Abstract
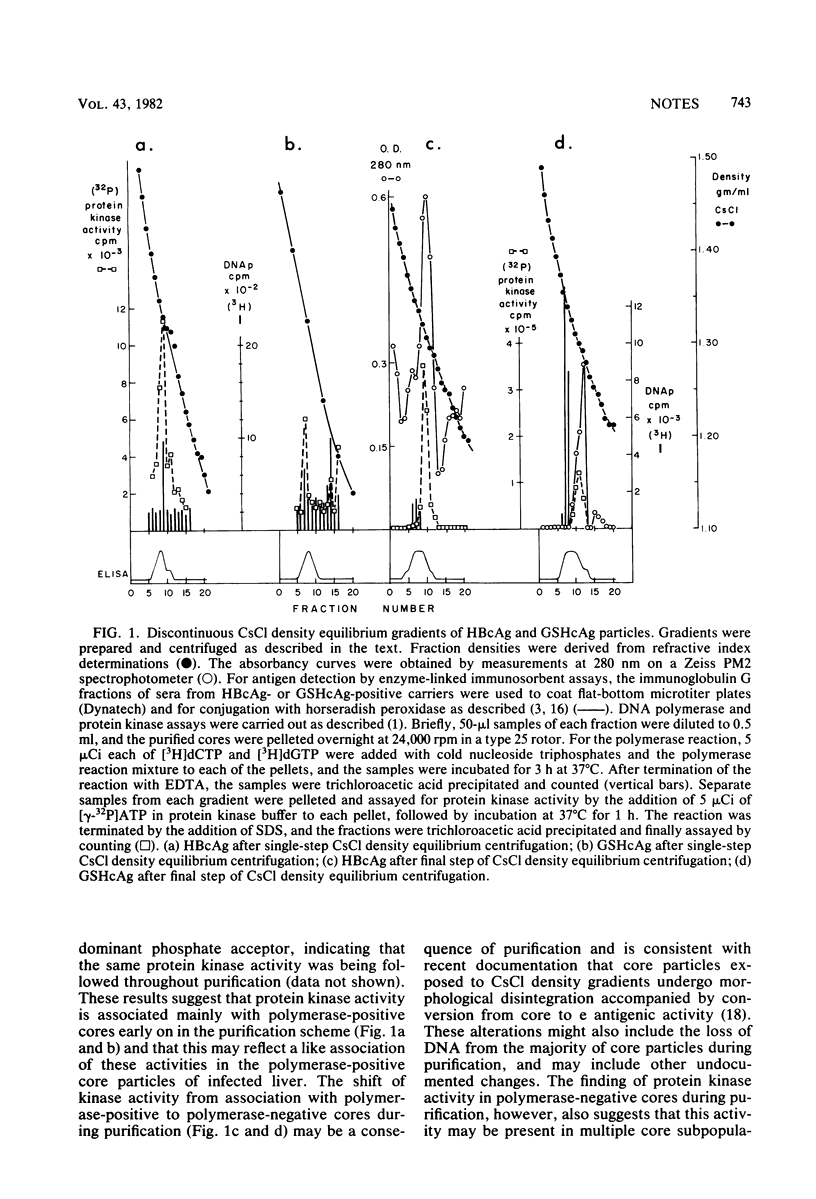
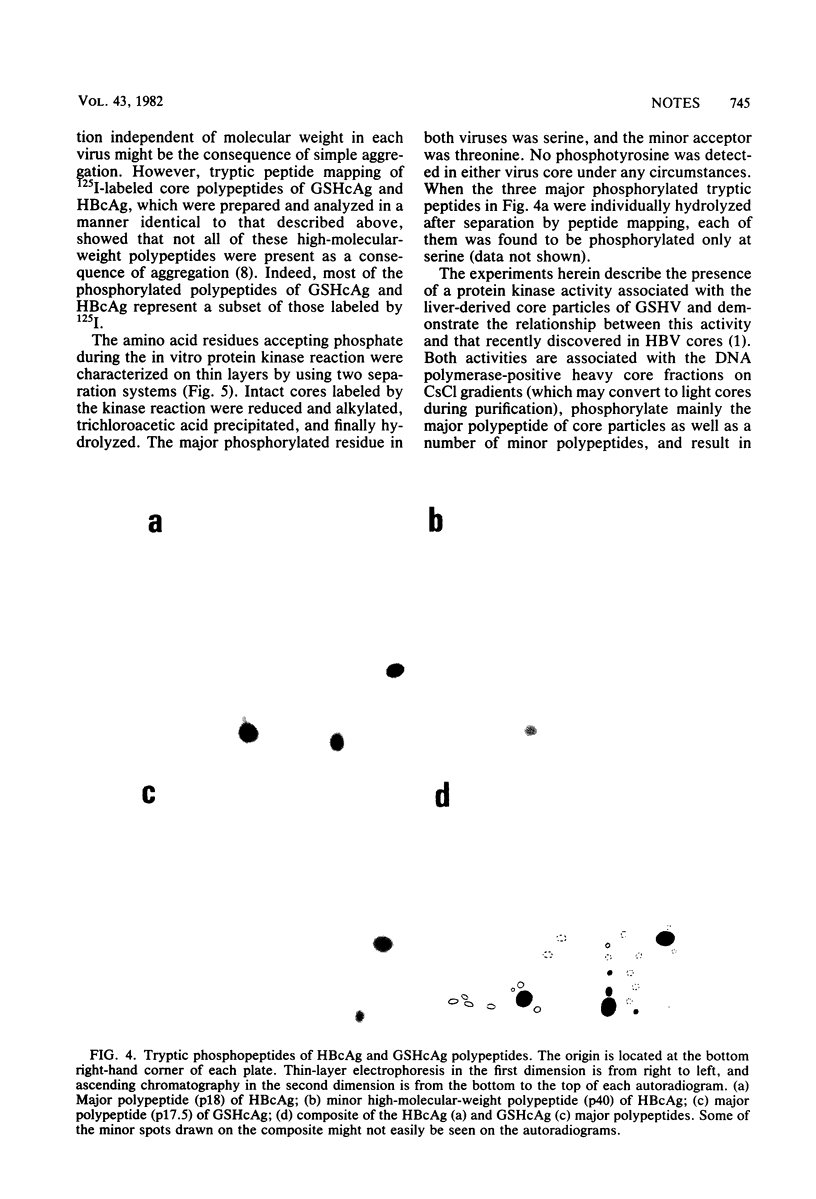
The recently described protein kinase activity in hepatitis B virus core antigen particles (Albin and Robinson, J. Virol. 34:297-302, 1980) has been demonstrated here in the liver-derived core particles of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. Both protein kinase activities were initially associated with DNA polymerase-positive heavy core particles in CsCl density equilibrium gradients and shifted to polymerase-negative cores during the course of purification. The major core-associated polypeptide of each virus was the dominant species labeled. A variable number of other polypeptide species were also labeled by this reaction. Tryptic peptide mapping of both major and minor phosphorylated polypeptides of each virus resulted in similar patterns, suggesting that many of the sites of phosphorylation were the same in the components of each core particle. Hydrolysis of these phosphorylated core particles revealed a major phosphoamino acid as serine and a minor phosphoamino acid as threonine. The products of the protein kinase reaction in both human hepatitis B and ground squirrel hepatitis virus core particles, then, share many characteristics. The possible function(s) of this protein kinase activity is discussed in the light of similarly characterized activities in other animal viruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albin C., Robinson W. S. Protein kinase activity in hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):297–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.297-302.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Peroxidase labelled antibody and Fab conjugates with enhanced intracellular penetration. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budkowska A., Kalinowska B., Nowosławski A. Identification of two HBeAg subspecificities revealed by chemical treatment and enzymatic digestion of liver-derived HBcAg. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1415–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Antigenic and structural relationships of the surface antigens of hepatitis B virus, ground squirrel hepatitis virus, and woodchuck hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):447–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.447-454.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Core particles of hepatitis B virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. I. Relationship between hepatitis B core antigen- and ground squirrel hepatitis core antigen-associated polypeptides by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and tryptic peptide mapping. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):687–696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.687-696.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Structural relationships between the surface antigens of ground squirrel hepatitis virus and human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):787–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.787-795.