Abstract
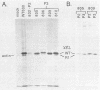
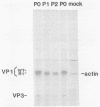
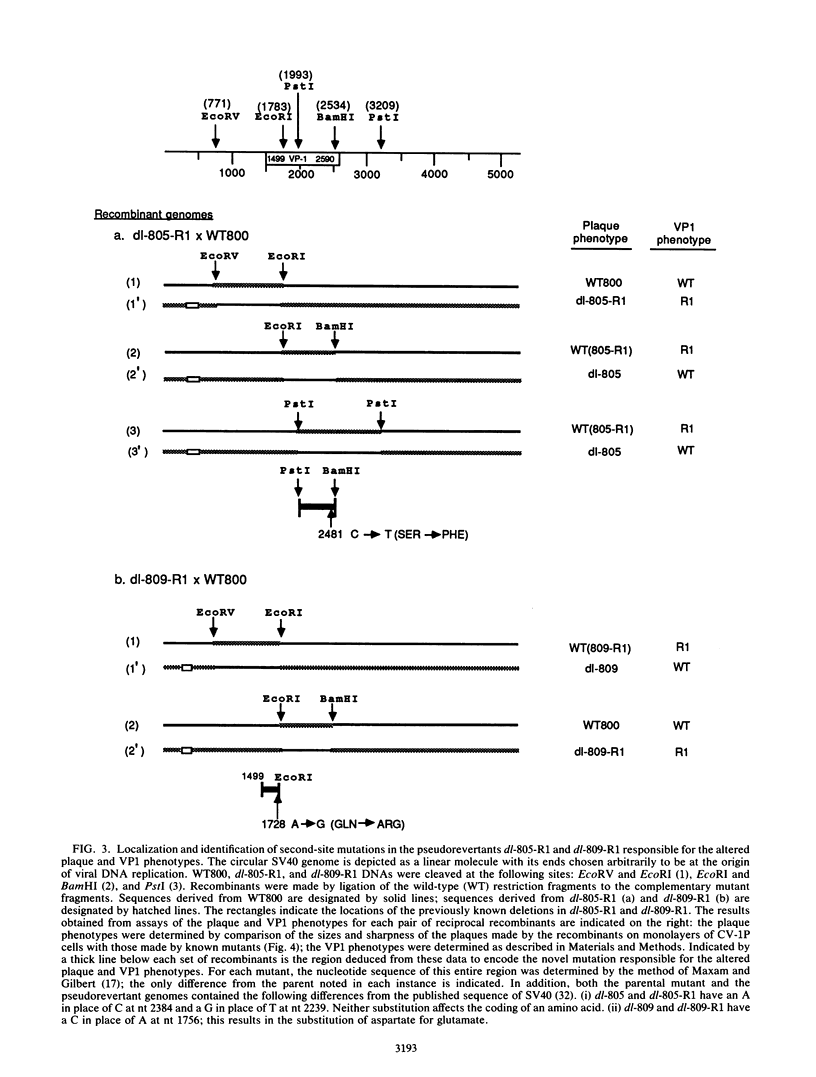
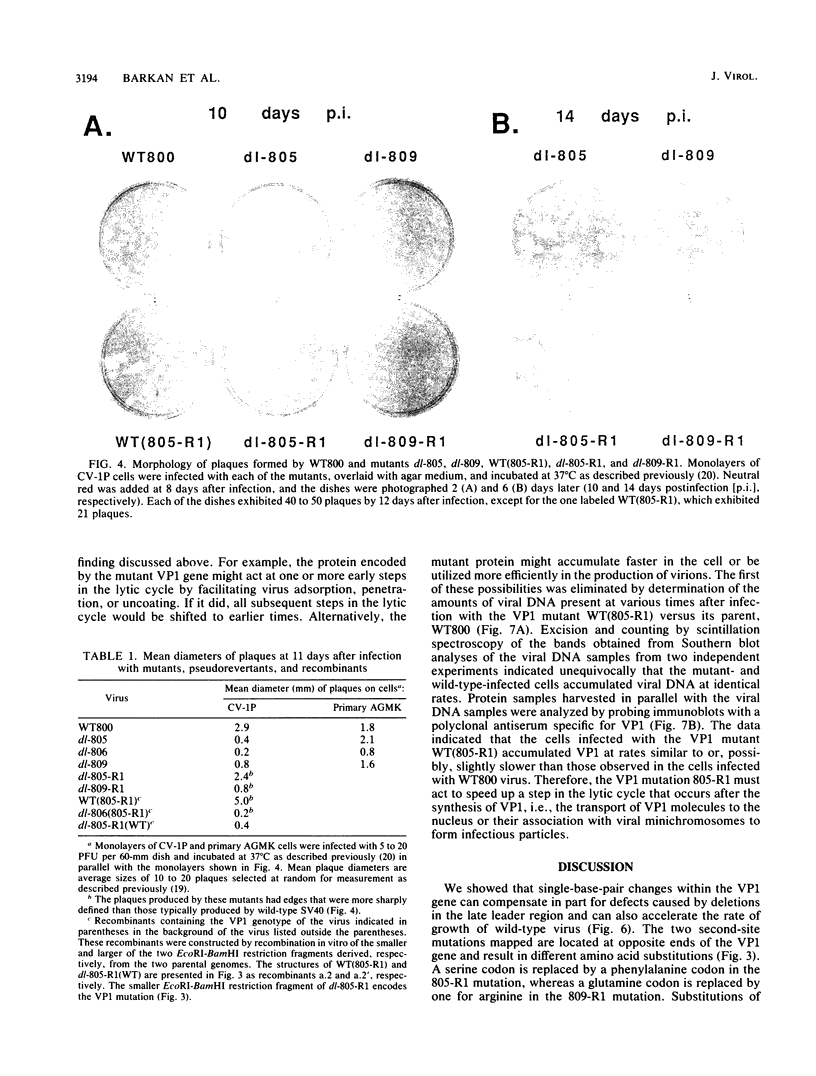
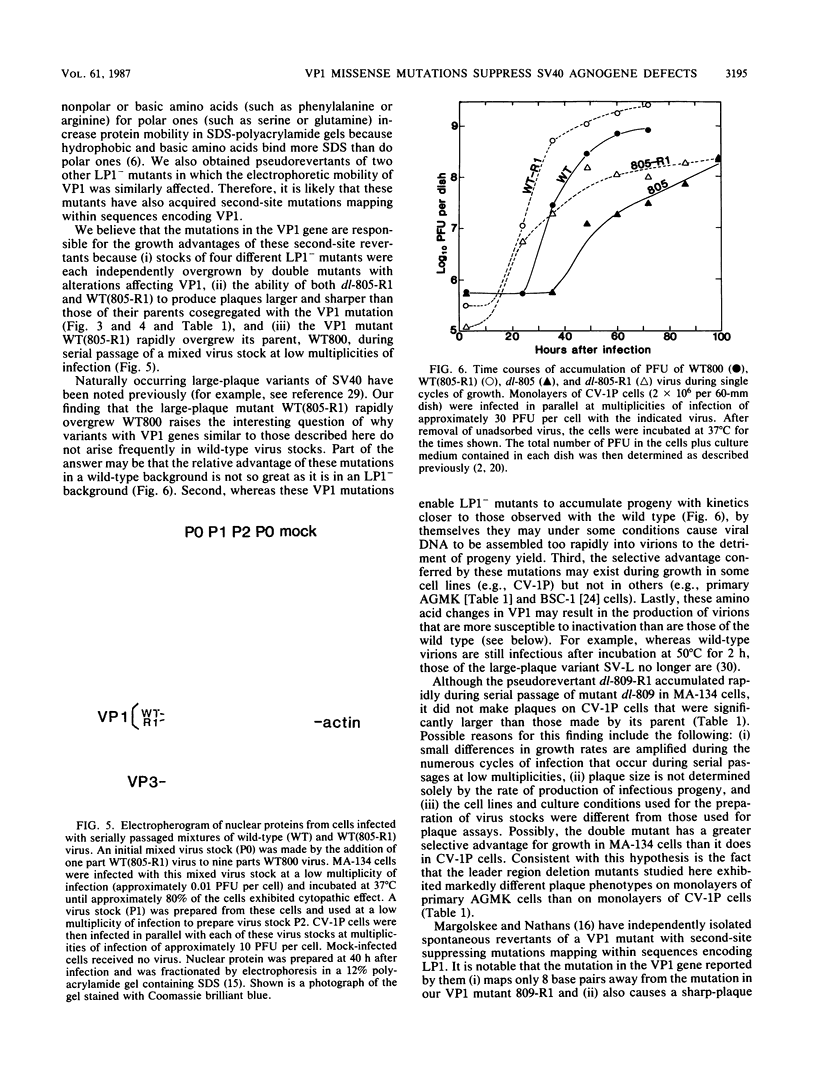
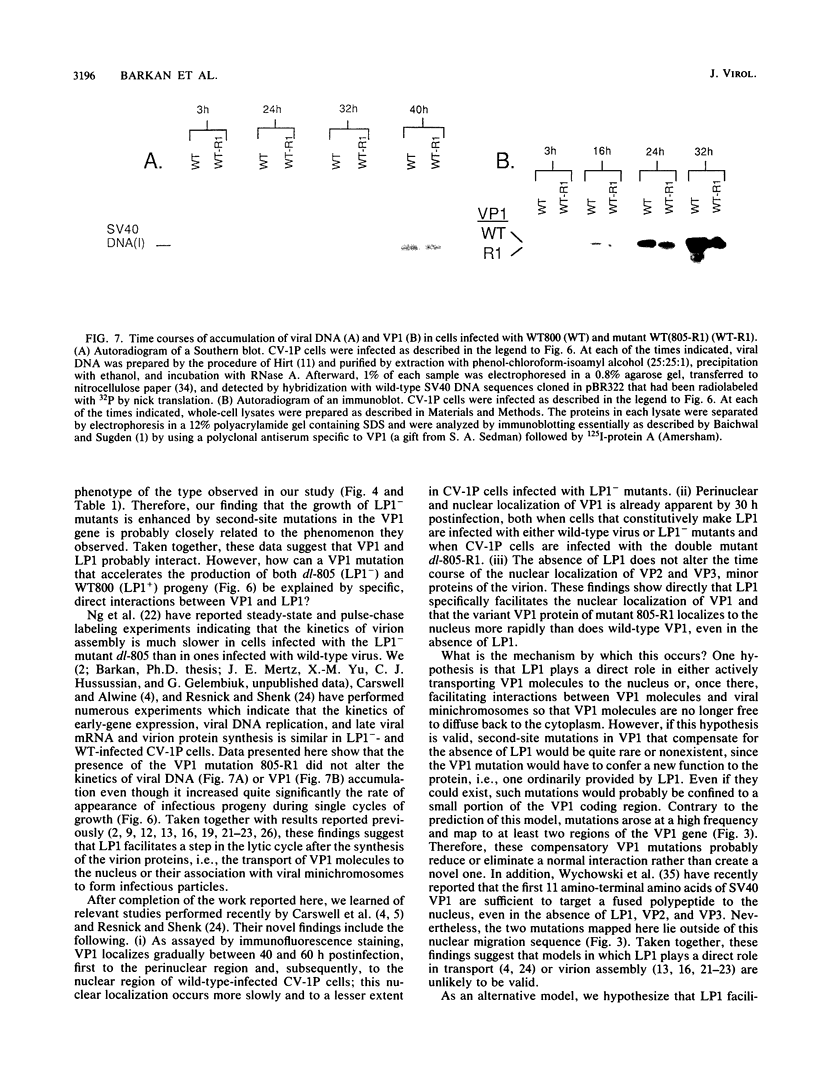
Simian virus 40 mutants lacking sequences in the late leader region are viable but produce smaller plaques than does wild-type virus. Within three passages at low multiplicities of infection, virus stocks of several such mutants accumulated variants that synthesized an altered form of the major virion protein, VP1, having a slightly faster mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels than did the wild-type protein. Because these variants overgrew the original virus stocks, we consider them to be second-site revertants. By construction and characterization of a series of recombinants, the second-site mutations were shown to map to at least two different regions of the VP1 gene. Nucleotide sequence analysis indicated that single-amino-acid changes were responsible for the rapid mobility of VP1. When combined in cis with either a wild-type or mutant leader region, these VP1 mutations sped up by 10 to 20 h the time course of accumulation of infectious progeny but not of viral DNA or VP1. LP1, the protein encoded by the agnogene, was shown previously to be necessary for the efficient transport of the virion proteins to the nucleus or for their efficient assembly with viral minichromosomes. The VP1 missense mutations reported here compensate for the lack of LP1 by facilitating this process. On the basis of these findings and findings reported previously by us and others, we hypothesize that LP1 facilitates the formation of infectious particles by inhibiting the polymerization of VP1 molecules until the time they interact with viral minichromosomes; the VP1 mutations reported here compensate