Abstract
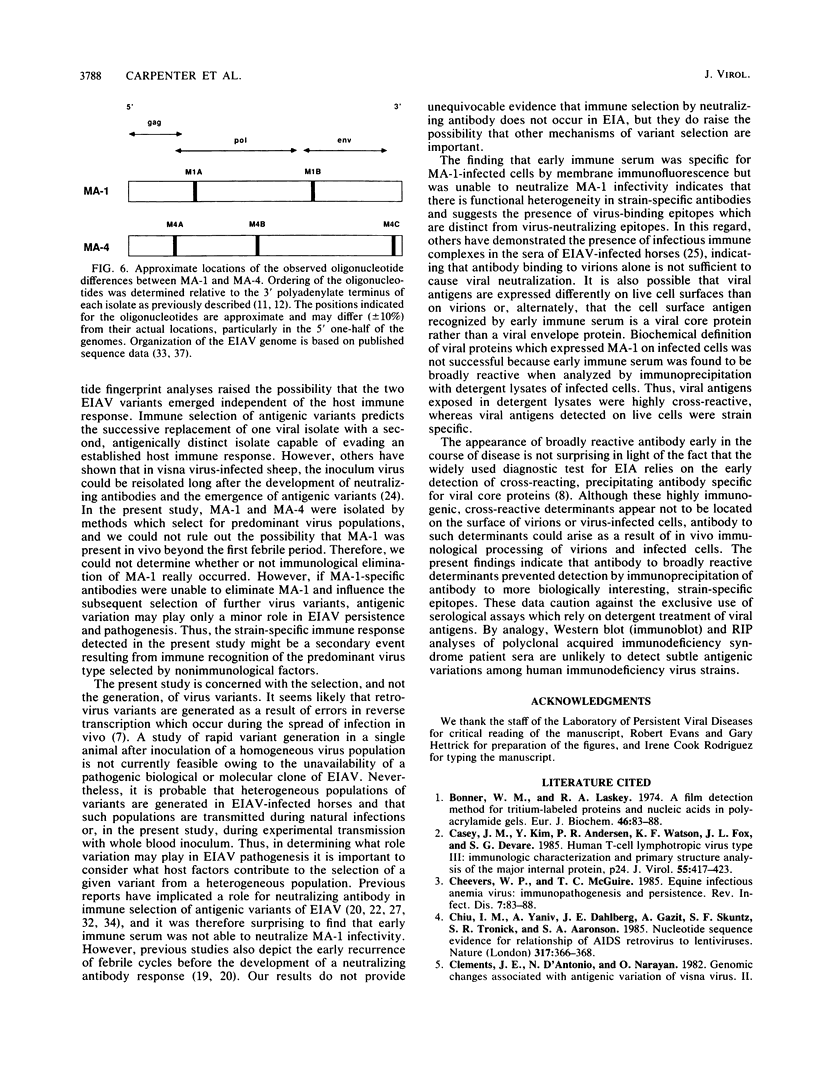
Equine infectious anemia virus was isolated from peripheral blood leukocytes collected during two early febrile cycles of an experimentally infected horse. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotide fingerprint analyses indicated that the nucleotide sequences of the isolates differed by approximately 0.25% and that the differences appeared randomly distributed throughout the genome. Serum collected in the interval between virus isolations was able to distinguish the isolates by membrane immunofluorescence on live cells. However, no neutralizing antibody was detected in the interval between virus isolations. In fact, multiple clinical cycles occurred before the development of a neutralizing antibody response, indicating that viral neutralization might not be the mechanism for selection of antigenic variants. The ability of early immune sera to recognize variant specific antigens on the surface of infected cells suggested that immune selection occurs through recognition and elimination of certain virus-infected cells. Alternately, the random distribution of the genomic differences observed between the two isolates may indicate that equine infectious anemia virus variants emerge as a result of nonimmunological selection processes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. M., Kim Y., Andersen P. R., Watson K. F., Fox J. L., Devare S. G. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III: immunologic characterization and primary structure analysis of the major internal protein, p24. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):417–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.417-423.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., McGuire T. C. Equine infectious anemia virus: immunopathogenesis and persistence. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. M., Yaniv A., Dahlberg J. E., Gazit A., Skuntz S. F., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence evidence for relationship of AIDS retrovirus to lentiviruses. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):366–368. doi: 10.1038/317366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., D'Antonio N., Narayan O. Genomic changes associated with antigenic variation of visna virus. II. Common nucleotide sequence changes detected in variants from independent isolations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):415–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., Pedersen F. S., Narayan O., Haseltine W. A. Genomic changes associated with antigenic variation of visna virus durig persistent infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4454–4458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Genetic variation in AIDS viruses. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Henson J. B. Detection of equine infectious anemia virus in vitro by immunofluorescence. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(4):332–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01242979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans K. S., Carpenter S. L., Sevoian M. Detection of equine infectious anemia virus in horse leukocyte cultures derived from horses in various stages of equine infectious anemia viral infection. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Generation of mink cell focus-forming viruses by Friend murine leukemia virus: recombination with specific endogenous proviral sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.772-781.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Duesberg P. H., Troxler D. H., Scolnick E. M. Spleen focus-forming Friend virus: identification of genomic RNA and its relationship to helper virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):133–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.133-146.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Braun M. J., Clements J. E., Pyper J. M., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Gilden R. V. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III shares sequence homology with a family of pathogenic lentiviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Charman H. P., Walker J. L., Coggins L. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of equine infectious anemia virus. Am J Vet Res. 1978 May;39(5):731–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudnadóttir M. Visna-maedi in sheep. