Abstract
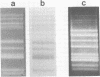
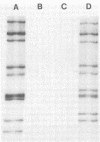
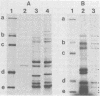
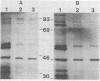
The RNA polymerase activities of a cultivatable (Wa) and a noncultivatable (DS-1) strain of human rotavirus were studied. Under optimal conditions, transcription of all of their RNA segments occurred, as evidenced by the hybridization of labeled transcripts to genomic RNA. Cross-hybridization between the two viruses showed that none of their 11 genes were completely homologous. The transcription products could be translated in vitro, yielding proteins with an electrophoretic pattern resembling that obtained with proteins labeled in vivo during infection with the Wa virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein J. M., Hruska J. F. Characterization of RNA polymerase products of Nebraska calf diarrhea virus and SA11 rotavirus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1071–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1071-1074.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Laporte J., Charpilienne A., Scherrer R. Activation of rotavirus RNA polymerase by calcium chelation. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):177–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01317489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):395–402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. Gene-coding assignments of rotavirus double-stranded RNA segments 10 and 11. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1099-1103.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Joklik W. K. Demonstration that the same strand of reovirus genome RNA is transcribed in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):450–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Notter M. F., Menegus M. A., Steinhoff M. C. RNA polymerase associated with human rotaviruses in diarrhea stools. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):544–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.544-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Banks C. E., James H. D., Jr, Flores J., Chanock R. M. Antigenic characterization of human and animal rotaviruses by immune adherence hemagglutination assay (IAHA): evidence for distinctness of IAHA and neutralization antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):415–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.415-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Nucleotide sequences of 5'-terminal ribosome-protected initiation regions from two reovirus messages. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):391–394. doi: 10.1038/269390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummert J., Lacroix J. P., Semal J. Heterology among the RNAs of tymoviruses as revealed by RNA-RNA hybridizations. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):306–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin K. H., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. purification and characterization of the small-sized class mRNAs of reovirus type 3: coding assignments and translational efficiencies. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. K., Scheible P. P., Keene J. D., Joklik W. K. The plus strand of reovirus gene S2 is identical with its in vitro transcript. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Zweerink H. J. Isolation and characterization of two types of bluetongue virus particles. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90400-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotono K., Miura K. Transcription of double-stranded RNA in cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus in vtro. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):283–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Arias M. L. In vitro transcription catalyzed by heat-treated human rotavirus. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]