Abstract
Objectives
Adverse effects have been reported of prenatal and/or postnatal passive exposure to smoking on children's health. Uncertainties remain about the relative importance of smoking at different periods in the child's life. We investigate this in a pooled analysis, on 53 879 children from 12 cross‐sectional studies—components of the PATY study (Pollution And The Young).
Methods
Effects were estimated, within each study, of three exposures: mother smoked during pregnancy, parental smoking in the first two years, current parental smoking. Outcomes were: wheeze, asthma, “woken by wheeze”, bronchitis, nocturnal cough, morning cough, “sensitivity to inhaled allergens” and hay fever. Logistic regressions were used, controlling for individual risk factors and study area. Heterogeneity between study‐specific results, and mean effects (allowing for heterogeneity) were estimated using meta‐analytical tools.
Results
There was strong evidence linking parental smoking to wheeze, asthma, bronchitis and nocturnal cough, with mean odds ratios all around 1.15, with independent effects of prenatal and postnatal exposures for most associations.
Conclusions
Adverse effects of both pre‐ and postnatal parental smoking on children's respiratory health were confirmed. Asthma was most strongly associated with maternal smoking during pregnancy, but postnatal exposure showed independent associations with a range of other respiratory symptoms. All tobacco smoke exposure has serious consequences for children's respiratory health and needs to be reduced urgently.
Keywords: tobacco smoke, fetus, child, respiratory symptoms, asthma
Considerable attention has focused recently on the harmful effects of involuntary or “passive” smoking. Many studies have reported adverse effects of prenatal and/or postnatal exposure on children's respiratory health, with much of the literature summarised in a number of reviews.1,2,3,4 Within a broad picture of harmful effects, uncertainties remain, including the relative importance of exposure at different periods in the child's life.
There is some evidence that prevalence of wheeze in childhood is associated more strongly to prenatal (intrauterine) exposure than with current parental smoking.5,6,7,8,9 In the Italian study of Agabiti et al, the effect of current parental smoking on wheeze was evident only in adolescents but not among younger children, while the effect of maternal smoking during pregnancy was greater in children.10 A Polish study found current exposure a stronger predictor than prenatal exposure,11 while a study in Chicago found a protective association with current maternal smoking.12 Similar inconsistencies have been seen for effects of tobacco exposure on child's asthma and other respiratory outcomes.2,4
Several studies have shown protective effects of current parental smoking on atopy, or on atopic‐related conditions such as eczema or hay fever.13,14,15,16 Yet Lam et al found increased risks of hay fever related to passive smoking,15 and passive smoking was also associated with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and hay fever among Swedish and Turkish schoolchildren.17,18
The Pollution And The Young (PATY) project assembled data on exposures and health for 58 561 children, from cross‐sectional studies carried out in 12 countries with comparable questionnaires. PATY was established primarily to investigate associations between air pollution and respiratory health. Here we use that subset of 53 879 children with information on parental smoking. This pooled analysis, on extensive, original data (with only three of the 12 studies as yet published on this topic),19,20,21 gives a powerful opportunity to examine critical periods of exposure to cigarette smoke, to address the problems of co‐linearity between prenatal and postnatal passive smoking and to assess independent effects of three exposures: maternal smoking during pregnancy, passive smoking during the first two years of the child's life, and current passive smoking. Associations found in this large dataset between prenatal and postnatal passive smoking on children's lung function have already been reported.22
METHODS
Comparable cross‐sectional studies were sought (published or otherwise), which assessed respiratory symptoms and individual risk factors at elementary school age by comparable parent's questionnaires,23 included cough and wheeze as primary outcomes, and (since a primary objective was to assess effects of ambient air pollution) allowed calculation of annual mean particulate matter. To improve comparability further, data were restricted to children aged 6–12 years. Table 1 describes the contributing studies, detailed in individual reports.10,19,20,24,25,26,27,28,29
Table 1 Participating studies: geographic units, period of data gathering, and number of children, aged 6–12 years, with information on age, sex, and parental smoking.
