Abstract
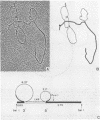
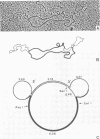
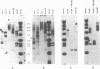
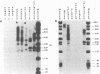
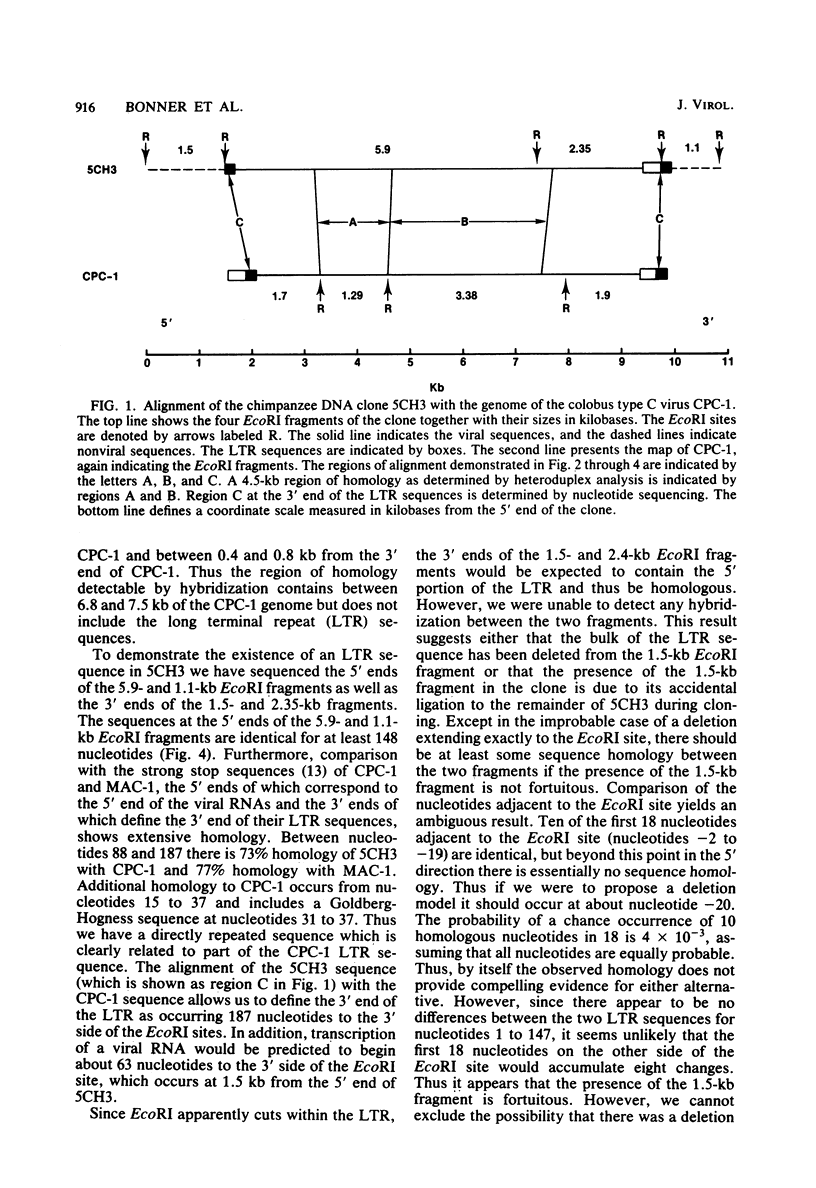
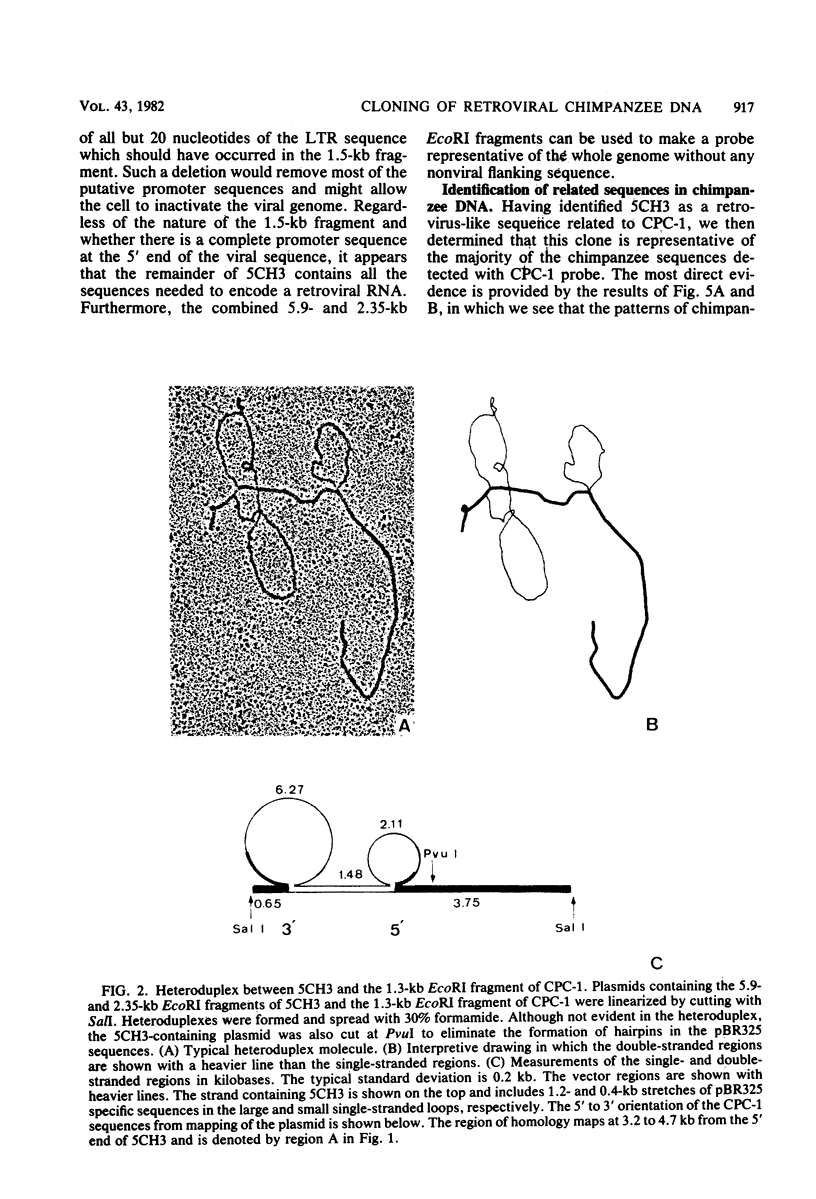
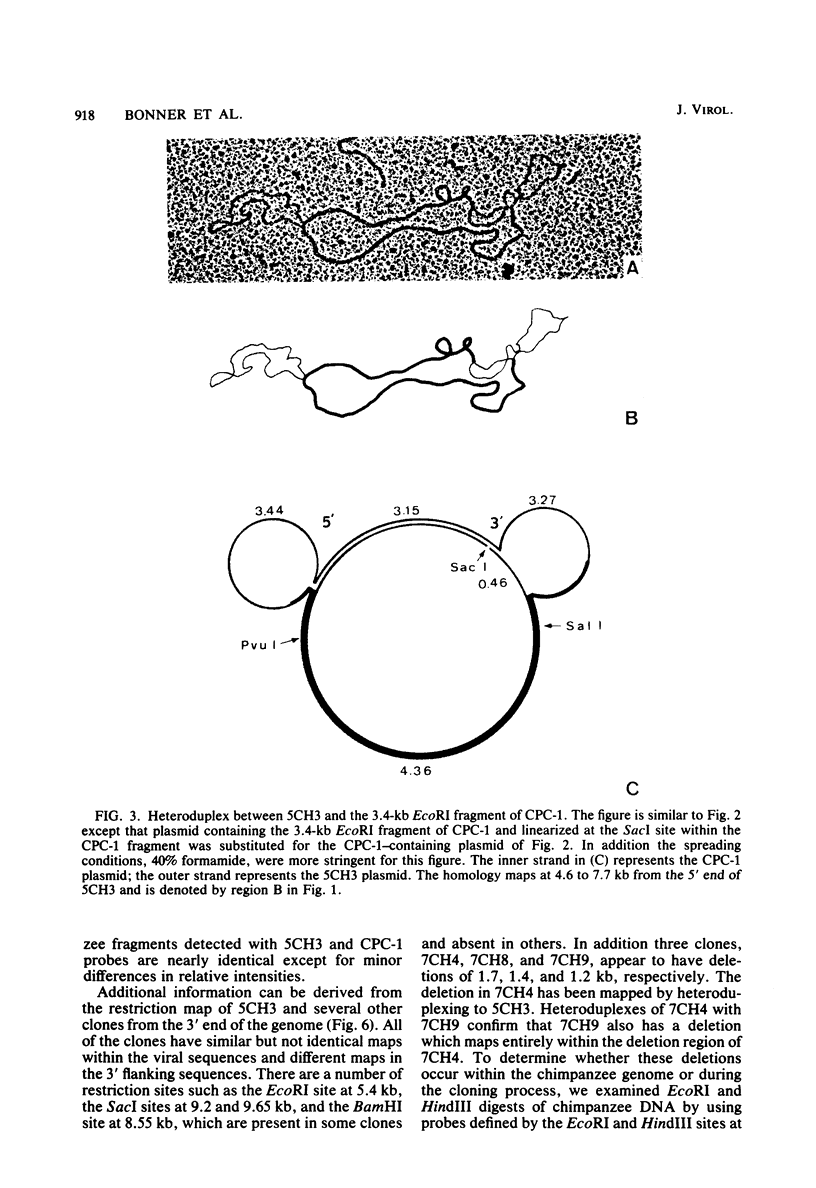
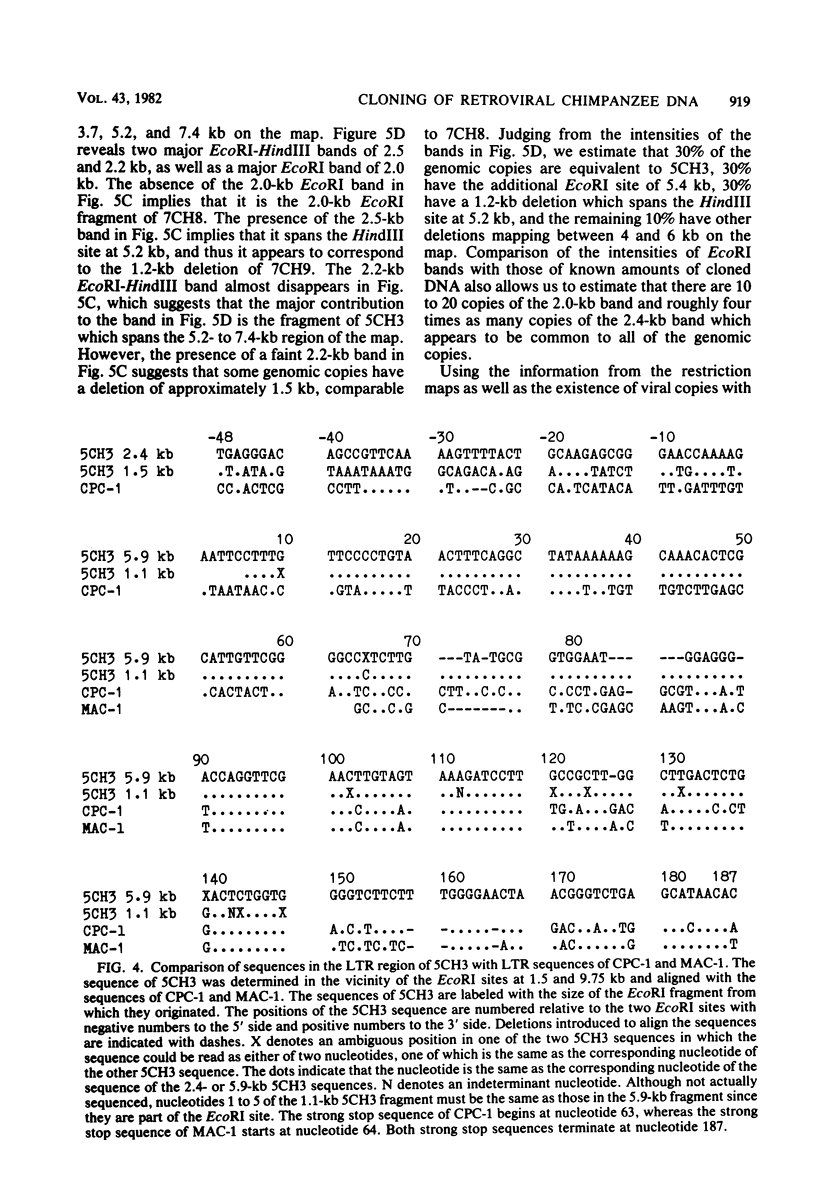
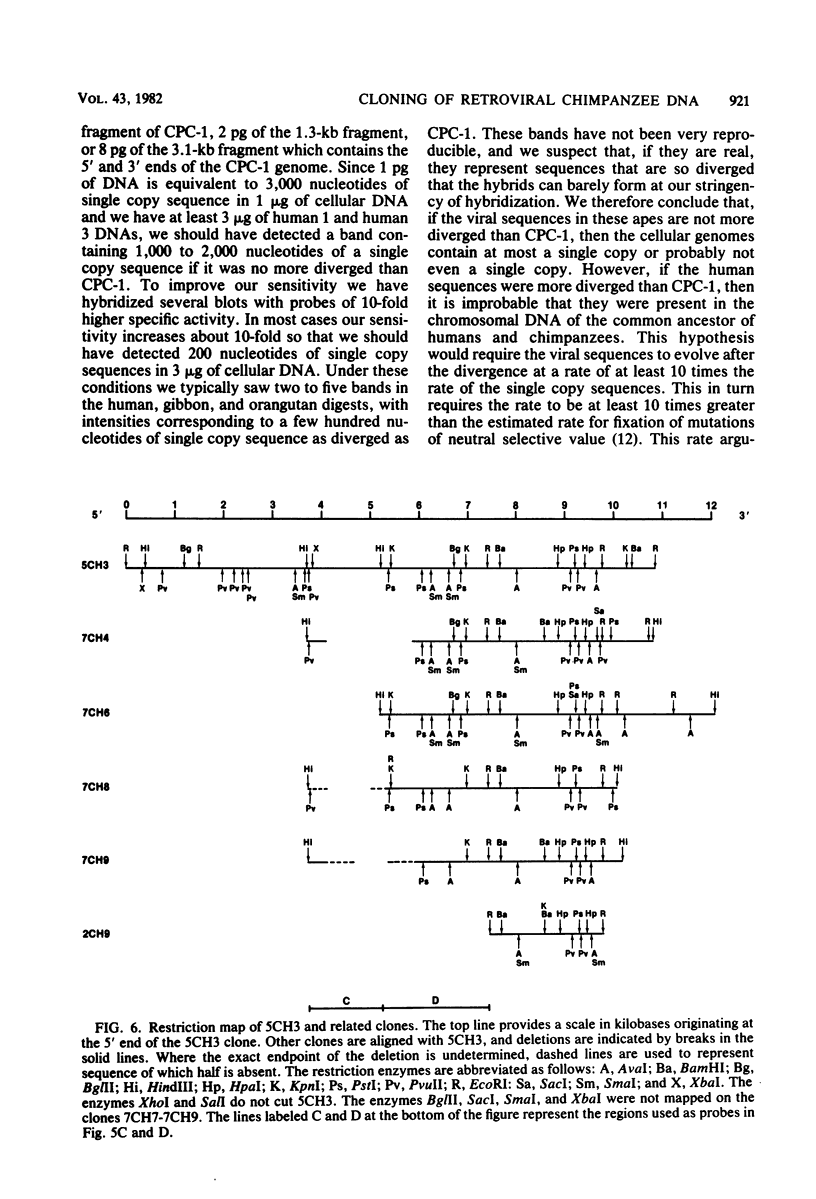
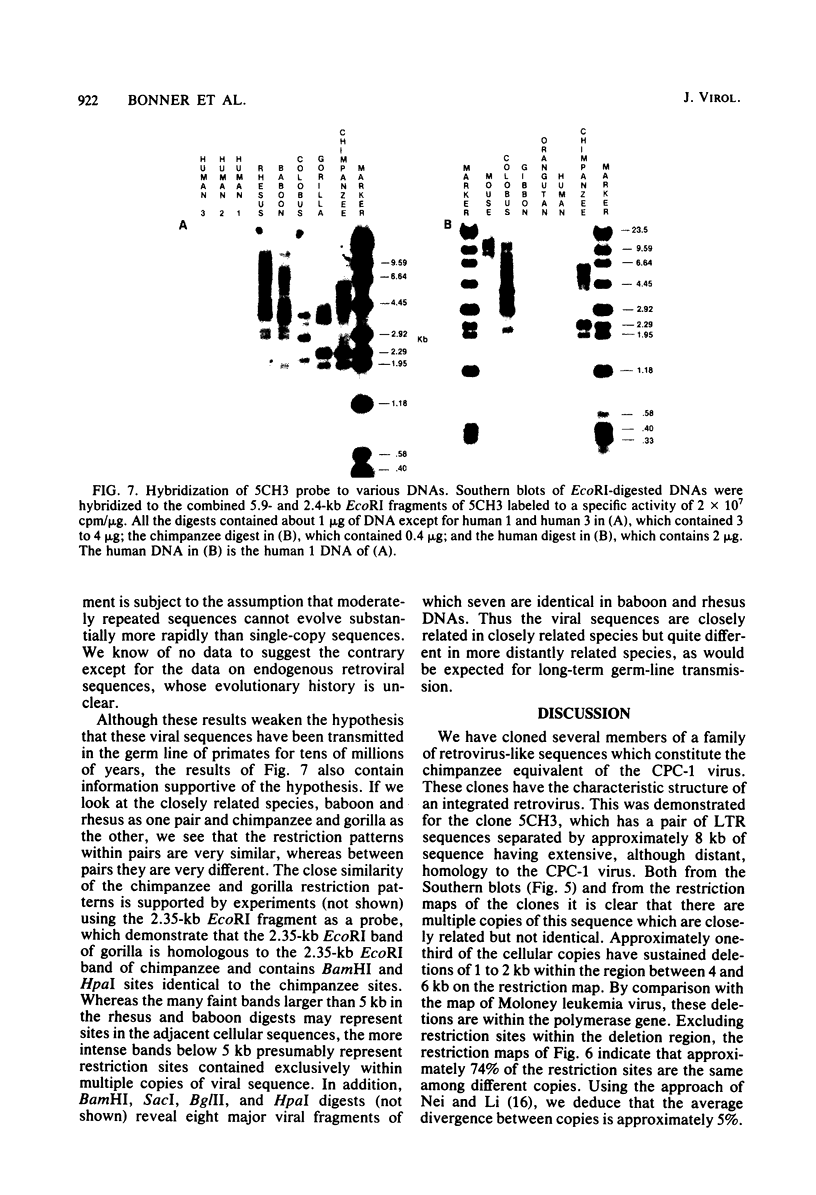
A number of retrovirus-like sequences have been cloned from chimpanzee DNA which constitute the chimpanzee homologs of the endogenous colobus type C virus CPC-1. One of the clones contains a nearly complete viral genome, but others have sustained deletions of 1 to 2 kilobases in the polymerase gene. The pattern of related sequences detected in other