Abstract
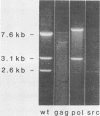
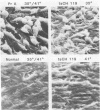
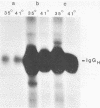
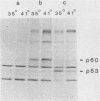
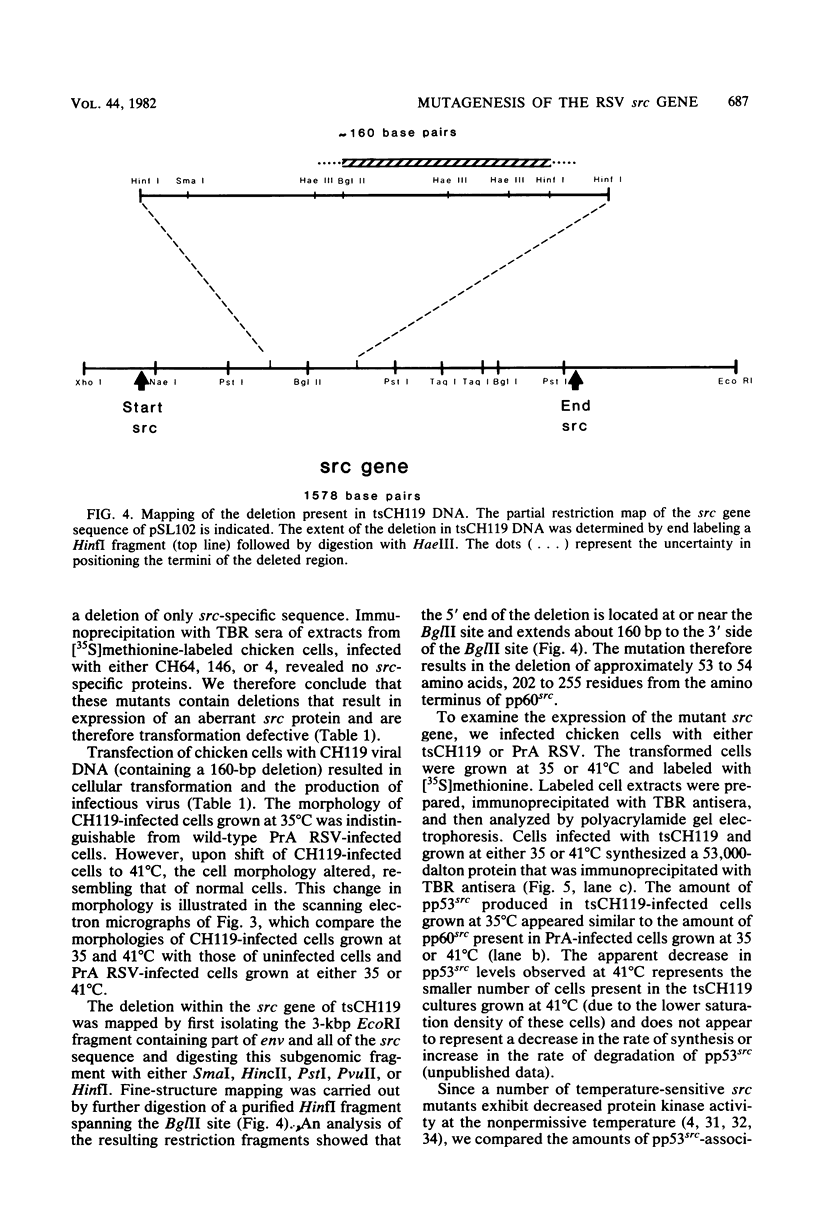
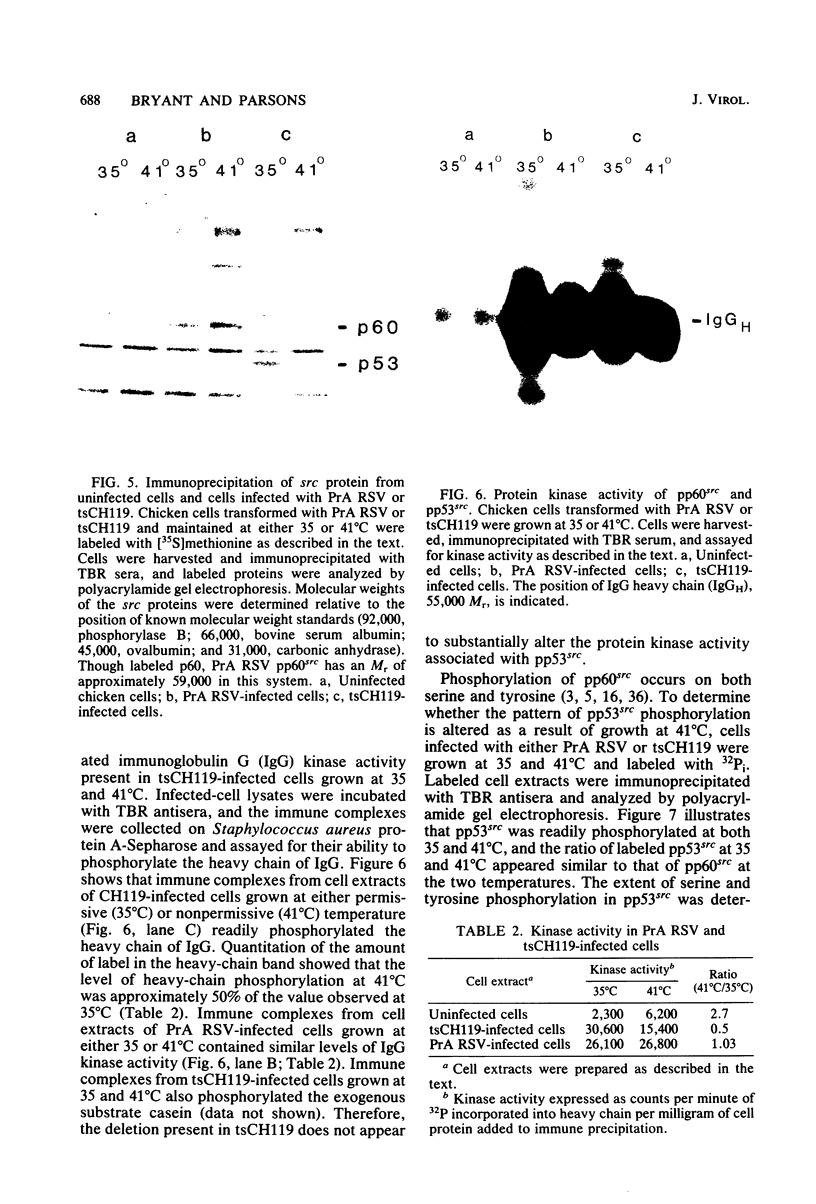
Transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus results from the expression of the viral src gene product, pp60src. Site-directed mutagenesis techniques have been used to construct defined deletion mutations within the src gene of Prague A strain of Rous sarcoma virus. The deletion of DNA sequences at the Bg/II restriction site in the src gene yielded both transformation-defective mutants (tdCH4, 64, and 146) and a mutant temperature sensitive for morphological transformation (tsCH119). The genome of tsCH119 contains an in-phase deletion of approximately 160 base pairs, which mapped to the immediate 3' side of the Bg/II restriction site. Upon infection of chicken cells, tsCH119 encoded a structurally altered src protein, pp53src, containing a deletion of amino acid residues 202 to 255. Immune complexes containing pp53src isolated from tsCH119-infected cells grown at 41 degrees C exhibited only 50% less tyrosine-specific kinase activity than immune complexes isolated from cells grown at 35 degrees C. pp53src immunoprecipitated from tsCH119-infected cells grown at either 35 or 41 degrees C contained phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. We suggest that tsCH119 represents a class of mutants containing mutations mapping within a functionally important domain of the src protein, distinct from the domain specifying the protein kinase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Rous sarcoma virus-induced phosphorylation of a 50,000-molecular weight cellular protein. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):250–253. doi: 10.1038/295250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Structural analysis of the avian sarcoma virus transforming protein: sites of phosphorylation. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):770–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.770-781.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of an avian sarcoma virus oncogene (src) and proposed amino acid sequence for gene product. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):198–203. doi: 10.1038/287198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F. Evidence that the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product is a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincham V. J., Chiswell D. J., Wyke J. A. Mapping of nonconditional and conditional mutants in the src gene of Prague strain Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Bechberger J., Nedic I. Four Rous sarcoma virus mutants which affect transformed cell morphology exhibit altered src gene products. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highfield P. E., Rafield L. F., Gilmer T. M., Parsons J. T. Molecular cloning of avian sarcoma virus closed circular DNA: structural and biological characterization of three recombinant clones. