clapham P. R., Cheingsong-Popov R., Dalgleish A. G., Carne C. A., Weller I. V., Tedder R. S. Neutralization of human T-lymphotropic virus type III by sera of AIDS and AIDS-risk patients. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):69–72. doi: 10.1038/316069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Dalgleish A. G., Lasky L. A., Berman P. W. Variable and conserved neutralization antigens of human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):572–575. doi: 10.1038/324572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]