Abstract
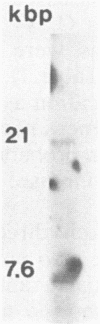
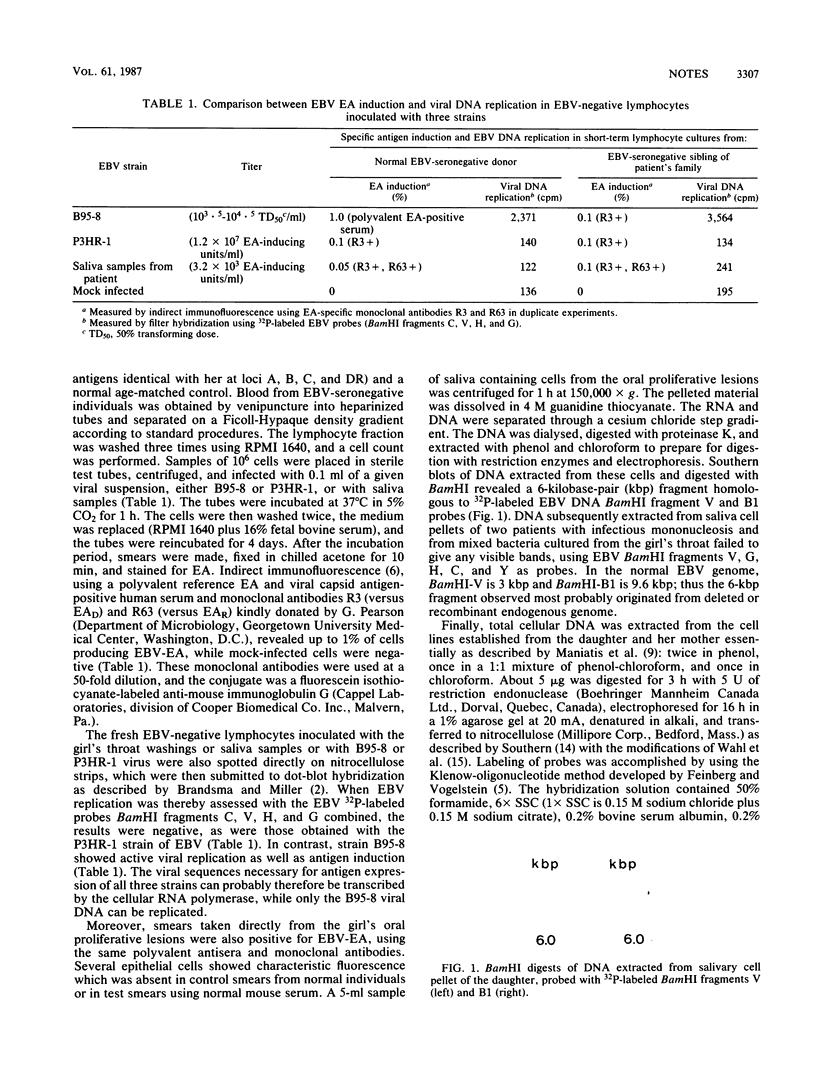
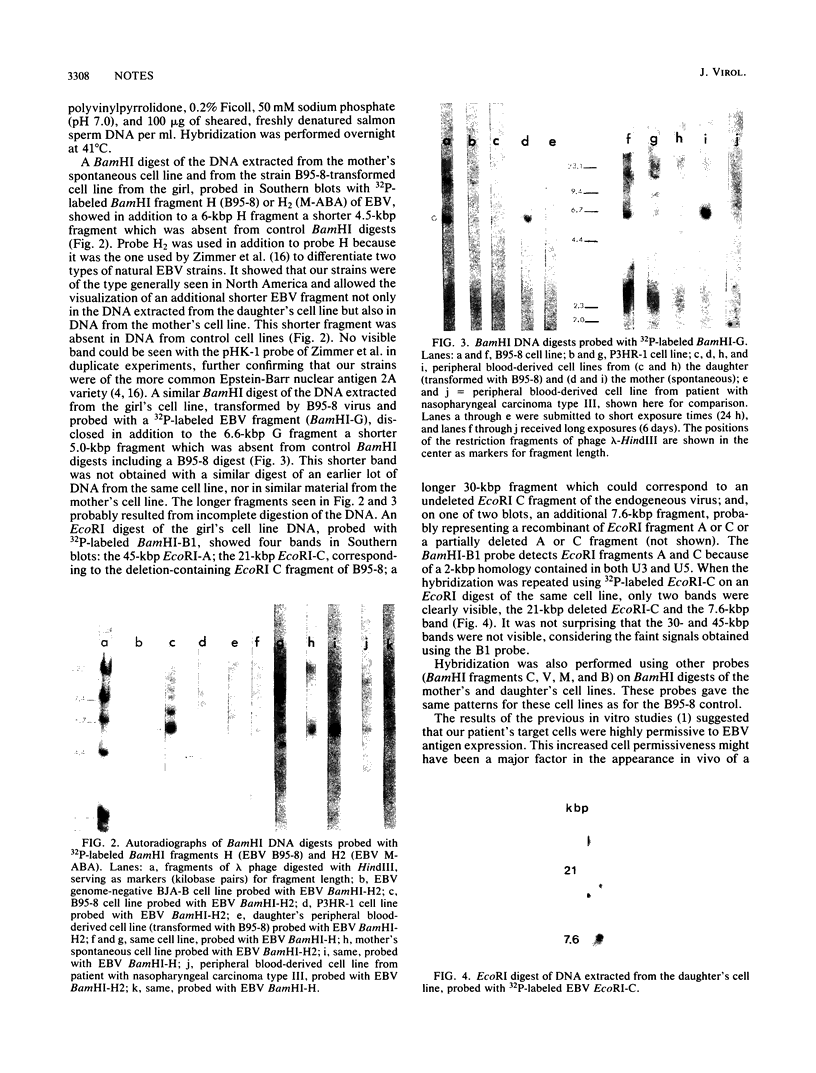
A virus recovered from the saliva of a child with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection for 8 years was shown to induce EBV early antigen (EBV-EA) in Raji cells and to be expressed into EBV-EA in fresh EBV-negative peripheral blood leukocytes. However, it did not replicate its DNA. Oropharyngeal epithelial cells scraped from recurrent mouth lesions were similarly positive for EBV-EA. DNA extracted from these cells and digested with BamHI contained a 6-kilobase-pair fragment homologous to BamHI fragment V and B1 EBV DNA probes. Furthermore, Southern blots of the BamHI and EcoRI digests of the DNA extracted from the cell lines of the patient (transformed with EBV strain B95-8) and of her mother (spontaneous) revealed, in addition to the expected BamHI G, H, H2, and B1 fragments used as probes, additional shorter ones of a presumably endogenous defective virus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Ghibu F., Joncas J. H. Lytic, nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) from a patient with chronic active EBV infection. Can Med Assoc J. 1984 Nov 15;131(10):1249–1252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J., Miller G. Nucleic acid spot hybridization: rapid quantitative screening of lymphoid cell lines for Epstein-Barr viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. Structure of defective DNA molecules in Epstein-Barr virus preparations from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.199-207.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joncas J. H., Ghibu F., Blagdon M., Montplaisir S., Stefanescu I., Menezes J. A familial syndrome of susceptibility to chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Can Med Assoc J. 1984 Feb 1;130(3):280–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Raab-Traub N. Two strains of Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8 and a P3HR-1 subclone) that lack defective genomes induce early antigen and cause abortive infection of Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1985–1991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1985-1991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Heston L., Countryman J. P3HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA is an independent replicon maintained by cell-to-cell spread. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.45-52.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Heston L., Miller G. Identification of a rare Epstein-Barr virus variant that enhances early antigen expression in Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Carey R. W., Miller G., Henle W., Eastman R., Mark E. J., Kenyon K., Wheeler E. O., Rubin R. H. Chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection associated with fever and interstitial pneumonitis. Clinical and serologic features and response to antiviral chemotherapy. Ann Intern Med. 1986 May;104(5):636–643. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-5-636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber U., Adldinger H. K., Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Knebel-Doeberitz M. V., Laux G., Desgranges C., Wittmann P., Freese U. K., Schneider U. Geographical prevalence of two types of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]