| Study | Number of study areas | Data collection | Number of children | Age range (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria, Linz Survey | 8 areas in 1 town | Jan 1996–Dec 1998 | 3776 | 6–8 |
| Bulgaria, CESAR study | 4 areas in 3 towns | Feb–May 1996 | 2973 | 7–11 |
| Czech Republic, CESAR study | 4 areas in 1 town | Feb–May 1996 | 2962 | 7–11 |
| Germany, Bitterfeldt study | 3 areas in 3 towns | Aug 1992–Jul 1993 | 1972 | 6–12 |
| Hungary, CESAR study | 5 areas in 5 towns | Feb–May 1996 | 3031 | 7–11 |
| Italy, Sidria study | 29 areas in 22 towns | Oct 1994–Mar 1995 | 9073 | 6–10 |
| Holland, 24 school study | 24 areas in 19 towns | Apr 1997–Jul 1998 | 1913 | 7–12 |
| North America, 24 city study | 24 areas in 24 towns | Sep–Nov in 1988–90 | 14845 | 8–11 |
| Poland, CESAR study | 4 areas in 4 towns | Feb–May 1996 | 2643 | 7–11 |
| Russia, 10‐city study | 13 areas in 10 towns | Apr–May 1999 | 5412 | 8–12 |
| Slovakia, CESAR study | 4 areas in 3 towns | Feb–May 1996 | 2531 | 7–11 |
| Switzerland, Scarpol study | 10 areas in 10 towns | Oct 1992–Mar 1993 | 2748 | 6–12 |
| Total | 132 areas in 105 towns | 53879 |
CESAR, Central European Study on Air pollution and Respiratory health.
All studies collected data on the children's health and individual/household risk factors (including exposure to tobacco smoke) via questionnaires, distributed in schools and filled in by the parents. Care was taken to select or construct variables which were as comparable as possible.23
Eight outcomes were analysed: wheeze in the last 12 months, “woken by wheeze in the last 12 months”, asthma ever, bronchitis in the last 12 months, nocturnal dry cough in the last 12 months, morning cough, “sensitivity to inhaled allergens”, and hay fever ever. Detailed wordings are reported elsewhere.23 Three “parental smoking” measures were defined: mother smoked during pregnancy, child lived with a smoker during the first two years of life (unavailable for Austria and Switzerland, in Germany “first year of life”), and child currently lives with a smoker. The latter included all smokers in the household, in all countries. Passive smoking during the first two years was restricted to parental smoking in Italy, Switzerland and the CESAR (Central European Study on Air pollution and Respiratory health) countries.
Only the exposures relate to different periods of the child's life. Health questionnaires were administered only once per child.
Statistical analyses
Analyses were done using STATA v8. A two‐stage approach was used. In stage 1, study‐specific parental smoking effects were estimated using logistic regression (on individual level records). Three models were used: The first (“confounder adjusted”) controlled for potential confounders (listed below), but not for the other smoking variables. The second and third models additionally adjusted for one and then both other smoking variables. In stage 2, the study specific results were entered into a meta‐analysis, to obtain forest plots of the estimates, a mean estimate (a weighted mean of the study specific estimates), and a measure and Cochran χ2 test of between‐study heterogeneity. Study specific estimates were assumed to follow a random distribution about a mean, and the estimation of this mean and its confidence interval took into account both variation among study‐specific estimates and uncertainty (due to sampling variability) related to each study‐specific estimate.30
We controlled for age, sex, maternal education, paternal education, nationality, household crowding, gas for cooking, unvented gas/oil/kerosene heater, mould, birth order, “ever had a pet”, and study area. Adjusting for study area accounts for risk factors such as ambient air pollution, climate, and neighbourhood socioeconomic differences.
Meta‐regressions assessed associations between study‐specific estimates and study‐characteristics. These potential sources of heterogeneity between estimates were: season of data collection; study period; proportion of younger children (6–8 years old); response rate (above/below 80%); Western or former “Eastern Block” countries.
We tested robustness of results to controlling for parental illness (a potentially problematic variable, since parental smoking may cause both parent's and child's illness), attendance at kindergarten, and breastfeeding. We also assessed effect modification by age (6–8 v 9–12), breastfeeding, household crowding and, since a recent study found that associations between maternal smoking during pregnancy and asthma were restricted to girls,31 for effect modification by the child's sex.
RESULTS
Table 2 shows study characteristics, frequency of exposure to passive smoking, and prevalences of respiratory and allergic disorders. Bronchitis was reported most frequently, prevalences exceeding 30% in four of the studies. Hay fever and “woken by wheeze in the last 12 months” were reported least frequently, with prevalences under 10% in most studies.
