Abstract
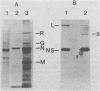
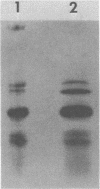
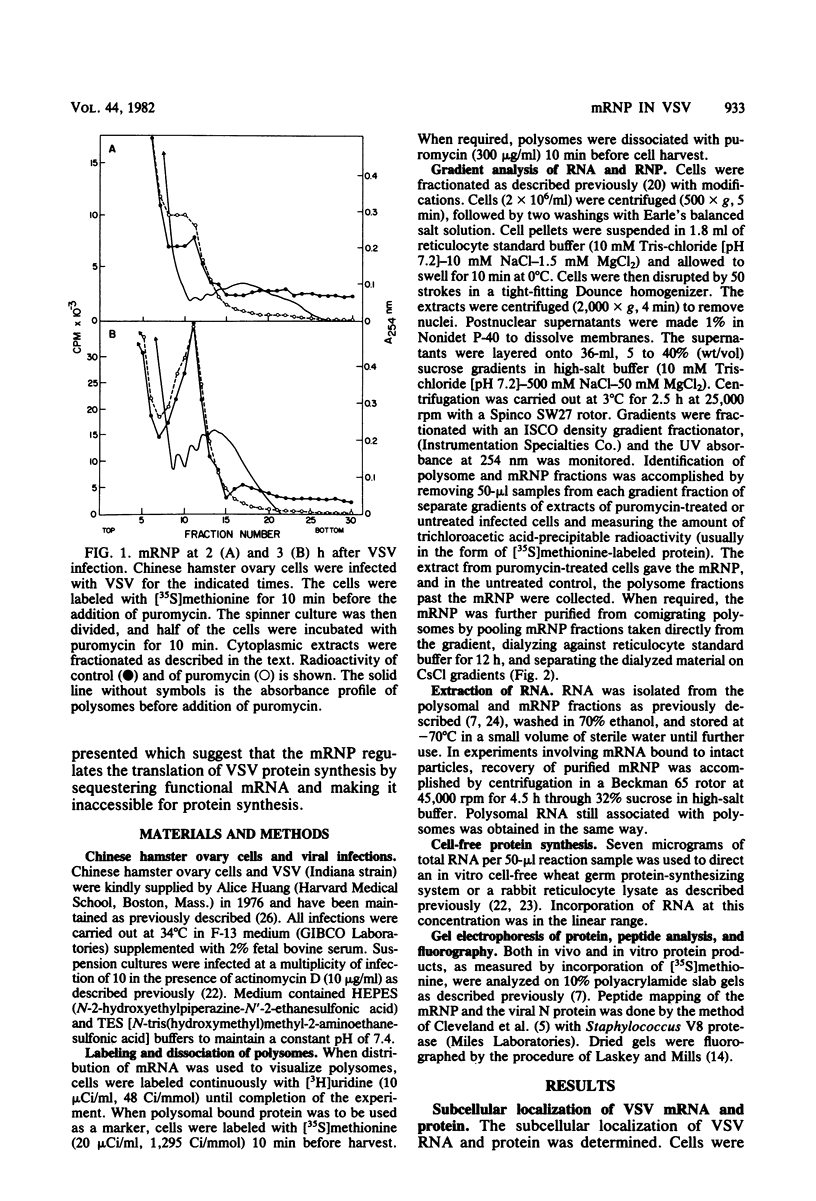
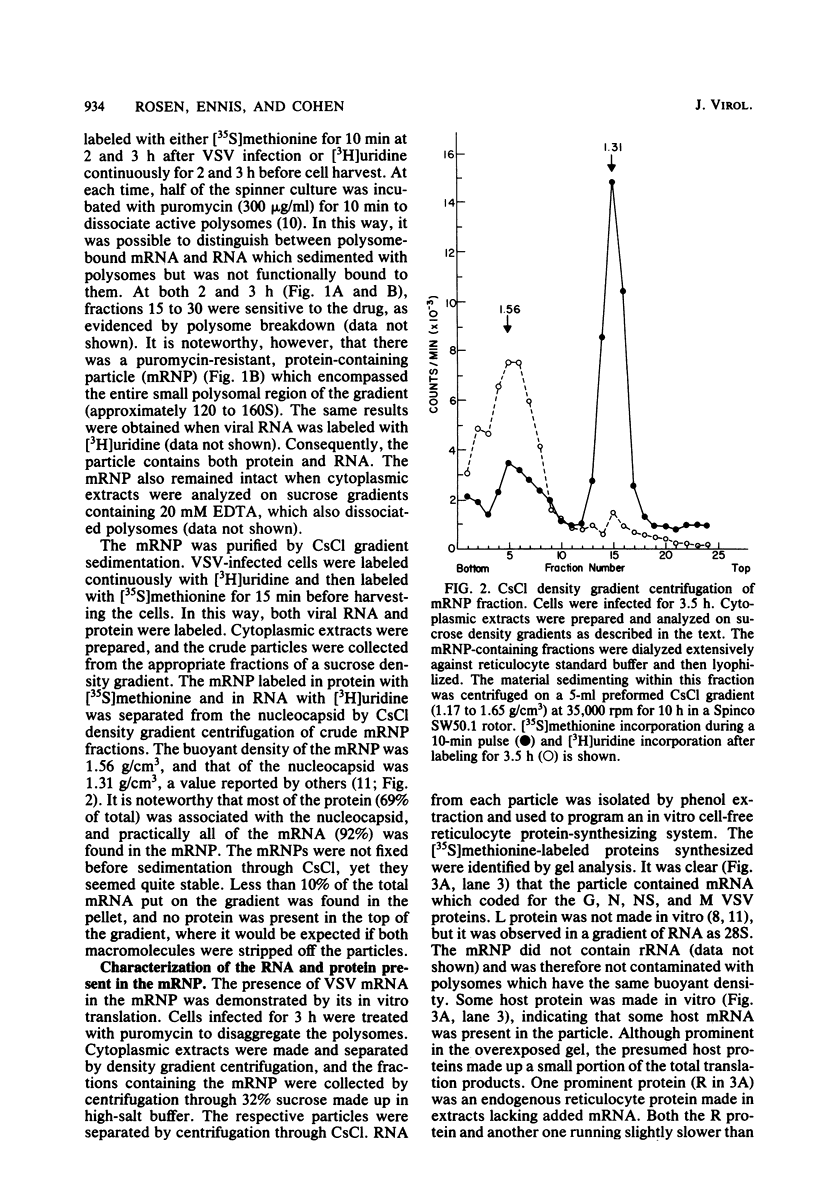
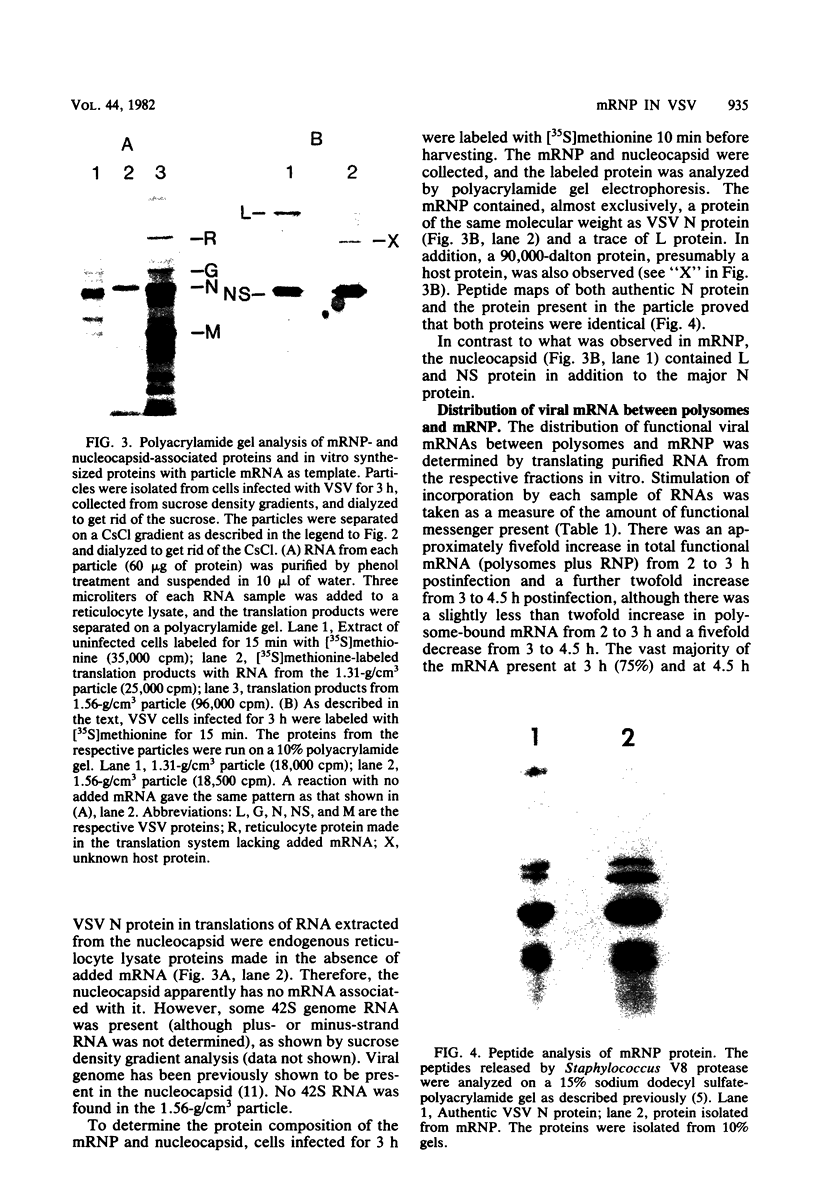
An mRNA-ribonucleoprotein particle (mRNP) was found in vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-infected Chinese hamster ovary cells. The particle was present 3 and 4.5 h after infection but was barely discernible at 2 h. The mRNP (buoyant density, 1.56 g/cm3), which cosedimented with viral nucleocapsid in a sucrose density gradient at approximately 120 to 160S, was separable from nucleocapsid (buoyant density, 1.31 g/cm3) by CsCl density gradient centrifugation. It contained all five VSV mRNAs and, almost exclusively, viral N protein. Some host mRNA and host protein was also present in the particle. The intact mRNP was incapable of stimulating protein synthesis in an in vitro protein-synthesizing system, although the VSV mRNA isolated from the particle by phenol extraction was functional in vitro. In contrast, intact polysomes stimulated cell-free protein synthesis to the same extent as purified polysomal mRNA. By 4.5 h after infection, 97% of the functional mRNA in vivo was associated with the mRNP, and only 3% was on polysomes. The amount of polysomal mRNA at 4.5 h after infection was only 31% of that found at 2 h after infection; this was reflected by the 76% decrease observed in the rate of in vivo protein synthesis at 4.5 h relative to that found at 2 h. Thus, it appears that the mRNP serves as an organelle which sequesters the large excess of VSV mRNA that is normally made during secondary transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Rhodes D. P., Banerjee A. K. The 5' terminal structure of the methylated mRNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Rhodes D. P. In vitro synthesis of RNA that contains polyadenylate by virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3566–3570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Intracellular vesicular stomatitis virus leader RNAs are found in nucleocapsid structures. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):568–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.568-576.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., Lucas-Lenard J. Regulation of protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected mouse L-929 cells by decreased protein synthesis initiation factor 2 activity. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.781-791.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Lund H. Untranslated vesicular stomatitis virus messenger RNA after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L., Pennica D., Hill J. M. Synthesis of macromolecules during microcyst germination in the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium pallidum. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Shafritz D. A. Identification and characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill V. M., Marnell L., Summers D. F. In vitro replication and assembly of vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsids. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Balitmore D. Initiation of polyribosome formation in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Intracellular synthesis and extracellular appearance of virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):678–690. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of viral antigens. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.404-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Translational control of protein synthesis after infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):719–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.719-733.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA and inhibition of translation of cellular mRNA--is there a P function in vesicular stomatitis virus? J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):504–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.504-517.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Pennica D., Ennis H. L., Cohen P. S. Separation and purification of the mRNAs for vesicular stomatitis virus NS and M proteins. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Pennica D., Ennis H. L., Cohen P. S. Temporal regulation of the rate of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA translation during infection of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister P. E., Wagner R. R. Differential inhibition of host protein synthesis in L cells infected with RNA - temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):550–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.550-558.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Polysomal ribonucleic acid of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):958–968. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Lynch K. R., Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. Decay of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNAs in vivo. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):484–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Knipe D. Nucleotide sequence complexities, molecular weights, and poly(A) content of the vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA species. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.994-1003.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger G., Lazzarini R. A. Analysis of the RNA of defective VSV particles. Cell. 1974 Sep;3(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]