Abstract
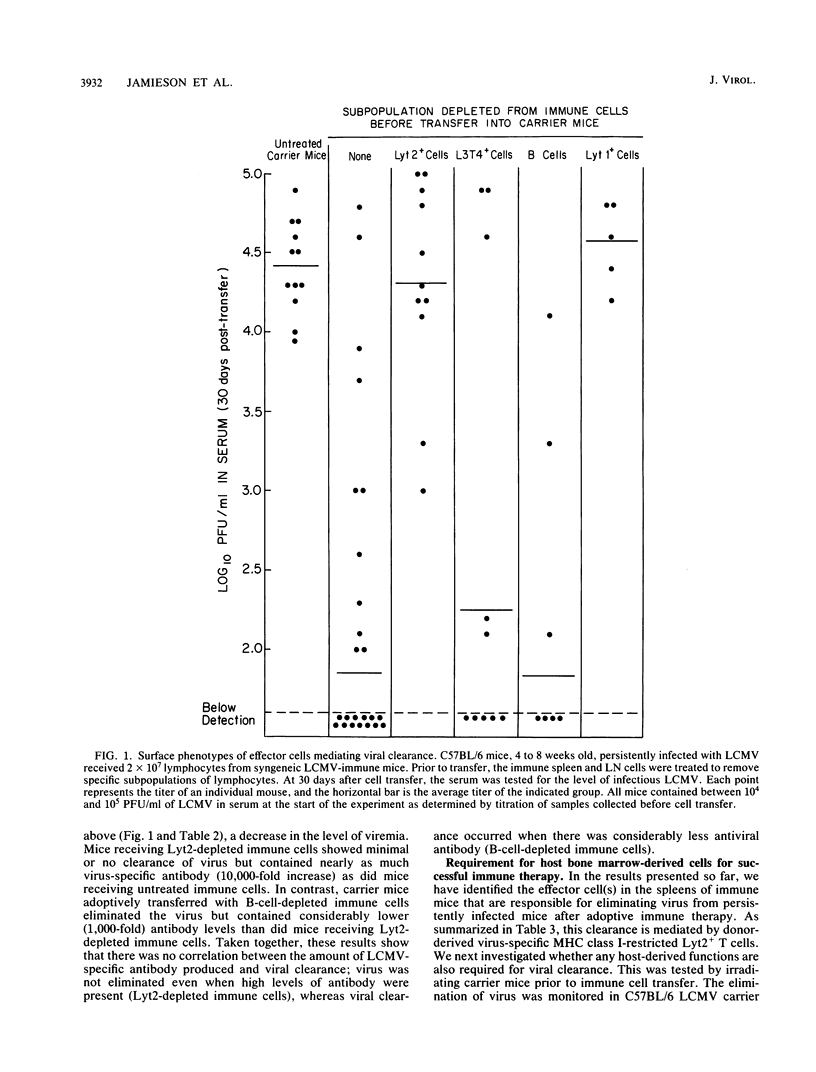
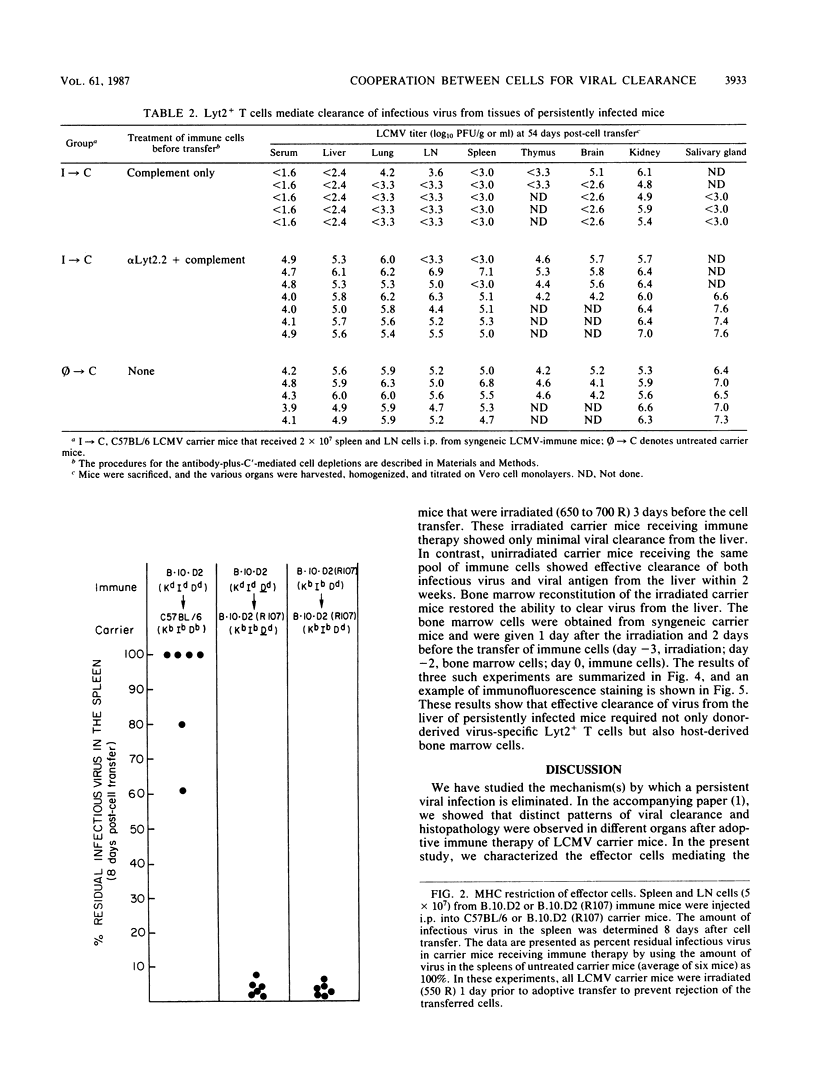
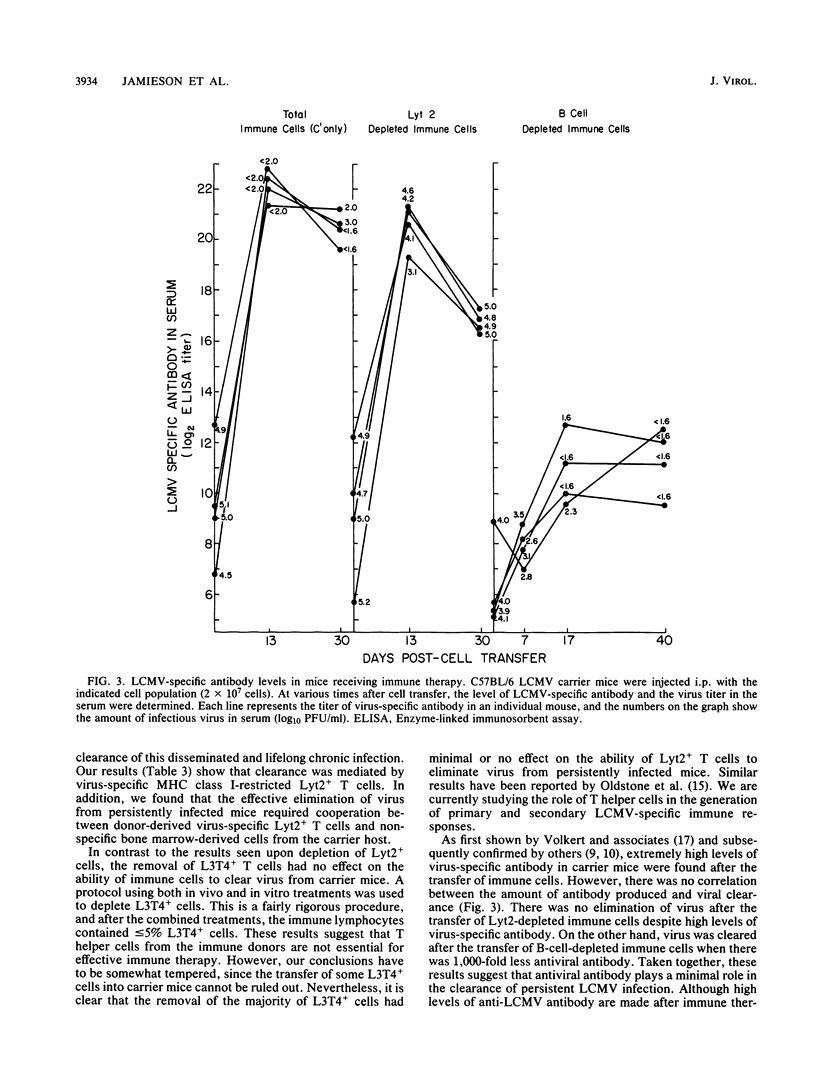
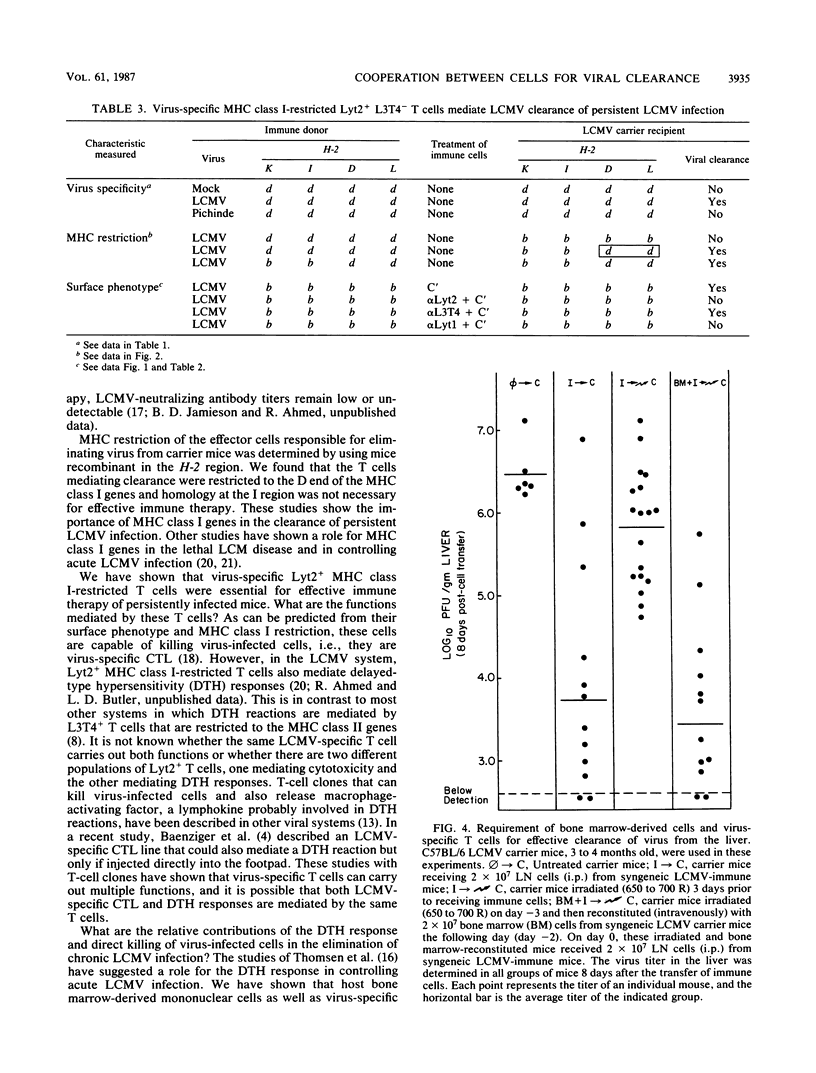
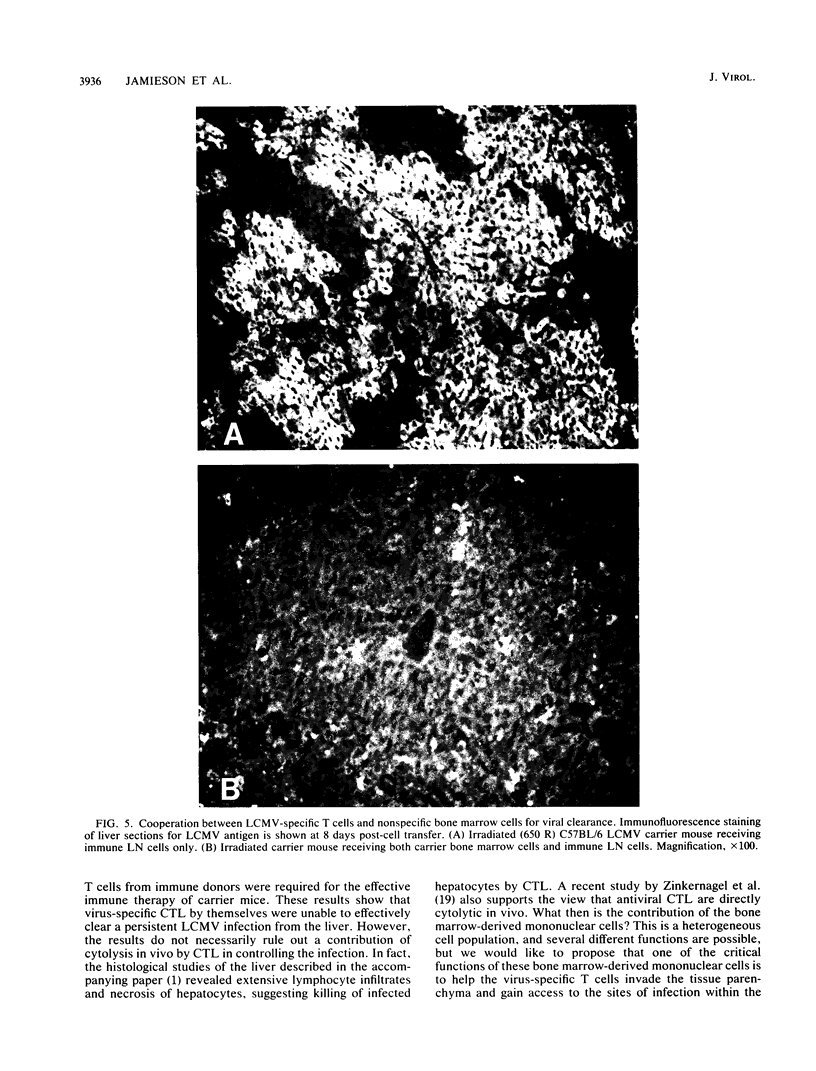
The lifelong chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection established in neonatally or congenitally infected mice can be eliminated by adoptive transfer of lymphoid cells from LCMV-immune mice. In this study, we have identified the effector cells mediating the clearance of persistent and disseminated LCMV infection. Using mice that are recombinant in the H-2 region and by selective depletion of lymphocyte subpopulations, we show that viral clearance was mediated by LCMV-specific Lyt2+ L3T4- T cells that are restricted to the class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex. In addition, our results show a requirement for host-derived bone marrow cells for the effective elimination of virus from the liver. These studies emphasize the importance of virus-specific T cells and an intact bone marrow function in viral clearance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alaba O., Bernstein I. D. Tumor-growth suppression in vivo: cooperation between immune lymphoid cells sensitized in vitro and nonimmune bone marrow cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1941–1946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M., Cole G. A. Induction or prevention of immunopathological disease by cloned cytotoxic T cell lines specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):387–393. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Cole G. A., Nathanson N. Immunopathogenesis of acute central nervous system disease produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. II. Adoptive immunization of virus carriers. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):874–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffsten P. E., Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunopathology of adoptive immunization in mice chronically infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Jan;7(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Rouse R. V., Micklem H. S., Herzenberg L. A. T cell subsets defined by expression of Lyt-1,2,3 and Thy-1 antigens. Two-parameter immunofluorescence and cytotoxicity analysis with monoclonal antibodies modifies current views. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):280–295. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. G., Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Immune interferon release when a cloned cytotoxic T-cell line meets its correct influenza-infected target cell. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):150–152. doi: 10.1038/295150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Rosenstein M., Shu S., Rosenberg S. A. Eradication of a disseminated syngeneic mouse lymphoma by systemic adoptive transfer of immune lymphocytes and its dependence upon a host component(s). Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Blount P., Southern P. J., Lampert P. W. Cytoimmunotherapy for persistent virus infection reveals a unique clearance pattern from the central nervous system. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):239–243. doi: 10.1038/321239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen A. R., Volkert M., Bro-Jørgensen K. Virus elimination in acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Correlation with virus-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity rather than cytotoxicity. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jun;17(6):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M., LARSEN J. H., PFAU C. STUDIES ON IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE TO LCM VIRUS. 4. THE QUESTION OF IMMUNITY IN ADOPTIVELY IMMUNIZED VIRUS CARRIERS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;61:268–282. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.61.2.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Haenseler E., Leist T., Cerny A., Hengartner H., Althage A. T cell-mediated hepatitis in mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Liver cell destruction by H-2 class I-restricted virus-specific cytotoxic T cells as a physiological correlate of the 51Cr-release assay? J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1075–1092. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Pfau C. J., Hengartner H., Althage A. Susceptibility to murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis maps to class I MHC genes--a model for MHC/disease associations. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):814–817. doi: 10.1038/316814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Welsh R. M. H-2 compatibility requirement for virus-specific T cell-mediated effector functions in vivo. I. Specificity of T cells conferring antiviral protection against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is associated with H-2K and H-2D. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1495–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]