Abstract
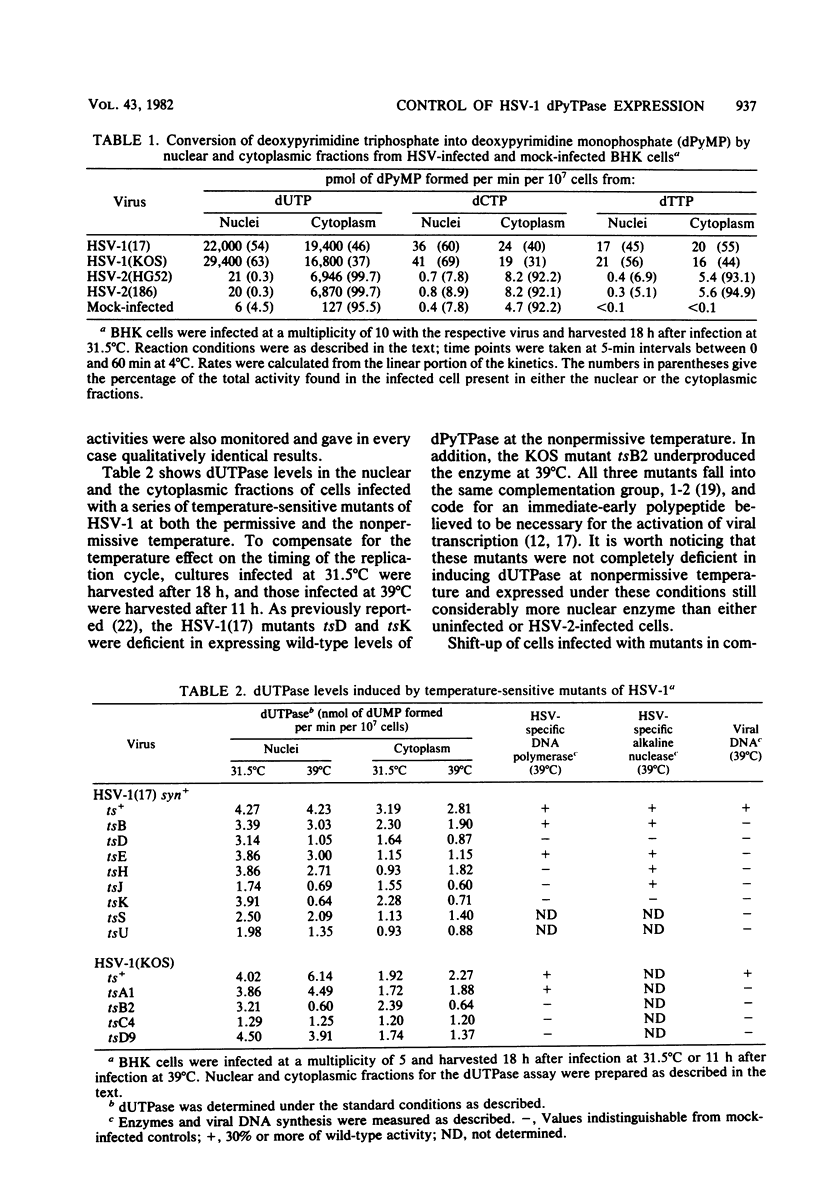
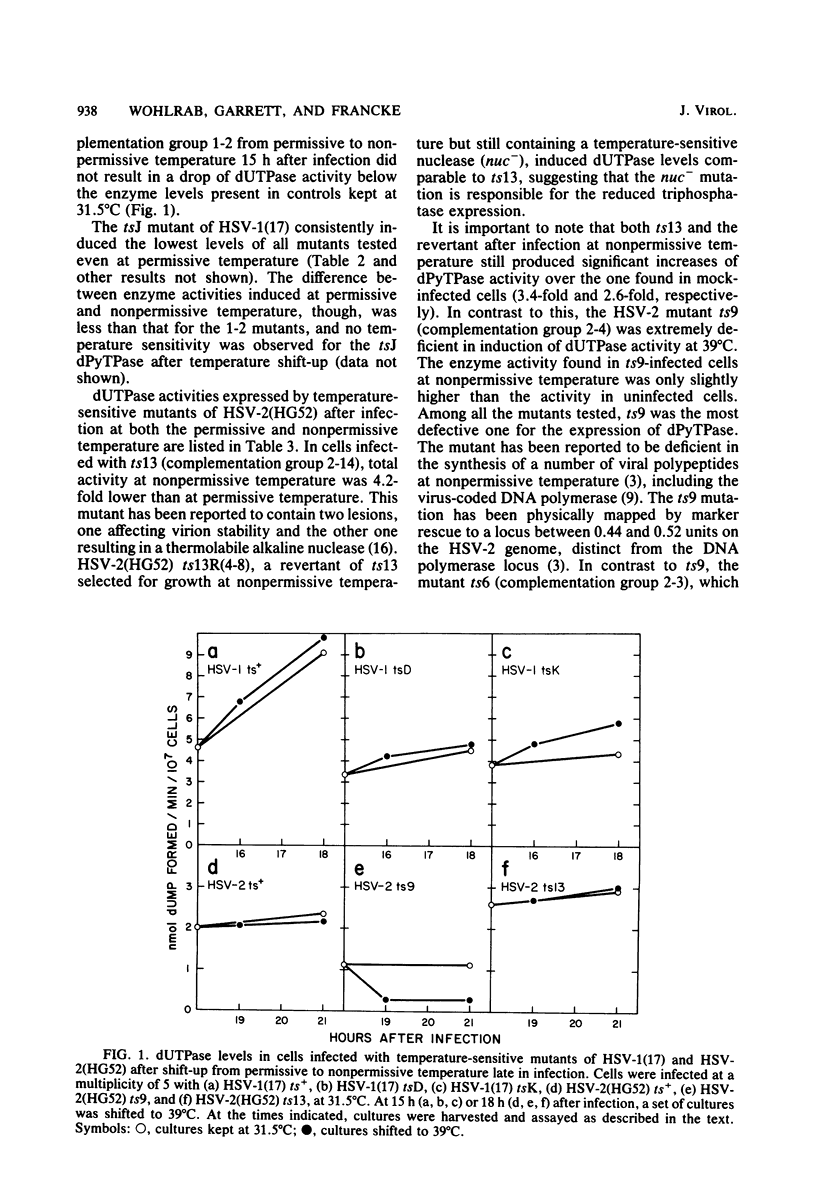
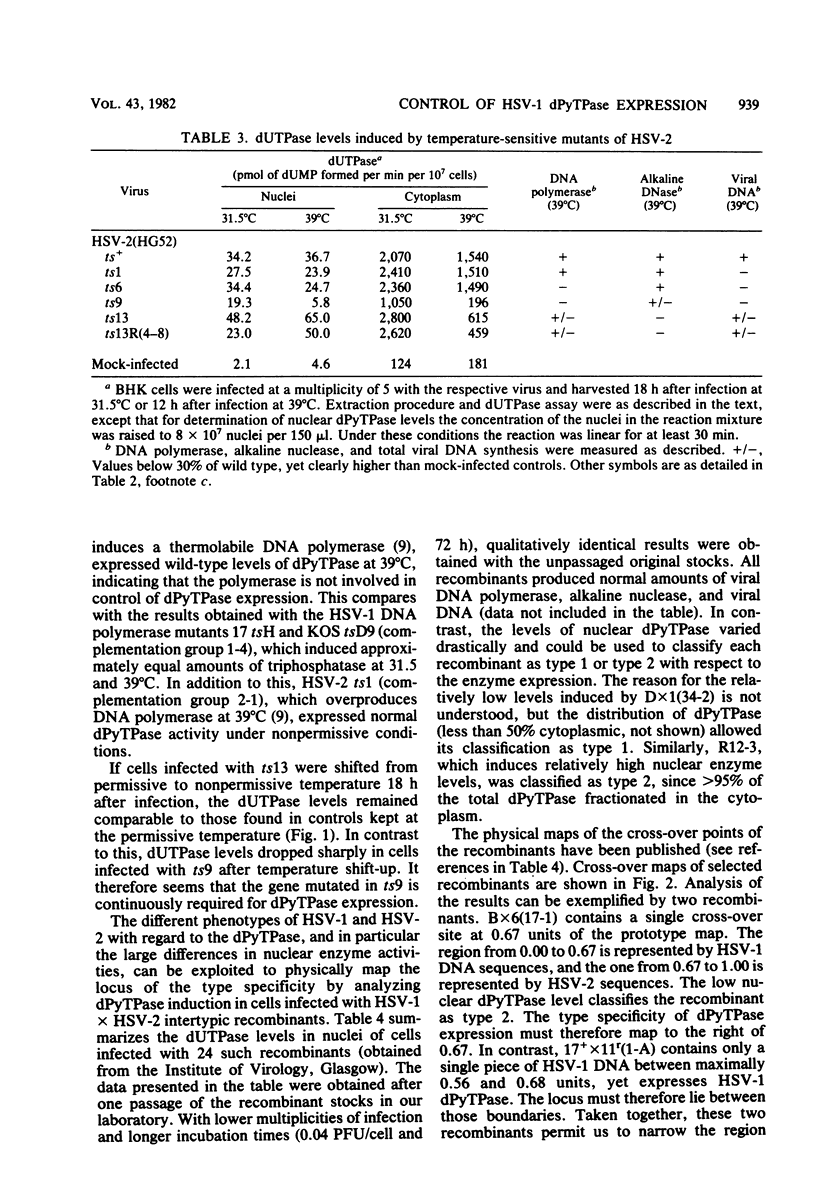
Infection of cells with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) induces high levels of deoxypyrimidine triphosphatase. The majority of the enzyme activity is found in infected cell nuclei. A similar activity is induced by HSV type 2 (HSV-2) which, in contrast to the HSV-1 enzyme, fractionates to more than 99% in the soluble cytoplasmic extract. Of a series of temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV-1 studied, only the immediate-early mutants in complementation group 1-2 (strain 17 mutants tsD and tsK and strain KOS mutant tsB2) induced reduced levels of triphosphatase at nonpermissive temperature. Of a series of temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV-2 strain HG52, ts9 and ts13 failed to induce wild-type levels of the enzyme at nonpermissive temperature; ts9 was the most defective mutant with regard to triphosphatase expression of both herpes simplex virus serotypes. After shift-up from permissive to nonpermissive temperature, triphosphatase activity in cells infected with ts9 decreased rapidly, whereas all other mutants continued to exhibit enzyme levels comparable with controls kept at the permissive temperature. The type 1-specific nuclear expression of the triphosphatase was mapped physically by the use of HSV-1 x HSV-2 intertypic recombinants, based on enzyme levels different by more than two orders of magnitude found in nuclei of HSV-1- and HSV-2-infected cells. The locus for the type-specific expression maps between 0.67 and 0.68 fractional length on the HSV genome.