Table 2 Study characteristics, prevalences of children's passive smoking and respiratory symptoms.
| Austria | Bulgaria | Czech | Germany | Hungary | Italy | Holland | N America | Poland | Russia | Slovakia | Switz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East/West (E or W) | W | E | E | E | E | W | W | W | E | E | E | W |
| 2/3 questionnaires in spring. 1 = yes, 0 = no | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Post 1995 study. 1 = yes, 0 = no | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Response rate <0.8. 1 = yes, 0 = no | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| % of children in age range 6–8 years | 98 | 44 | 34 | 32 | 30 | 61 | 33 | 5 | 37 | 17 | 34 | 55 |
| Frequencies of exposures (%): | ||||||||||||
| Maternal smoking during pregnancy | 17.5% | 6.4% | 8.9% | 4.9% | 12.7% | 17.2% | 28.7% | 26.6% | 25.3% | 4.4% | 6.0% | 17.0% |
| Smoking during first 2 years of life | – | 70.1% | 62.0% | 18.7% | 62.9% | 57.6% | 60.7% | 63.4% | 74.8% | 46.3% | 54.9% | – |
| Current smoker in household | 62.5% | 70.9% | 57.4% | 45.8% | 55.9% | 58.2% | 58.1% | 50.4% | 64.9% | 46.1% | 48.4% | 48.2% |
| Prevalences of symptoms (%): | ||||||||||||
| Wheeze in last 12 months | 13.67 | 16.41 | 19.76 | 10.21 | 9.92 | 6.76 | 9.45 | 19.40 | 11.84 | 13.29 | 9.37 | 10.32 |
| Asthma ever | 8.49 | 16.50 | 9.72 | 8.52 | 22.35 | 8.99 | 8.06 | 9.69 | 10.21 | 1.86 | 6.88 | 9.00 |
| Bronchitis in the last 12 months | – | 23.69 | 41.12 | – | 32.57 | 12.40 | 7.82 | 6.19 | 34.60 | 14.71 | 30.94 | 18.26 |
| Nocturnal dry cough | 10.40 | 5.35 | 18.54 | 18.57 | 9.42 | 15.66 | 21.74 | – | 13.55 | – | 12.83 | 21.57 |
| Morning cough | 5.28 | 16.02 | 25.61 | 13.82 | 6.17 | – | – | 6.02 | 45.71 | 11.35 | 14.40 | 11.83 |
| Sensitivity to inhaled allergens | 12.85 | 12.37 | 16.67 | – | 14.02 | 10.92 | 15.17 | 21.00 | 13.90 | 6.44 | 14.65 | 13.70 |
| Hay fever ever | 5.32 | – | – | 4.55 | – | 7.78 | 7.19 | 14.34 | – | 1.20 | – | 10.10 |
| Woken by wheeze in the last 12 months | – | 7.07 | 14.78 | – | 8.37 | 1.87 | 4.92 | 5.18 | 8.62 | 4.25 | 8.58 | 4.59 |
Numbers living with a reported current smoker ranged from 45.8% in Germany to 70.9% in Bulgaria. Passive smoking during the first two years of life ranged from 18.7% in Germany (first year of life only), then from 46.3% in Russia, to 74.8% in Poland. Reported prenatal exposure tended to be rarer in Eastern countries and ranged from 4.4% in Russia to 28.7% in Holland.
The exposures were correlated, as anticipated. Coefficients of correlation (r) between current exposure and exposure during the first two years ranged from 0.22 in Germany to 0.75 in the Czech Republic. Between prenatal exposure and exposure in the first two years, r ranged from 0.16 in Bulgaria to 0.42 in North America and the Netherlands, and between current and prenatal exposure, r ranged from 0.14 in Bulgaria to 0.42 in North America.
Confounder adjusted results
Wheeze and nocturnal cough were associated with all three smoking measures, with harmful effects seen in nearly all studies (fig 1). Mean odds ratios for wheeze ranged from 1.17 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02 to 1.33) for the effect of smoking during the first two years, to 1.25 (95% CI 1.14 to 1.37) for smoking during pregnancy (table 3).