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):271–279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.271-279.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Boone L., Skalka A. M. Isolation and characterization of recombinant DNA clones of avian retroviruses: size heterogeneity and instability of the direct repeat. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1026-1033.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R., Hanafusa H. Changes in amino-terminal sequences of pp60src lead to decreased membrane association and decreased in vivo tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzek R. A., Mitchell R. L., Lau A. F., Faras A. J. Association of pp60src and src protein kinase activity with the plasma membrane of nonpermissive and permissive avian sarcoma virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):805–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.805-815.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E. The structure and protein kinase activity of proteins encoded by nonconditional mutants and back mutants in the sec gene of avian sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):47–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90526-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Lewis P., Dierks P. Purification of virus-specific RNA from chicken cells infected with avian sarcoma virus: identification of genome-length and subgenome-leghth viral RNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., Riley S. C., Mullen E. E., Brock E. J., Benjamin D. C., Kuehl W. M., Parsons J. T. Immune response to the src gene product in mice bearing tumors induced by injection of avian sarcoma virus-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):40–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.40-46.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G. G., Hu J. Reverse transcriptase as the major determinant for selective packaging of tRNA's into Avian sarcoma virus particles. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):692–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.692-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Friis R. R., Bauer H. Src Gene product from different strains of avian sarcoma virus: Kinetics and possible mechanism of heat inactivation of protein kinase activity from cells infected by transformation-defective, temperature-sensitive mutant and wild-type virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):967–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Ziemiecki A., Friis R. R., Bauer H. The expression of pp60src and its associated protein kinase activity in cells infected with different transformation-defective temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K. Temperature-sensitive transformation by Rous sarcoma virus and temperature-sensitive protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):220–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.220-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]