Full text
PDF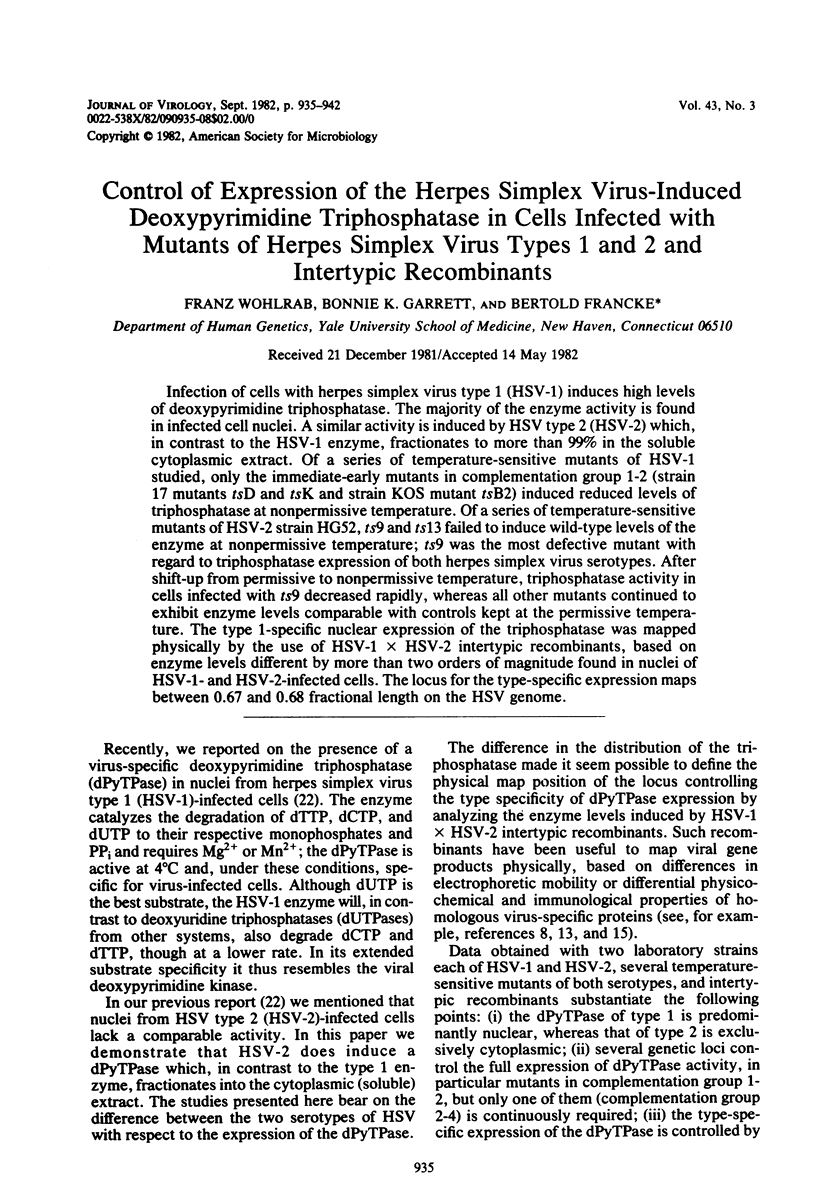



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bone D. R., Brown M., Crombie I., Francke B. Viral DNA synthesis in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.14-19.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of paar mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 by intertypic marker rescue. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):265–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.265-276.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Timbury M. C., Hay J., Moss H. Mutant of herpes simplex virus type 2 with temperature-sensitive lesions affecting virion thermostability and DNase activity: identification of the lethal mutation and physical mapping of the nuc-lesion. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.140-146.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Wilkie N. M., Timbury M. C. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 2 by marker rescue. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):121–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Wilkie N. M. One functional copy of the long terminal repeat gene specifying the immediate-early polypeptide IE 110 suffices for a productive infection of human foetal lung cells by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):179–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B. Cell-free synthesis of herpes simplex virus DNA: conditions for optimal synthesis. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5655–5664. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Garrett B. The effect of a temperature-sensitive lesion in the alkaline DNase of herpes simplex virus type 2 on the synthesis of viral DNA. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):116–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Moss H., Timbury M. C., Hay J. Alkaline DNase activity in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):209–213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.209-213.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Morse L. S., Roizman B., Quinn K. E. Mapping of the thymidine kinase genes of type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses using intertypic recombinants. J Gen Virol. 1980 Aug;49(2):235–253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B., Halliburton I. W. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus: demonstration of regions of obligatory and nonobligatory identity within diploid regions of the genome by sequence replacement and insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Crombie I. K., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Control of protein synthesis in herpesvirus-infected cells: analysis of the polypeptides induced by wild type and sixteen temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV strain 17. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):347–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. M., Keir H. M. A new DNA-exonuclease in cells infected with herpes virus: partial purification and properties of the enzyme. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):337–347. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Abnormal properties of an immediate early polypeptide in cells infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):357–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.357-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutations by marker rescue. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F., Francke B. Deoxyribopyrimidine triphosphatase activity specific for cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1872–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