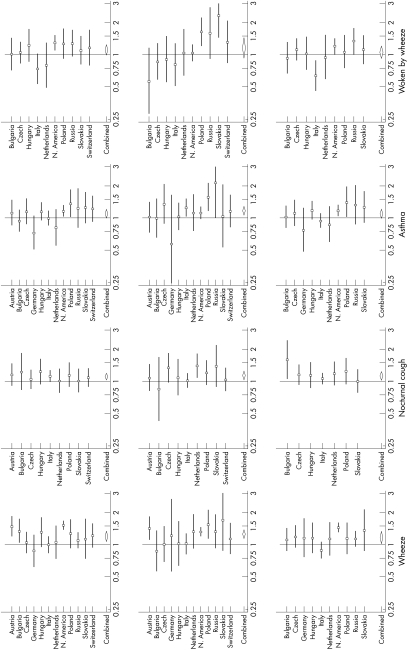
Figure 1 Forest plots of study‐specific odds ratios, and mean odds ratios, for effects of “current smoker” (top row), “smoking during pregnancy” (middle row) and “smoking during first two years of life” (bottom row), on wheeze, nocturnal cough, asthma, and woken by wheeze. Odds ratios are not mutually adjusted, but adjusted for all other potential confounders listed above. Vertical line indicates null position (odds ratio of 1). Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals. Diamond shapes indicates the positions, and confidence intervals, of the mean estimates. Extreme confidence intervals are truncated at 0.25 and 3.0.
Table 3 Mean odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for associations between smoking exposures and each outcome.
| Outcome | Exposure to: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current smoking | Smoking in pregnancy | Smoking in first 2 years | ||||
| Confounder adjusted | Fully adjusted | Confounder adjusted | Fully adjusted | Confounder adjusted | Fully adjusted | |
| Wheeze | 1.20 (1.06 to 1.35)H ** | 1.12 (0.98 to 1.27)H | 1.25 (1.14 to 1.37)** | 1.12 (1.04 to 1.22)** | 1.17 (1.02 to 1.33)H* | 1.06 (0.95 to 1.19) |
| Asthma | 1.09 (1.01 to 1.19)* | 1.03 (0.95 to 1.12) | 1.18 (1.08 to 1.28)** | 1.17 (1.04 to 1.31)* | 1.10 (1.00 to 1.21)* | 1.04 (0.95 to 1.14) |
| Bronchitis | 1.11 (1.05 to 1.18)** | 1.10 (1.03 to 1.19)** | 1.03 (0.92 to 1.16)H | 0.98 (0.86 to 1.11)H | 1.08 (1.02 to 1.14)* | 1.03 (0.94 to 1.12) |
| Nocturnal dry cough | 1.11 (1.03 to 1.19)** | 1.05 (0.94 to 1.17) | 1.13 (1.03 to 1.24)** | 1.15 (1.00 to 1.32) | 1.11 (1.03 to 1.21)** | 1.05 (0.94 to 1.18) |
| Morning cough | 1.07 (0.98 to 1.16) | 1.04 (0.95 to 1.13) | 1.12 (0.97 to 1.30)H | 1.14 (0.94 to 1.39)H | 1.12 (0.99 to 1.27)H | 1.09 (0.96 to 1.25)H |
| Sensitivity to inhaled allergens | 0.96 (0.91 to 1.02) | 0.96 (0.88 to 1.04) | 0.98 (0.91 to 1.05) | 0.98 (0.91 to 1.07) | 1.02 (0.94 to 1.12)H | 1.06 (0.94 to 1.20)H |
| Hay fever | 0.92 (0.81 to 1.04) | 0.99 (0.81 to 1.20)H | 0.87 (0.79 to 0.96)** | 0.89 (0.80 to 1.00)* | 0.91 (0.83 to 0.98)* | 0.97 (0.87 to 1.07) |
| Woken by wheeze | 1.12 (0.99 to 1.25) | 1.16 (1.03 to 1.30)** | 1.15 (0.93 to 1.43)H | 1.13 (0.88 to 1.45)H | 1.04 (0.91 to 1.20)H | 0.98 (0.85 to 1.12) |
*p<0.05 **p<0.01.
Differences between estimates from the two models may include the loss of up to two studies when adjusting for smoking during the first two years of life.
HHeterogeneity between study specific results (p<0.10).
Odds ratios are from confounder adjusted models, and from fully adjusted (for previous covariates plus both other smoking variables).
There was evidence of heterogeneity (within a strong predominance of positive results) among results for both current smoking and smoking during the first two years. Mean odds of nocturnal cough were raised by around 12% for all three smoking variables, with no evidence of heterogeneity.
Asthma was clearly related to smoking during pregnancy, with a mean odds ratio of 1.18 (95% CI 1.08 to 1.28). Odds ratios for the other periods of exposure were also above one in nine of the 12 countries, with no evidence of heterogeneity.
Associations between current smoking and “woken by wheeze” were predominantly positive, with a mean odds ratio of 1.12 (95% CI 0.99 to 1.25). For the other two smoking measures results were less clear—mean associations were positive, but with considerable heterogeneity.
