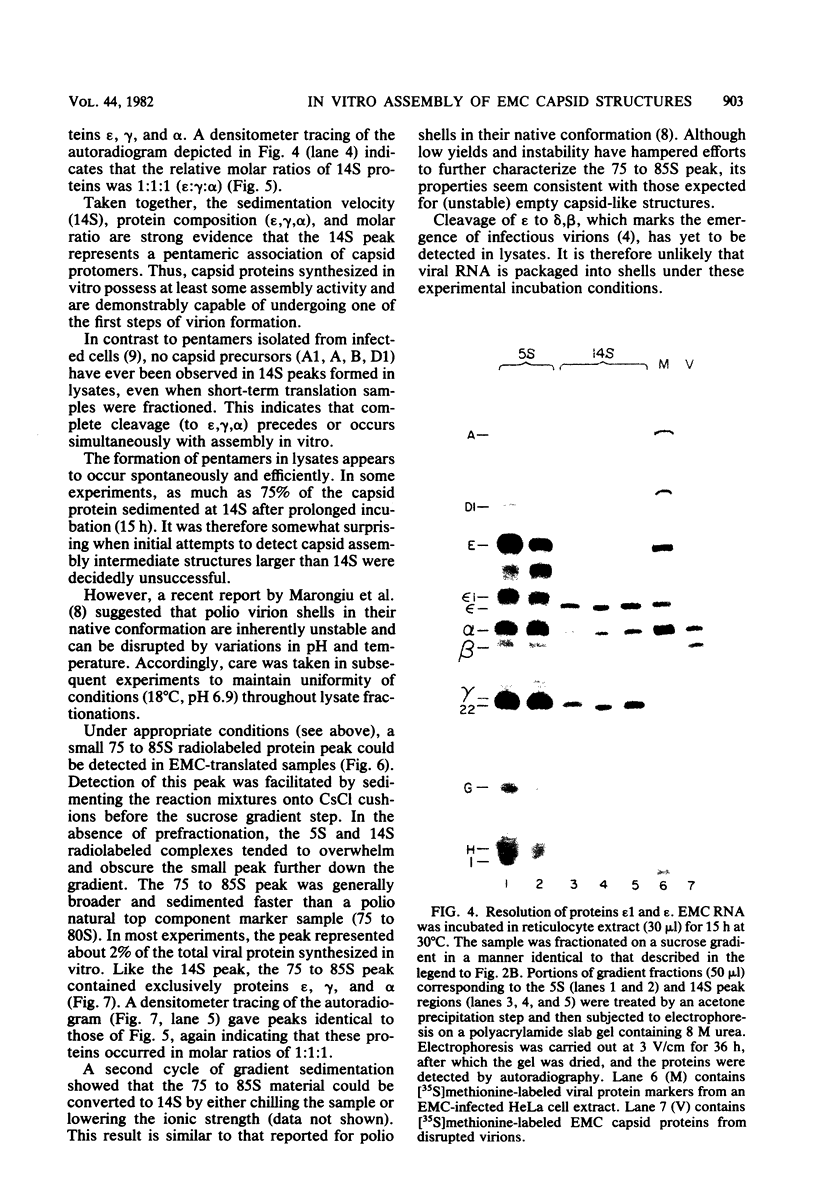
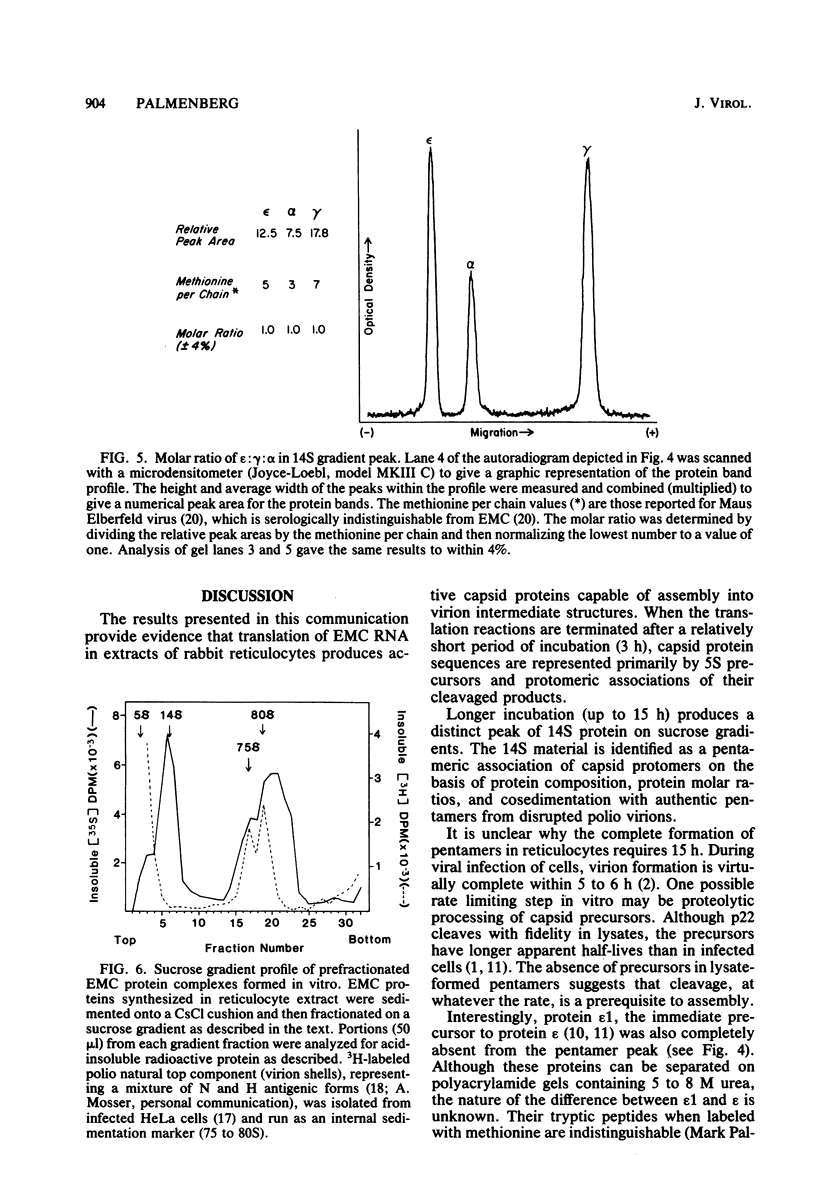
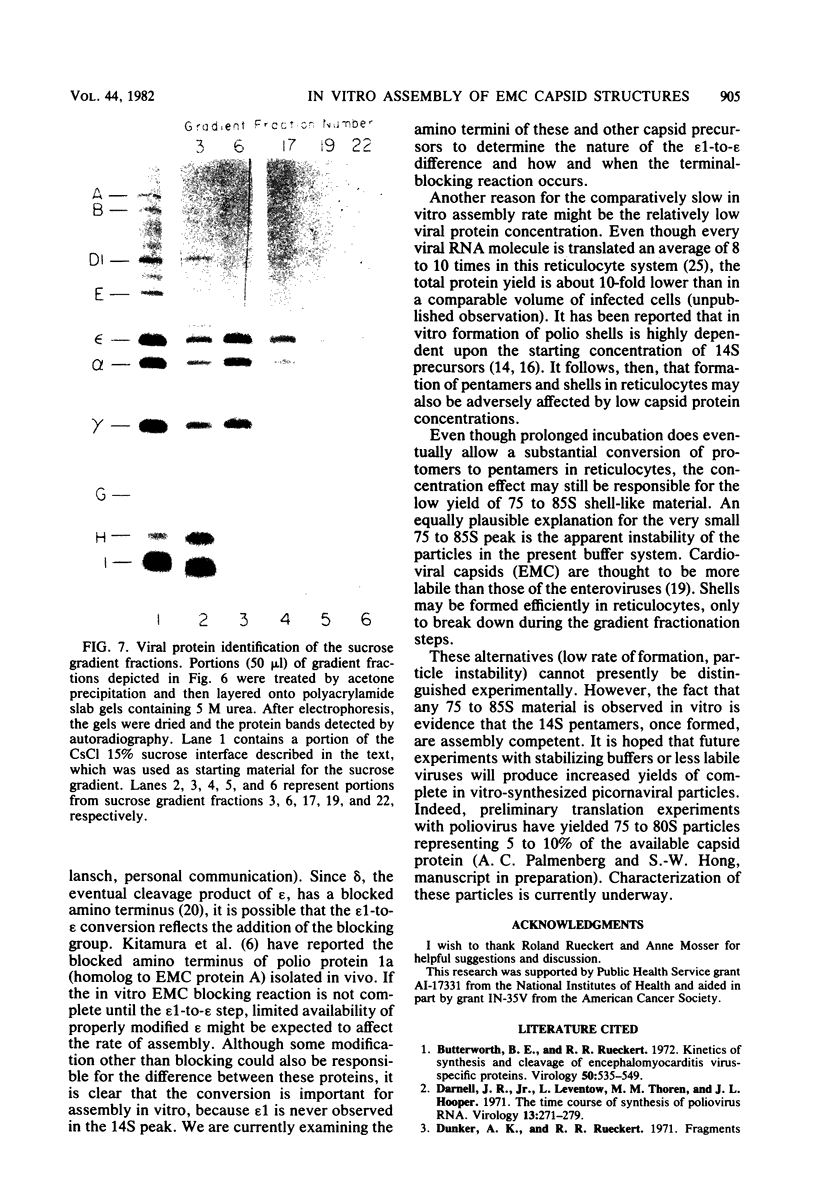
Abstract
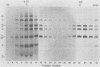
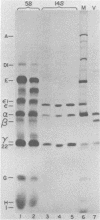
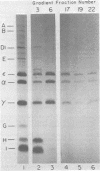
Cell-free translation of encephalomyocarditis RNA in extracts of rabbit reticulocytes results in the synthesis of viral proteins indistinguishable from those produced during virus infection of cells. The viral capsid proteins are produced in an active form capable of assembly into viral capsid intermediate structures. Protomers (5S), pentamers (14S), and shell-like structures (75 to 85S) can be detected after prolonged incubation in the extracts. Proteolytic cleavage of capsid precursor proteins appears to be a prerequisite for assembly, in apparent contrast to cell-associated assembly. Assembly of pentamers is also preceded by conversion of protein epsilon 1 to epsilon in a step which may reflect an amino-terminal blocking reaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Kinetics of synthesis and cleavage of encephalomyocarditis virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90405-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARNELL J. E., Jr, LEVINTOW L., THOREN M. M., HOOPER J. L. The time course of synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1961 Mar;13:271–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Colter J. S. Further characterization of Mengo subviral particles: a new hypothesis for picornavirus assembly. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu M. E., Pani A., Corrias M. V., Sau M., La Colla P. Poliovirus morphogenesis. I. Identification of 80S dissociable particles and evidence for the artifactual production of procapsids. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.341-347.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Rueckert R. R. Evidence for intramolecular self-cleavage of picornaviral replicase precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.244-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of poliovirus. II. Evidence for the self-assembly of 14 S particles into empty capsids. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Wiemert S. In vitro assembly of poliovirus. V. Evidence that the self-assembly activity of 14 S particles is independent of extract assembly factor(s) and host proteins. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):92–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Differences between poliovirus empty capsids formed in vivo and those formed in vitro: a role for the morphopoietic factor. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):173–183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.173-183.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Poliovirus empty capsid morphogenesis: evidence for conformational differences between self- and extract-assembled empty capsids. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.792-800.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. Y., Shih D. S. Cleavage of the capsid protein precursors of encephalomyocarditis virus in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):942–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.942-945.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]