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L., Emerson S. U. Transcriptional activities of different phosphorylated species of NS protein purified from vesicular stomatitis virions and cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1097–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1097-1105.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Greenberg H. B., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA and nature of the endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):368–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.368-376.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N. Association of hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg) determinants with the core of Dane particles. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):645–649. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohori H., Yamaki M., Onodera S., Yamada E., Ishida N. Antigenic conversion from HBcAg to HBeAg by degradation of hepatitis B core particles. Intervirology. 1980;13(2):74–82. doi: 10.1159/000149110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plimmer R. H. Esters of phosphoric acid: Phosphoryl hydroxyamino-acids. Biochem J. 1941 Apr;35(4):461–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0350461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Greenman R. L. DNA polymerase in the core of the human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1231-1236.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA molecules have cohesive ends. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.226-233.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Phosphorylation of murine type C viral p12 proteins regulates their extent of binding to the homologous viral RNA. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Specific binding of the type C viral core protein p12 with purified viral RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Ground squirrel hepatitis virus DNA: molecular cloning and comparison with hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):393–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.393-397.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Clark H. F. Phosphoproteins, structural components of rhabdoviruses. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):246–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Akahane Y., Gotanda T., Mishiro T., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Demonstration of hepatitis B e antigen in the core of Dane particles. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B. Comparative study of the protein kinase associated with animal viruses. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):566–570. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Charnay P., Vyas G. N. Biology of hepatitis B virus. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):406–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6264599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M. Chemical modification of DNA polymerase phosphoprotein from avian myeloblastosis virus. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):27–31. doi: 10.1038/266027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]