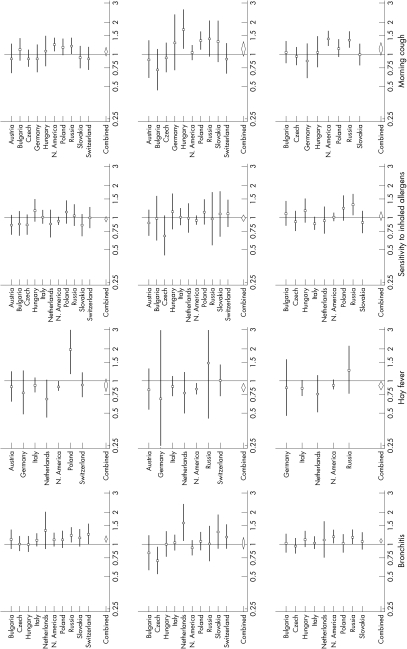
Bronchitis was related to current smoking, and to smoking during the first two years, with mean odds ratios of about 1.10 (fig 2). Associations of bronchitis with smoking during pregnancy were heterogeneous, within no clear pattern.
Figure 2 Forest plots of study‐specific odds ratios, and mean odds ratios, for the effects of “current smoker” (top row), “smoking during pregnancy” (middle row), and “smoking during first two years of life” (bottom row), on bronchitis, hay fever, sensitivity to inhaled allergens, and morning cough.
For all three exposures, effect estimates for hay fever were predominantly negative, with Russia the main exception (fig 2). Mean odds ratios for both the effect of smoking during the first two years and of smoking during pregnancy were around 0.90. The Russian estimate for current smoking was large, giving rise to some between study heterogeneity (p = 0.10).
Effect estimates of current smoking on “sensitivity to inhaled allergens” showed some apparently protective effect, with mean odds ratio of 0.96 (95% CI 0.91 to 1.02). For smoking during pregnancy, and smoking during the first two years, estimates tended to be small and mean odds ratios essentially null.
Mean effect estimates for morning cough were positive for all exposures, up to 1.12 (95% CI 0.99 to 1.27) for smoking during the first two years, but with heterogeneity between studies within unclear patterns of association.
Few consistent associations were seen between study specific results and potential sources of heterogeneity tested, and differences between groups of studies were generally small. Odds ratios tended to be inversely related to the proportion of younger children in the study. For smoking during pregnancy, estimates were higher in the later studies for most outcomes, and also in the studies with lower response rates (categorisations which overlapped considerably).
Independent effects of the exposure periods
For most of the outcomes strongly associated with smoking during pregnancy (wheeze, asthma, hay fever), associations remained robust to all adjustments. For nocturnal cough, the association became of borderline statistical significance. Mean, fully‐adjusted odds ratios were 0.89 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.00) for hay fever, and around 1.15 for these other four outcomes (table 3).
Of those outcomes most strongly associated with smoking during the first two years of life (wheeze, asthma, bronchitis, nocturnal cough, hay fever), associations with bronchitis, wheeze and nocturnal cough were independent of smoking during pregnancy (data not shown), but were weakened in the fully adjusted model.
For current smoking, associations with bronchitis and “woken by wheeze” remained robust after all adjustments (table 3). Those for wheeze and nocturnal cough were independent of smoking during pregnancy (data not shown), and odds ratios remained raised after all adjustments, albeit not statistically significant. The mean odds ratio for asthma was considerably reduced by these adjustments.
Sensitivity analyses
There was no consistent effect modification by age within the individual studies.
In more crowded households than less crowded ones mean effects were greater for wheeze, bronchitis, and both coughs, but lower for asthma and sensitivity to inhaled allergens. The strongest interaction was found for morning cough: a mean odds ratio 17% higher (95% CI −1% to 39%) in crowded households than in less crowded ones.
In those studies for which parental illness data were available, parental allergy did not confound associations between child's “sensitivity to inhaled allergens” and parental smoking, nor parental lung disease for nocturnal cough, nor parental asthma for child's asthma. For hay fever, some odds ratios changed a little towards the null on adjusting for parental allergy, and similarly for bronchitis and morning cough, on adjusting for parental lung disease (data not shown). Neither attendance at kindergarten nor breastfeeding had any confounding effect.
