Abstract
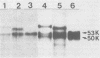
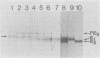
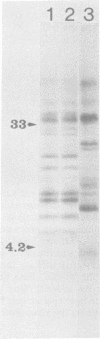
Cytoplasmic extracts prepared from Sindbis virus-infected chicken embryo fibroblasts pulse-chase-labeled with [35S]methionine 6 h postinfection were analyzed on a highly resolving sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel either directly or after various treatments. The results we obtained suggest that (i) the proteolytic cleavage which converts PE2 to E2 glycoprotein takes place intracellularly, before or at least during the formation of complex-type oligosaccharide side chains; and (ii) E1 glycoprotein undergoes a complex maturation pattern. Newly synthesized E1 has a molecular weight of 53,000: shortly thereafter, this 53,000 (53K) form was converted to a 50K form. Subsequently, the 50K form decreased its apparent molecular weight progressively and eventually comigrated with E1 glycoprotein present in the extracellular virus, which displays a molecular weight of 51,000 to 52,000. The conversion of the 53K to the 50K form was not the result of a proteolytic processing and did not depend on glycosylation or disulfide bridge formation and exchange. The possible mechanisms of this conversion are discussed. The second conversion step (from the 50K to the 51-52K form) was due to the formation of complex-type oligosaccharide and was reversed by incubating the cellular extracts with neuraminidase before electrophoretic analysis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmann J. E., Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. Passage of an integral membrane protein, the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, through the Golgi apparatus en route to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti S., Blobel G. Absence of a cleavable signal sequence in Sindbis virus glycoprotein PE2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12261–12264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti S., Cancedda R., Blobel G. Membrane biogenesis. In vitro cleavage, core glycosylation, and integration into microsomal membranes of sindbis virus glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):219–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Defects in RNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus and evidence for a complex of PE2-E1 viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Bonatti S., Leone A. One extra oligosaccharide chain of the high-mannose class in the E2 protein of a Sindbis virus isolate. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.8-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Simons K., Dobberstein B. Assembly of the Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 5;124(4):587–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen M., Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Biosynthesis of the major human red cell sialoglycoprotein, glycophorin A, in a continuous cell line. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):604–607. doi: 10.1038/279604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Pauli G. The influence of intramolecular disulfide bonds on the structure and function of Semliki forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):300–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Rott R., Schwarz R. T. Carbohydrate-induced conformational changes of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins determine antigenicity. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):286–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Localization of two cellular forms of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1121–1127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1121-1127.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Hashimoto K., Saraste J., Virtanen I., Penttinen K. Monensin and FCCP inhibit the intracellular transport of alphavirus membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):783–791. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Impaired intracellular migration and altered solubility of nonglycosylated glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and Sindbis virus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9018–9023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone A., Colantuoni V., Pontarelli G., Cancedda R. Defective mutant of Sindbis virus with a smaller-molecular-weight form of the E1 glycoprotein. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):598–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.598-603.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martire G., Bonatti S., ALIPERTI G., De Giuli C., Cancedda R. Free and membrane-bound polyribosomes in BHK cells infected with Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):610–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.610-618.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Hubbard S. C., Turco S. J., Wirth D. F. Proposal for a common oligosaccharide intermediate in the synthesis of membrane glycoproteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Corser J. A., Schlesinger M. J. Isolation and characterization of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies directed against the structural proteins of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Fine R. E. Coated vesicles transport newly synthesized membrane glycoproteins from endoplasmic reticulum to plasma membrane in two successive stages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):780–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savige W. E., Fontana A. Cleavage of the tryptophanyl peptide bond by dimethyl sulfoxide-hydrobromic acid. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:459–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of Sindbis virus proteins: identification of a precursor for one of the envelope proteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):925–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.925-932.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Relation of fatty acid attachment to the translation and maturation of vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3334–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D., Blobel G. Cell-free synthesis of fish preproinsulin, and processing by heterologous mammalian microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2059–2063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Sefton B. M. Two small virus-specific polypeptides are produced during infection with Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1186–1195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1186-1195.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth D. F., Katz F., Small B., Lodish H. F. How a single Sindbis virus mRNA directs the synthesis of one soluble protein and two integral membrane glycoproteins. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Garoff H., Simons K. Formation of the Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoprotein complexes in the infected cell. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):111–123. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]