Abstract
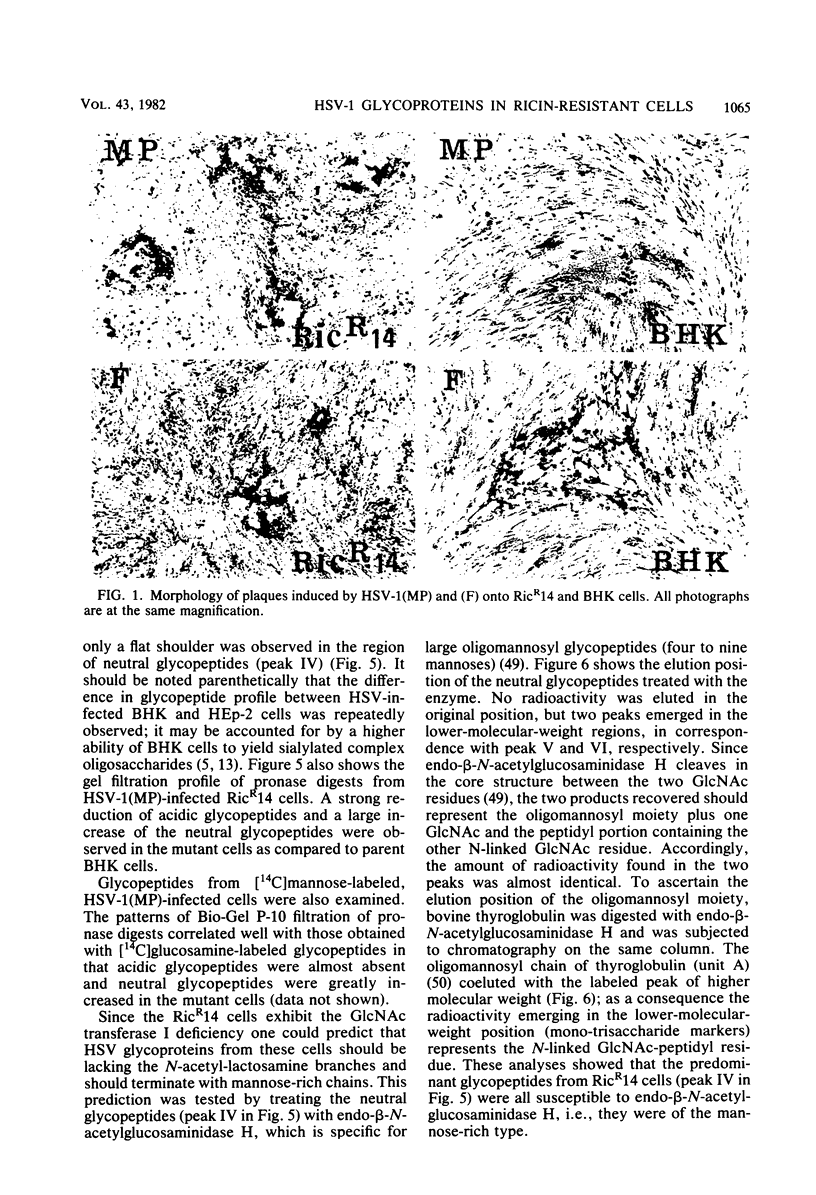
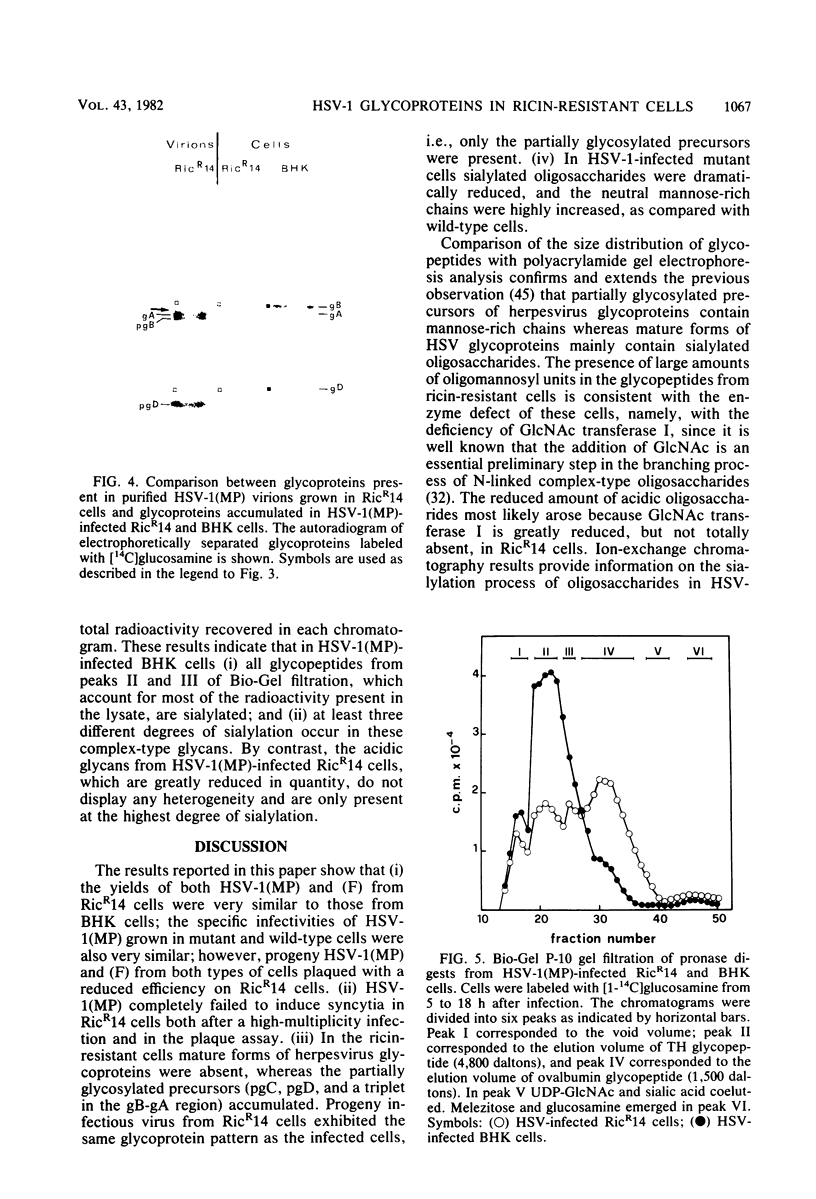
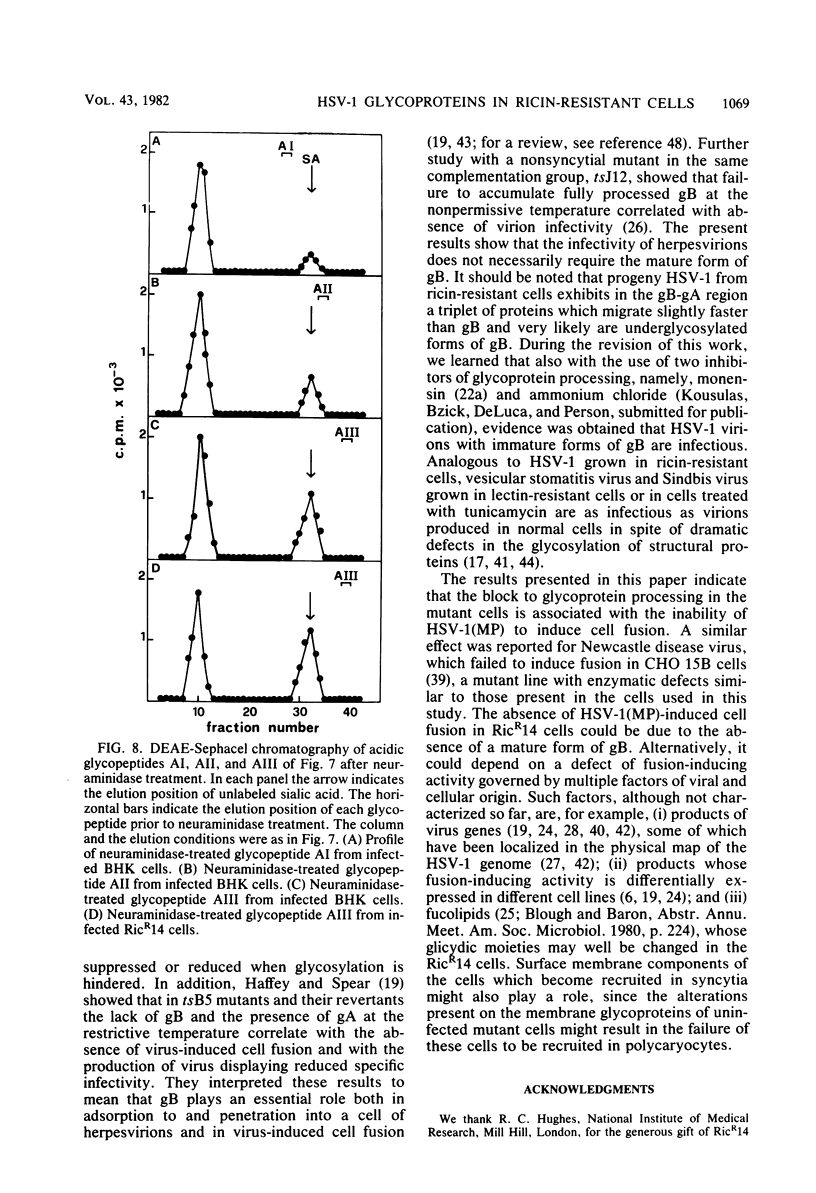
We report on the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and viral glycoprotein processing in RicR14 cells, a mutant ricin-resistant cell line defective in N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase I activity. In these cells HSV-1(MP) and (F) replicated to yields very similar to those in parental BHK cells. The kinetics of HSV-1 adsorption in mutant and in parent cells was also essentially identical. Progeny virions from ricin-resistant and wild-type cells displayed comparable specific infectivities. However, in the mutant cells the efficiency of plating of progeny virus from both RicR14 and BHK cells was reduced. HSV-1(MP) failed to induce syncytia in RicR14 cells either in a plaque assay or after a high-multiplicity infection. Moreover, the fully glycosylated forms of glycoproteins (gB, gC, and gD) were totally absent, and only the partially glycosylated precursors (pgC, pgD. and a triplet in the gB-gA region) accumulated in HSV-1-infected ricin-resistant cells and in herpesvirions made in these cells. Consistent with these results analysis of pronase glycopeptides from cells labeled with [14C]glucosamine showed a strong decrease of sialylated complex-type oligosaccharides and a dramatic accumulation of the neutral mannose-rich chains. The latter chains predominate in partially glycosylated precursors, whereas the complex acidic chains predominate in the fully processed forms of HSV glycoproteins. These results taken together indicate that (i) host-cell N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase I participates in the processing of HSV glycoproteins; and (ii) infectivity of herpesvirions does not necessarily require the mature form of gB. The absence of HSV-1(MP)-induced fusion in RicR14 cells is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbondanza A., Franceschi C., Licastro F., Serafini-Cessi F. Properties of a glycopeptide isolated from human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Interaction with leucoagglutinin and anti-(human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein) antibodies. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):525–528. doi: 10.1042/bj1870525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afonso A. M. Isolation and characterisation of glycopeptides from digests of human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Mar 2;89(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando T., Arai H. Stimulation of herpes simplex type I infection of C6 cells by trypsin-EDTA. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jun;48(Pt 2):319–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Keegstra K. Carbohydrate structure of Sindbis virus glycoprotein E2 from virus grown in hamster and chicken cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):546–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.546-554.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Person S. Dependence of herpes simplex virus type 1-induced cell fusion on cell type. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Sinibaldi-Vallebona P., Cavrini V., Mannini-Palenzona A. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein synthesis by a benz-amidinohydrazone derivative. Arch Virol. 1980;66(3):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01314732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J., Steiner S. M., Benyesh-Melnick M. Effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on herpes simplex virus replication. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. gA and gB glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 1: two forms of a single polypeptide. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.665-675.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Hydrean-Stern C., Cohen G. H. Structural analysis of precursor and product forms of type-common envelope glycoprotein D (CP-1 antigen) of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):608–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.608-620.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison J. R., Robertson J. S., Summers D. F. Host cell-dependent differences in the oligosaccharide moieties of the VSV G protein. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):43–52. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., MARKS G. S., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 5. Procedures for the isolation of glycopeptides from hen's-egg albumin and their oxidation by periodate. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:265–273. doi: 10.1042/bj0870265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Levitan D. B., Blough H. A. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on cell fusion induced by Newcastle disease and herpes simplex viruses. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Leavitt R., Kornfeld S., Schlesinger S. Synthesis and infectivity of vesicular stomatitis virus containing nonglycosylated G protein. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B. The isolation and properties of a variant of Herpes simplex producing multinucleated giant cells in monolayer cultures in the presence of antibody. Am J Hyg. 1959 Sep;70:208–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S. Two-dimensional gel analysis of HSV type 1-induced polypeptides and glycoprotein processing. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffey M. L., Spear P. G. Alterations in glycoprotein gB specified by mutants and their partial revertants in herpes simplex virus type 1 and relationship to other mutant phenotypes. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):114–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.114-128.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XIII. Glycosylation of viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1308–1326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1308-1326.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Monensin inhibits the processing of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, and the egress of virions from infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1102–1112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1102-1112.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. W., Person S. Effects of 2-deoxyglucose, glucosamine, and mannose on cell fusion and the glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):644–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.644-651.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Spear P. G. Viral and cellular factors that influence cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):402–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan D. B., Blough H. A. Preliminary biochemical characterization of the factors(s) responsible for herpesvirus-induced exogenous fusion. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1081–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1081-1087.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Schaffer P. A. Expression of the syncytial (syn) phenotype in HSV-1, strain KOS: genetic and phenotypic studies of mutants in two syn loci. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):686–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Ungkitchanukit A., Hughes R. C. Variants of hamster fibroblasts resistant to Ricinus communis toxin (ricin). Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):113–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1540113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Ungkitchanukit A., Nairn R., Hughes R. C. Ricin resistance in baby hamster kidney cells. Nature. 1975 Sep 11;257(5522):137–139. doi: 10.1038/257137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil J. Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1980;37:157–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan S., Stanley P., Schachter H. Control of glycoprotein synthesis. Lectin-resistant mutant containing only one of two distinct N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activities present in wild type Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3926–3933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Blomberg J., Lycke E. O-glycosidic carbohydrate-peptide linkages of Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01320247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Khanna B., Lycke E. Altered kinetic properties of sialyl and galactosyl transferases associated with herpes simplex virus infection of GMK and BHK cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Mar;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Norrild B., Roizman B. Differential immunologic reactivity and processing of glycoproteins gA and gB of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 made in Vero and HEp-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Person S., Kousoulas K. G., Knowles R. W., Read G. S., Holland T. C., Keller P. M., Warner S. C. Glycoprotein processing in mutants of HSV-1 that induce cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polos P. G., Gallaher W. R. Insensitivity of a ricin-resistant mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells to fusion induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.69-75.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Person S., Keller P. M. Genetic studies of cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.105-113.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. A., Etchison J. R., Robertson J. S., Summers D. F., Stanley P. Specific changes in the oligosaccharide moieties of VSV grown in different lectin-resistnat CHO cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90325-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Gottlieb C., Feil P., Gelb N., Kornfeld S. Growth of enveloped RNA viruses in a line of chinese hamster ovary cells with deficient N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.239-246.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Campadelli-Fiume G. Studies on benzhydrazone, a specific inhibitor of herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis. Size distribution of glycopeptides and endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase-H treatment. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):331–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01320248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. A beta-mannosidic linkage in the unit A oligosaccharide of bovine thyroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5547–5548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer P., Hughes R. C. Glycosyl transferases of baby-hamster-kidney (BHK) cells and ricin-resistant mutants. N-glycan biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