Child's sex was not a strong modifier of effects of maternal smoking in pregnancy. Contrary to Alati's findings,31 the mean odds ratio for asthma was higher in boys: 1.24 (95% CI 1.12 to 1.38) versus 1.10 (95% CI 0.95 to 1.27) in girls. However, outcome‐ and country‐specific interactions were generally small and varied in direction. There was little evidence of breastfeeding modifying the effect of either postnatal exposure, particularly for smoking in the first two years of life. For current exposure, the strongest evidence was seen for wheeze where, in six of nine countries, stronger effects of exposure were seen among children who were breastfed (the great majority of the children) than in those who were not. (This pattern was little changed by controlling for other smoking measures, or the interaction between breastfeeding and smoking in the first two years of life.) The interaction was statistically significant in Bulgaria and Germany, and the mean of the nine interaction terms was also statistically significant. In the German dataset, the existing, apparently protective effect became more pronounced among children not breastfed, with a null effect among breastfed children. We tested these results by restricting the analysis to children who were breastfed, and testing for a trend in environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) effect across length of breastfeeding. The resulting interaction terms bore no correspondence to the interactions seen with the yes/no breastfeeding variable.
DISCUSSION
Adverse effects of parental smoking were seen with considerable consistency for several health outcomes, in particular asthma, wheeze, bronchitis, and nocturnal cough. By contrast, negative effects predominated for hay fever, though results were available for fewer studies, and based on fewer cases.
Correlations between exposures hamper efforts to distinguish between their effects. But generally, odds ratios for our three exposure periods remained raised (if with reduced statistical significance) after mutual adjustment, demonstrating some independence of effect. Maternal smoking during pregnancy showed independent effects particularly on wheeze, asthma, nocturnal cough and (inversely) hay fever. Distinguishing between effects of early‐life and current exposure proved harder. But estimated effects of postnatal exposure on wheeze, bronchitis and nocturnal cough were independent of smoking during pregnancy.
Smoking in pregnancy has been linked to low birth weight, which in turn is linked to later morbidity.1,4,32 Details of possible harmful mechanisms of smoking during pregnancy have been discussed elsewhere, including alterations in the pulmonary neuroendocrine system, reduced lung volume, reduced number of lung saccules, and reduced length of elastin fibres in the lung interstitium, resulting in a loss of lung elasticity.1,33,34
If respiratory diseases of children or parents lead to smoking cessation, this may result in underestimation of effects of tobacco smoke in cross‐sectional studies and could even cause inverse swings in observed associations (the “healthy smoker” effect). Observed effects would combine real exposure effects and inverse behavioural effects and, for outcomes where true effects are small, behavioural effects could predominate. Observed negative associations between smoking and hay fever could be related to these behavioural effects, rather than to some true protective effect. For asthma and respiratory symptoms behavioural effects have to be assumed as well; however, the adverse effects of tobacco smoke on these outcomes seems to be much larger and therefore are not masked by behavioural effects.
We rely on parents' questionnaire answers, both for exposure and outcome. Prevalences of smoking in pregnancy were noticeably low in Russia and (apart from Poland) Eastern Europe, and we do not have external data by which to check this, though the consistency across these Eastern countries gives some reassurance. Smokers misclassifying themselves as non‐smoking would probably cause underestimation of effects (unless parents of healthy children misclassified themselves more). Since all studies were explicitly focused on outdoor air pollution, self‐misclassifications may have been few. There is evidence of reasonable validity of parental responses on smoking, and validation studies carried out in several countries have found a strong correlation between passive smoking exposure in children assessed by measuring the level of urinary cotinine and the amount of parental self‐report smoking.1,21 However, parental smokers under‐report cough, and among children with asthmatic symptoms, smokers' children are less likely to be diagnosed asthmatic than non‐smokers' children.35,36 Such outcome misclassifications would also tend to cause underestimation of effects.
The relative importance of pre‐ and postnatal exposure is under debate. We were concerned whether our blunt yes/no exposure measures were adequate in teasing apart the effects of different periods. “Maternal smoking in pregnancy”, for example, may be thought partly to represent residual effects of heavy current smoking. For three primary outcomes (asthma, wheeze and bronchitis) we repeated analyses for the effects of smoking during pregnancy among the subset of children with no current exposure, and likewise for the effects of current smoking, in children whose mothers did not smoke in pregnancy. All six analyses showed clear adverse effects (data not shown). We were reassured about interpreting our primary results, guided by consistency and relative strength of evidence seen for effects of exposures at different periods. Recent studies—for example, Kharrazi et al37—have found harmful effects on the children of the mother's passive smoking during pregnancy. This exposure was not assessed in most of the PATY studies and could not be analysed here. Evidence that breastfeeding might modify the effect of exposure was tenuous. There was not a clear dose–response relationship, suggesting that the variable might only be an indicator for something else, or that apparent modifications were chance findings.
