Abstract
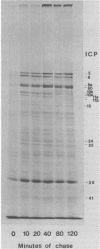
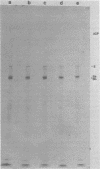
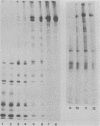
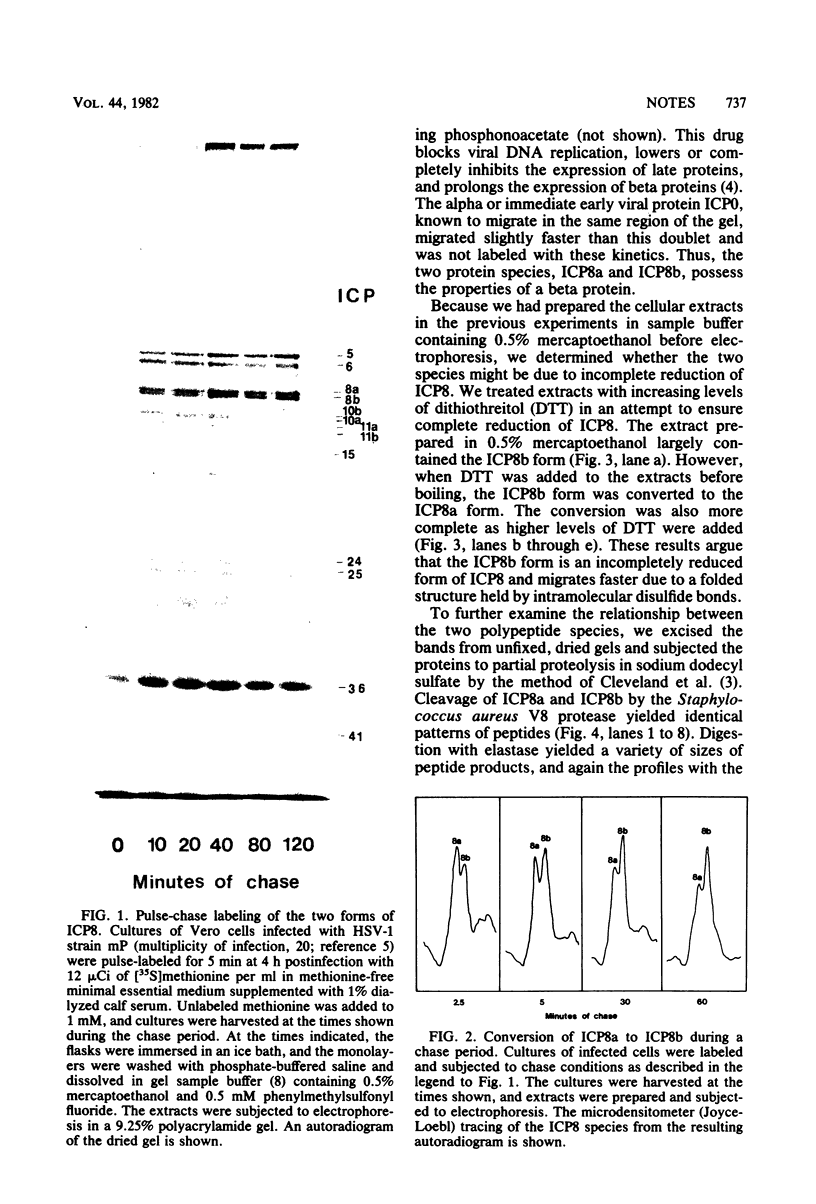
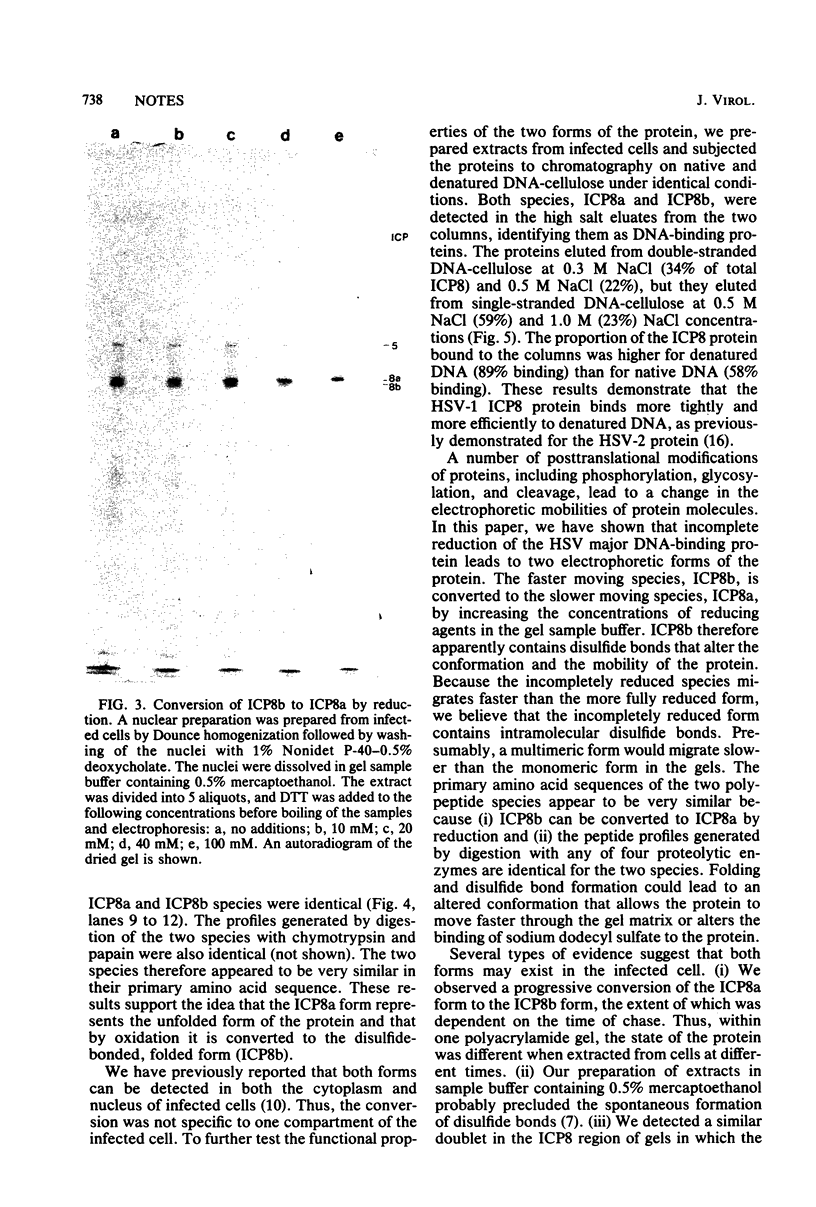
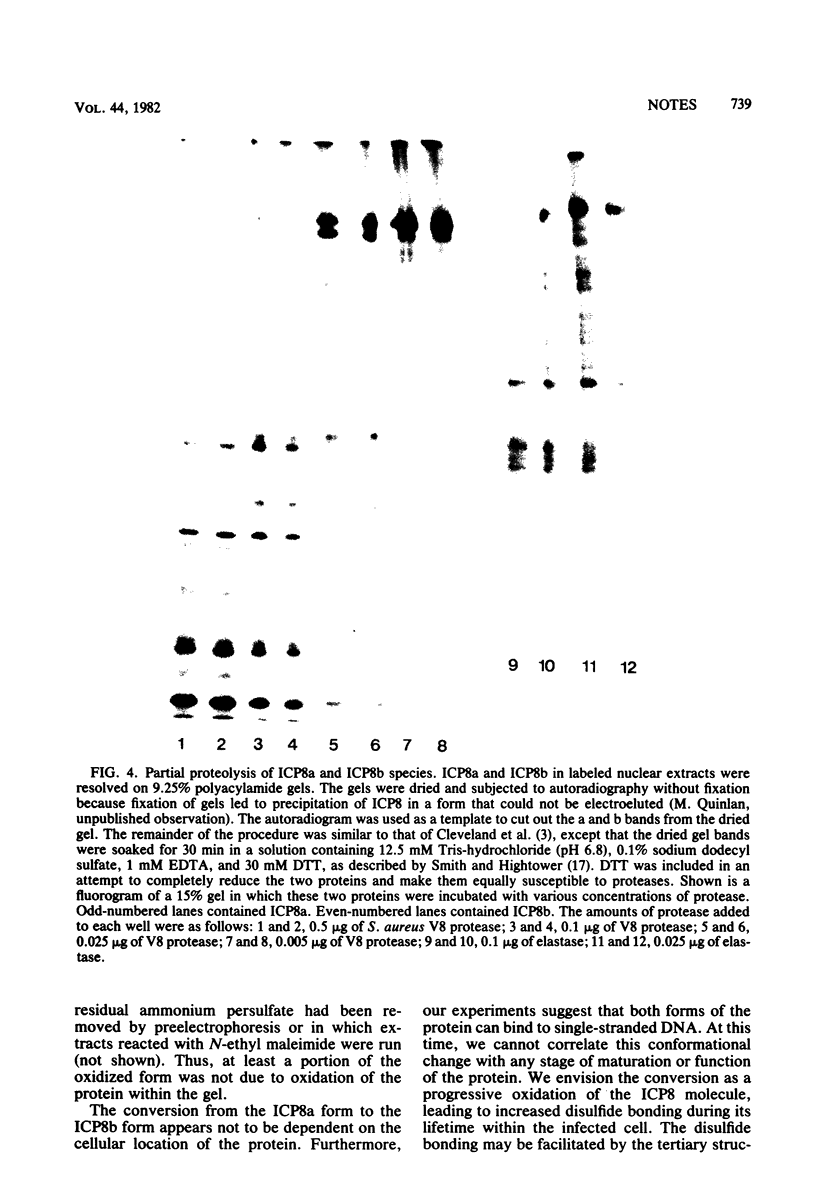
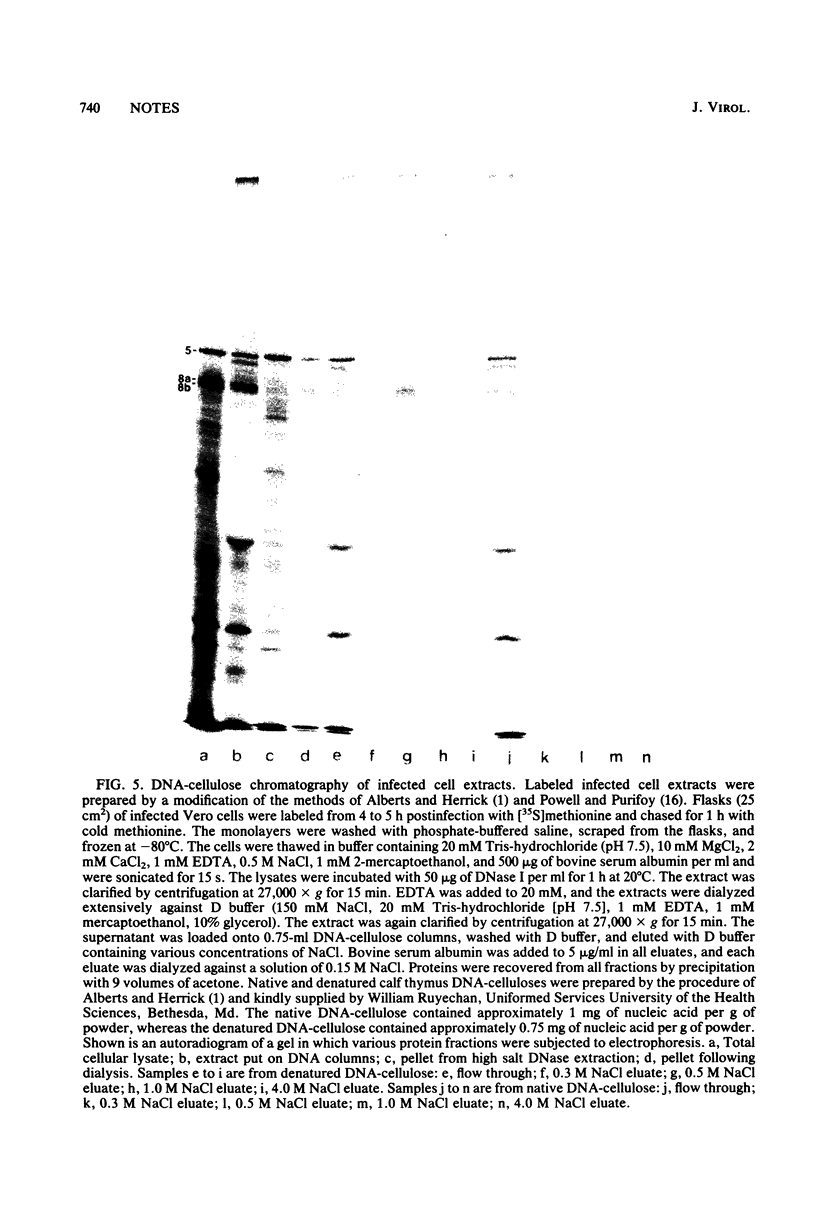
We have resolved two electrophoretic species of the major DNA-binding protein, infected cell polypeptide 8 (ICP8), encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. In pulse-chase experiments, we observed the conversion of the ICP8a form, the slower migrating species, to the faster migrating form, ICP8b. Thus, the two species appear to be related as precursor-product. The conversion was not due to proteolytic cleavage, because higher concentrations of reducing agents in the sample buffer shifted the faster moving form to the slower moving species. Also, the two forms have identical peptide patterns as analyzed by partial proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Thus, the faster moving species appears to be a conformational isomer containing intramolecular disulfide bonds. The functional significance of the two forms of the protein is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss G. J., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Herpes simplex virus proteins: DNA-binding proteins in infected cells and in the virus structure. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J., Petkevich J. M. On the association of virus proteins with the nuclei of cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):519–529. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R., Milner R. J., Reske K., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Subunit structure, cell surface orientation, and partial amino-acid sequences of murine histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Spang A. E. Definition of a series of stages in the association of two herpesviral proteins with the cell nucleus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):314–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.314-324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Littler E., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. II. Major virus-specific DNa-binding protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):894–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.894-902.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. DNA-binding proteins of cells infected by herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2. Intervirology. 1976;7(4-5):225–239. doi: 10.1159/000149955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. W., Hightower L. E. Identification of the P proteins and other disulfide-linked and phosphorylated proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):256–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.256-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]