Abstract
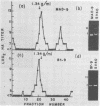
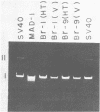
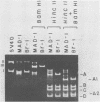
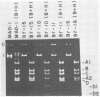
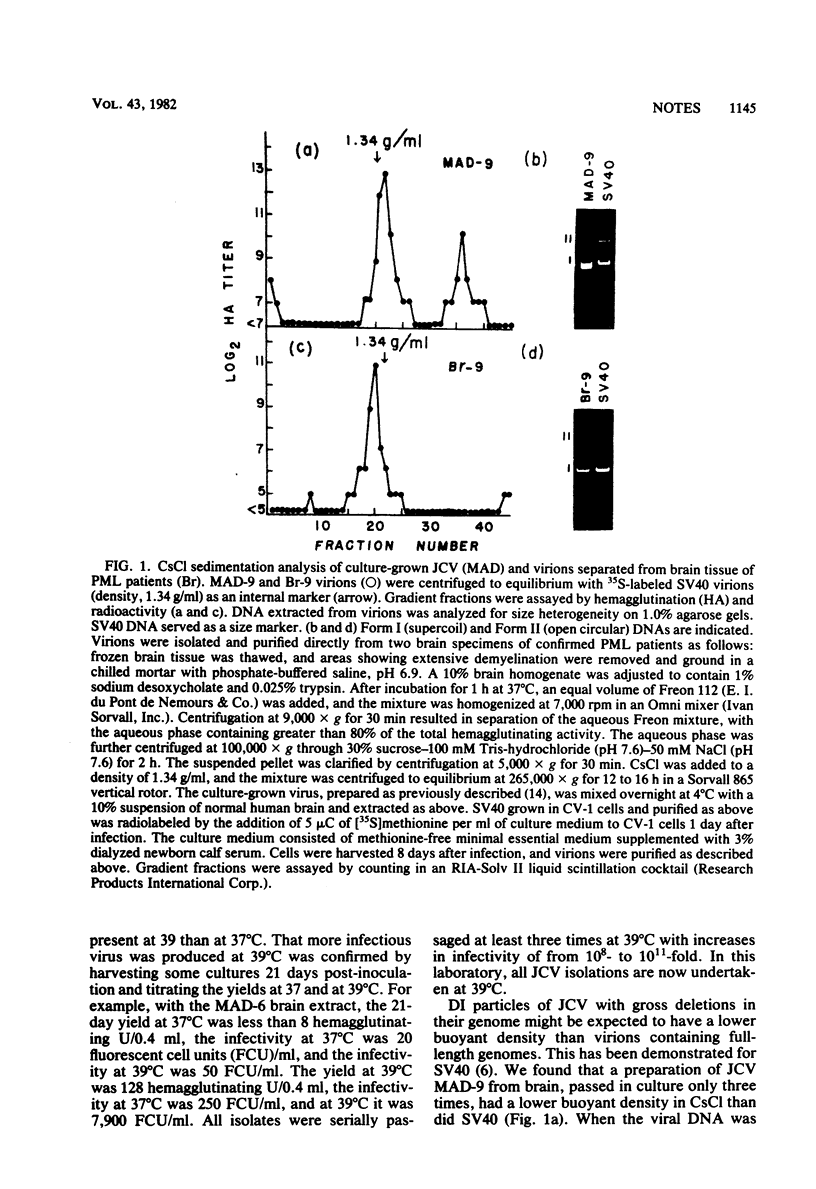
JC virus was examined for temperature sensitivity and for evidence of defective interfering particles as a means of explaining the slow chronic nature of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). JC virus direct from the brain tissue of seven persons with PML was not temperature sensitive as indicated by in vitro assay at 37 and 39 degrees C. In fact, more cells contained viral antigen at 39 than at 37 degrees C. The amount of infectious virus also was increased at 39 degrees C. Virions isolated directly from diseased brain tissue had a higher buoyant density than did virus from the same PML patient passaged in culture and containing genomic deletions. In contrast to DNA from culture-passed virus, DNA extracted from virions direct from brain tissue was homogeneous in length. In 13 separate cases examined, the viral DNA direct from the brain was homogeneous although variations in length were noted among DNAs from different cases. Restriction enzyme cleavage patterns identified all as JC virus DNA. It was concluded that neither temperature sensitivity nor DI particles can be used to explain the slow, progressive nature of PML.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brockman W. W., Lee T. N., Nathans D. The evolution of new species of viral DNA during serial passage of simian virus 40 at high multiplicity. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):384–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M., Holland J. J. Prophylaxis and immunization in mice by use of virus-free defective T particles to protect against intracerebral infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2105–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries K., Johnson R. T., ter Meulen V. Detection of polyoma virus DNA in PML-brain tissue by (in situ) hybridization. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N. Genetic manipulation of reovirus--a model for modification of disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 16;287(20):1026–1033. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211162872007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Martin J. D., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Infectivity of the DNA from four isolates of JC virus. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.476-482.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Martin J. D., Takemoto K. K., Howley P. M. The colinear alignment of the genomes of papovaviruses JC, BK, and SV40. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):576–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D., Frisque R. J., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map of the DNA of JC virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):846–855. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.846-855.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C. The emergence of simian virus 40 variants in a persistent infection of rhesus monkey kidney cells and their interaction with standard simian virus 40. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill F. J., Carroll D. Amplification of papovavirus defectives during serial low multiplicity infections. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):800–803. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Robertson S. M., Padgett B. L., ZuRhein G. M., Walker D. L., Weisblum B. Comparison of JC and BK human papovaviruses with simian virus 40: restriction endonuclease digestion and gel electrophoresis of resultant fragments. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):614–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.614-622.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Rogers C. M., Walker D. L. JC virus, a human polyomavirus associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: additional biological characteristics and antigenic relationships. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.656-662.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Prevalence of antibodies in human sera against JC virus, an isolate from a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):467–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Hodach A. E., Chou S. M. JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):686–690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive viruses and the etiology of chronic and inapparent infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):467–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G., Dal Canto M. C., Johnson T. C. Comparison of central nervous system disease produced by wild-type and temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1242–1249. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1242-1249.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G., Dal Canto M. C., Johnson T. C. Infection of the central nervous system produced by mixtures of defective-interfering particles and wild-type vesicular stomatitis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):59–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentier-Delrue F., Lubiniecki A., Howley P. M. Analysis of JC virus DNA purified directly from human progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy brains. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):761–769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.761-769.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Sakaguchi A. Y., Weiner L. P. Characterization of the cold-sensitive murine hepatitis virus mutants rescued from latently infected cells by cell fusion. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90567-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. Molecular epidemiology of DNA viruses: applications of restriction endonuclease cleavage site analysis. Yale J Biol Med. 1980 Jan-Feb;53(1):55–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Narayan O., Penney J. B., Jr, Herndon R. M., Feringa E. R., Tourtellotte W. W., Johnson R. T. Papovavirus of JC type in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Rapid identification and subsequent isolation. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jul;29(1):1–3. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490250019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]