Selected outcomes had similar questionnaire wordings across studies, except for asthma, where, for example, some referred to the doctor's diagnosis, others did not.23 Study specific results proved independent of reference to diagnosis (data not shown). Lack of power prevented comparisons across other wording differences. We note that, even given identical wordings, interpretation and diagnosis of “asthma” may vary between, even within, studies.38
Cross‐sectional studies have limitations, but can access far more individuals than is usually feasible in cohort studies. Evidence on independent effects of pre‐ and postnatal passive smoking from cohort studies is sparse. A recent Norwegian cohort study was the first to show that prenatal and postnatal passive smoking induce lasting vulnerability for developing asthma or respiratory symptoms in adults (significant for exposure to maternal smoking, but not that of other household members).39 Independent effects of prenatal smoking remained difficult to assess in this cohort because of small numbers.
In conclusion, the large cross‐sectional dataset of the PATY study allowed us to assess independent effects of exposures to passive smoking at different times of a child's life, which had been proven difficult in earlier studies.40 The results confirm long‐lasting harmful effects of smoking during pregnancy, and, independently, of smoking later in the child's life. Average, conservative effect estimates at school age were not large, but exposures (particularly postnatal) were widespread. The public health consequence for our populations of children—and our future populations of adults—remains a serious one.
What this paper adds
Many studies have linked parental smoking to respiratory disease in children, but most of them have lacked the power to demonstrate independent effects of intrauterine and postnatal passive smoking at school age.
This pooled analysis finds long‐lasting effects of maternal smoking during pregnancy on wheeze, asthma, and nocturnal cough, independent of postnatal exposure. Independent of smoking during pregnancy, bronchitis, wheeze and nocturnal cough are associated with postnatal exposure.
Acknowledgements
We thank all who took part, in whatever role, in the original studies. Professor Bojidar Nikiforov, who initially led this work, died before its completion. Той е винаги в нашите сьрца.
Footnotes
Funding: The PATY study was funded by the EU 5th Framework Quality of Life Program (proposal no. QLRT‐2001‐02544). Details of funding of component studies were given with their publications.
There are no competing interests of the authors, as defined in BMJ 1998;317:291–2.
References
- 1.US Environmental Protection Agency Respiratory health effects of passive smoking. Washington, DC, 1992. Publication No EPA/600/6‐90/006F
- 2.Cook D G, Strachan D P. Summary of effects of parental smoking on the respiratory health of children and implications for research. Thorax 199954357–366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.International Agency for Research on Cancer Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. Summary of data reported and evaluation, 2002, Volume 83. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol83/volume83.pdf
- 4.California Environmental Protection Agency Proposed identification of Environmental Tobacco Smoke as a Toxic Air Contaminant. Part B – Health assessment. Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment 2004. http://www.arb.ca.gov/toxics/ets/finalreport/finalreport.htm
- 5.Cunningham J, O'Connor G T, Dockery D W.et al Environmental tocacco smoke, wheezing and asthma in children in 24 communities. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996153218–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ehrlich R I, DuToit D, Jordaan E.et al Risk factors for childood asthma and wheezing: importance of maternal and household smoking. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996154681–688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Strachan D P, Cook D G. Health effects of passive smoking: 6. Parental smoking and childhood asthma: longitudinal and case‐control studies. Thorax 199853204–212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gold D R, Burge H A, Carey V.et al Predictors of repeated wheeze in the first year of life: the relative roles of cockroach, birth weight, acute lower respiratory illness, and maternal smoking. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999160227–236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gilliand F, Li Y F, Peters J. Effect of maternal smoking during pregnancy and environmental tobacco smoke on asthma and wheezing in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001163429–436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Agabiti N, Mallone S, Forastiere F.et al The impact of parental smoking on asthma and wheezing. Epidemiology 199910692–698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jedrychowski W, Flak E. Maternal smoking during pregnancy and postnatal exposure to environmental tobacco smoke as predisposition factors to acute respiratory infections. Environ Health Perspect 1997105302–306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hu F B, Persky V, Flay B R.et al Prevalence of asthma and wheezing in public schoolchildren: association with maternal smoking during pregnancy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 19977980–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Butland B K, Strachan D P, Lewis S.et al Investigation into the increase in hay fever and eczema at age 16 observed between the 1958 and 1970 British birth cohorts. BMJ 