for the loss of LP1 by lessening the potential of VP1 for self-polymerization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Posttranslational processing of an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane protein expressed in cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):866–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.866-875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A., Mertz J. E. DNA sequence analysis of simian virus 40 mutants with deletions mapping in the leader region of the late viral mRNA's: mutants with deletions similar in size and position exhibit varied phenotypes. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):730–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.730-737.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A., Mertz J. E. The number of ribosomes on simian virus 40 late 16S mRNA is determined in part by the nucleotide sequence of its leader. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):813–816. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Alwine J. C. Simian virus 40 agnoprotein facilitates perinuclear-nuclear localization of VP1, the major capsid protein. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1055-1061.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Resnick J., Alwine J. C. Construction and characterization of CV-1P cell lines which constitutively express the simian virus 40 agnoprotein: alteration of plaquing phenotype of viral agnogene mutants. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):415–422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.415-422.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Sugawara K., Rho H. M., Harter M. L., Green M. Immunological identification of two adenovirus 2-induced early proteins possibly involved in cell transformation. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):263–266. doi: 10.1038/264263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., van Heuverswyn H., Gheysen D., Fiers W. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of late mRNA induced by a viable simian virus 40 deletion mutant. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.484-493.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz G. Z., Mertz J. E. Bidirectional promoter elements of simian virus 40 are required for efficient replication of the viral DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3513–3522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. Use of whole-cell fixation to visualize replicating and maturing simian virus 40: identification of new viral gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Suppression of a VP1 mutant of simian virus 40 by missense mutations in serine codons of the viral agnogene. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):405–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.405-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Defective simian virus 40 genomes: isolation and growth of individual clones. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40: selective isolation by means of a restriction endonuclease from Hemophilus parainfluenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4879–4883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Murphy A., Barkan A. Mutants deleted in the agnogene of simian virus 40 define a new complementation group. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):36–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.36-46.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. C., Mertz J. E., Sanden-Will S., Bina M. Simian virus 40 maturation in cells harboring mutants deleted in the agnogene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1127–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Khoury G., Jay G. Subcellular localization of the simian virus 40 agnoprotein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):428–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.428-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick J., Shenk T. Simian virus 40 agnoprotein facilitates normal nuclear location of the major capsid polypeptide and cell-to-cell spread of virus. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1098–1106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1098-1106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N. Segments of simian virus 40 DNA spanning most of the leader sequence of the major late viral messenger RNA are dispensable. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2556–2560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Kirschstein R. L., Habel K. Mutants of simian virus 40 differing in plaque size, oncogenicity, and heat sensitivity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):990–994. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.990-994.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. SV40 thermosensitive mutant: synthesis of viral DNA and virus-induced proteins at nonpermissive temperature. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):938–945. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zaane D., Dekker-Michielsen J. A., Bloemers H. P. Virus-specific precursor polypeptides in cells infected with Rauscher leukemia virus: synthesis, identification, and processing. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., Benichou D., Girard M. A domain of SV40 capsid polypeptide VP1 that specifies migration into the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Zweers A., Cohen L. H. Influence of single amino acid substitutions on electrophoretic mobility of sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]