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):336–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. Pathogenesis of lentivirus infections. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):130–136. doi: 10.1038/322130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R. C., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Chemical and immunological characterizations of equine infectious anemia virus gag-encoded proteins. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1116–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1116-1124.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Antigenic drift of equine infectious anemia virus in chronically infected horses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;41(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01249923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Serological comparison among various strains of equine infectious anemia virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01242993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y. Viremia and immunological responses in horses infected with equine infectious anemia virus. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1969 Spring;9(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutley R., Pétursson G., Pálsson P. A., Georgsson G., Klein J., Nathanson N. Antigenic drift in visna: virus variation during long-term infection of Icelandic sheep. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1433–1440. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B. Equine infectious anemia: detection of infections virus-antibody complexes in the serum. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(6):545–551. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Parekh B., Orrego A., Issel C. J. Antigenic variation during persistent infection by equine infectious anemia virus, a retrovirus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10539–10544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tajima M., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Physicochemical studies of equine infectionus anemia virus. 3. Purification and electron microscopic observation of the virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;28(3):348–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01240949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Clements J. E., Griffin D. E., Wolinsky J. S. Neutralizing antibody spectrum determines the antigenic profiles of emerging mutants of visna virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1045-1050.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Chase J. Antigenic shift of visna virus in persistently infected sheep. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):376–378. doi: 10.1126/science.195339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Equine infectious anemia virus, a putative lentivirus, contains polypeptides analogous to prototype-C oncornaviruses. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):520–525. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S., Parekh B., Montelaro R. C., Issel C. J. Genomic alterations associated with persistent infections by equine infectious anaemia virus, a retrovirus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1395–1399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K., Olsen K., Stiegler G., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Issel C. J. Lentivirus genomic organization: the complete nucleotide sequence of the env gene region of equine infectious anemia virus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L. Rapid emergence of novel antigenic and genetic variants of equine infectious anemia virus during persistent infection. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.71-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Stowring L., Haase A. T., Narayan O., Vigne R. Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Casey J. W., Rice N. R. Equine infectious anemia virus gag and pol genes: relatedness to visna and AIDS virus. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):589–594. doi: 10.1126/science.3003905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thormar H., Barshatzky M. R., Arnesen K., Kozlowski P. B. The emergence of antigenic variants is a rare event in long-term visna virus infection in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1427–1432. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]