1997315717–721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Olesen A B, Ellingsen A R, Olesen H.et al Atopic dermatitis and birth factors: historical follow up by record linkage. BMJ 19973141003–1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lam T H, Chung S F, Betson C L.et al Respiratory symptoms due to active and passive smoking in junior secondary school students in Hong Kong. Int J Epidemiol 19982741–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ronmark E, Lundback B, Jonsson E.et al Asthma, type‐1 allergy and related conditions in 7‐ and 8‐year old children in northern Sweden: prevalence rates and risk factor pattern. Respir Med 199892316–324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Norman E, Rosenhall L, Nystrom L.et al Prevalence of positive skin prick tests, allergic asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis in teenagers in northern Sweden. Allergy 199449808–815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Selcuk Z T, Caglar T, Enunlu T.et al The prevalence of allergic diseases in primary school children in Edirne, Turkey. Clin Exp Allergy 199727262–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rudnai P, Virágh Z, Varró M J.et al Epidemiological studies directed towards reducing adverse health effects of the residential environment in Hungary. Egészségtudomány 200448173–182. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hajnala L B, Braun‐Fahrländer C, Grize L.et al Effect of environmental tobacco smoke exposure on respiratory symptoms in children. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1999129723–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jaakkola J J, Kosheleva A A, Katsnelson B A.et al Prenatal and postnatal tobacco smoke exposure and respiratory health in Russian children. Respir Res 2006748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Moshammer H, Hoek G, Luttmann‐Gibson H.et al Parental smoking and lung function in children: an international study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 20061731255–1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gehring U, Pattenden S, Slachtova H.et al Parental education and children's respiratory and allergic symptoms in the PATY study. Eur Respir J 20062795–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leonardi G S, Houthuijs D, Nikiforov B.et al Respiratory symptoms, bronchitis and asthma in children of Central Europe. Eur Respir J 200220890–898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Neuberger M, Moshammer H, Kundi M. Declining ambient air pollution and lung function improvement in Austrian children. Atmospheric Environment 2002361733–1736. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Heinrich J, Hölscher B, Wjst M.et al Respiratory diseases and allergies in two polluted areas in East Germany. Environ Health Persp 199910753–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Janssen N A H, Brunekreef B, van Vliet P.et al The relationship between air pollution from heavy traffic and allergic sensitisation, bronchial hyperresponsiveness and respiratory symptoms in Dutch school children. Environ Health Perspect 20031111512–1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Spengler J D, Jaakkola J J K, Parise H.et al Housing characteristics and children's respiratory health in the Russian Federation. Am J Public Health 200494657–662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dockery D W, Cunningham J, Damokosh A I.et al Health effects of acid aerosols on North American children: respiratory symptoms. Environ Health Perspect 1996104500–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 19867177–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Alati R, Al Mamun A, O'Callaghan M.et al In utero and postnatal maternal smoking and asthma in adolescence. Epidemiology 200617138–144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Misra D P, Nguyen R H. Environmental tobacco smoke and low birth weight: a hazard in the workplace? Environ Health Perspect 1999107(suppl 6)897–904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dempsey D A, Benowitz N L. Risks and benefits of nicotine to aid smoking cessation in pregnancy. Drug Saf 200124277–322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dell'Orco V, Forastiere F, Agabiti N.et al Household and community determinants of exposure to involuntary smoking: a study of urinary cotinine in children and adolescents. Am J Epidemiol 1995142419–427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dales R E, White J, Bhumgara C.et al Parental reporting of childrens' coughing is biased. Eur J Epidemiol 199713541–545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Siersted H C. Factors associated with undiagnosed asthma in schoolchildren. Eur Respir Rev 200010411–412. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kharrazi M, DeLorenze G N, Kaufman F L.et al Environmental tobacco smoke and pregnancy outcome. Epidemiology 200415660–670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Asher M I, Keil U, Anderson H R.et al International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC): rationale and methods. Eur Respir J 19958483–491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Skorge T D, Eagan T M, Eide G E.et al The adult incidence of asthma and respiratory symptoms by passive smoking in utero or in childhood. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 200517261–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stocks J, Dezateux C. The effect of parental smoking on lung function and development during infancy. Respirology 20038266–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]