primate species is consistent with the genetic transmission of these sequences for millions of years. However, the appropriately related sequences have not been detected in human, gibbon, or orangutan DNAs. These results suggest either that this family of sequences has been deleted from humans, gibbons, and orangutans, or that the genes were recently acquired in the chimpanzee and gorilla lineages.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of primate oncornaviruses: An endogenous virus from langurs (Presbytis spp.) with related virogene sequences in other Old World monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4557–4561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: evidence for an Asian origin of man. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):101–108. doi: 10.1038/261101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Todaro G. J. The evolution of baboon endogenous type C virus: related sequences in the DNA of distant species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Varmus H. E. Endogenous mammary tumour virus DNA varies among wild mice and segregates during inbreeding. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):418–423. doi: 10.1038/278418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D. P., Weiss R. A., Roussel M., Stehelin D. The distribution of endogenous chicken retrovirus sequences in the DNA of galliform birds does not coincide with avian phylogenetic relationships. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):624–626. doi: 10.1038/217624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger G. G., Mark G., Todaro G. J., Schochetman G. 5'-terminal nucleotide noncoding sequences of retroviruses: relatedness of two old world primate type C viruses and avian spleen necrosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.238-245.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Bryan T., Rasheed S., Khan A. S. Identification and cloning of endogenous retroviral sequences present in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Benton C. V., Tainsky M. A., Rice N. R., Gilden R. V. Isolation and characterization of an endogenous type C virus of rhesus monkeys. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):841–842. doi: 10.1126/science.87013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Todaro G. J. A new endogenous primate type C virus isolated from the Old World monkey Colobus polykomos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Sherwin S. A., Sherr C. J. MAC-1, a new genetically transmitted type C virus of primates: "low frequency" activation from stumptail monkey cell cultures. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Sherr C. J., Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Melnick J. L. Type C viruses of baboons: isolation from normal cell cultures. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Gonda M. A., De Feo D., Ellis R. W., Nagashima K., Scolnick E. M. Heteroduplex analysis of cloned rat endogenous replication-defective (30 S) retrovirus and Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]