Abstract
Background
After a recent report on the role of the Ipr1 gene in mediating innate immunity in a mouse model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, the human Ipr1 homologue, Sp110, was considered a promising candidate for an association study in human tuberculosis.
Methods
In a sample of >1000 sputum positive, HIV negative West African patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and >1000 exposed, apparently healthy controls, we have genotyped 21 Sp110 gene variants that were either available from public databases, including HapMap data, or identified by DNA re‐sequencing.
Results
No significant differences in the frequencies of any of the 21 variants were observed between patients and controls. This applied also for HapMap tagging variants and the corresponding haplotypes, when including sliding window analyses with three adjacent variants, and when stratifying controls for positivity and negativity according to the results of intradermal tuberculin (purified protein derivative, PPD) skin tests. DNA re‐sequencing revealed 13 novel Sp110 variants in the 5′‐UTR, exons, and adjacent intronic regions.
Conclusions
Based on the results obtained in this case‐control study, the hypothesis that Sp110 variants and haplotypes might be associated with distinct phenotypes of human M tuberculosis infection is doubtful.
Keywords: innate resistance, interferon‐inducible gene, PPD, purified protein derivative
Susceptibility to tuberculosis has been known for years to be strongly influenced by human genetic factors. However, only a few distinct genetic variants so far have been reported to be associated with susceptibility or resistance to the disease, and these variants have been found to exert moderate effects only.1
Recently, the mouse gene Ipr1 (intracellular pathogen resistance‐1) on the locus sst1 (super‐susceptibility to tuberculosis 1) has been shown to essentially contribute to innate immunity in a murine model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.2 Upregulation of Ipr1 after infection occurs in macrophages from sst1 resistant mice, but not in those from susceptible mice, and expression of an Ipr1 transgene construct in macrophages from susceptible animals resulted in the control of mycobacterial replication and eventually induced death of infected cells. Thus, Ipr1 might play an important role in preventing tuberculosis by mediating control of M tuberculosis within its prime target cell, the macrophage.
The human homologue of Ipr1 is Sp110 (51 037 bp on 2q37.1; MIM 604457).3 The corresponding protein, SP110 (nuclear body protein SP110; also known as transcriptional coactivator SP110 or interferon induced protein 41/75), shows 41% identity to the murine protein encoded by Ipr1. Three transcripts designated Sp110a, ‐b, and ‐c have been identified and contain 18, 15, and 19 exons, respectively. The first exon of all transcripts is invariably untranslated. Exons 15a and 15b define the alternate transcripts Sp110a and Sp110b, and Sp110c contains exon 15a and an additional short exon 17.
SP110 is a component of the nuclear body, a multi‐protein complex assumed to participate in the regulation of gene transcription. SP110 has considerable homology with the nuclear body proteins SP100 and SP140. After induction by interferon‐α and interferon‐γ, SP110 is preferentially expressed in leukocytes and spleen cells, but also at lower levels in many other tissues.3,4
SP110 proteins contain structural motifs which suggest participation in protein‐protein interactions, such as the N‐terminal SP100‐like domain.5,6 The conserved SAND domain (Sp100, AIRE‐1, NucP41/75, and DEAF‐1/suppressin) is most likely involved in transcriptional regulation through DNA binding.7,8 In addition, the proteins are characterised by nuclear localisation signal sequences and the nuclear receptor binding motif LXXLL (leucine/any two amino acids/leucine/leucine). SP110a differs from SP110b in exhibiting a C‐terminal bromodomain that enhances transcription of genes with retinoic acid response elements.3,9 The absence of the bromodomain in SP110b is thought to cause suppression of transcription of these genes.
A number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been identified in the Sp110 gene (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db = snp). Several of the variants have been claimed to be associated with distinct clinical phenotypes of hepatitis C.10 Furthermore, SP110b has been reported to interact with hepatitis C core and Epstein‐Barr virus SM proteins.9,11
If Ipr1 is essential in the control of M tuberculosis and of apoptosis of infected cells in mice, Sp110 might also be relevant to the course of human M tuberculosis infection. Therefore, we have tested whether variants of Sp110 are associated with susceptibility or resistance to human tuberculosis. Since the individual reactivity to intradermal purified protein derivative (tuberculin, PPD) M tuberculosis antigens reflects the extent of the T cell immune response and is grouped into PPD positivity and PPD negativity, the control group of our association study was stratified according to the different sizes of the skin reaction measured after tuberculin application.
Methods
Patients and controls
Study subjects were recruited in Ghana, West Africa, between September 2001 and July 2004. Patients were enrolled at Korle Bu Teaching Hospital, Accra, Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital, Kumasi, 15 additional hospitals or polyclinics in Accra and Kumasi, at the district hospitals of Obuasi, Agona, Mampong, Agogo, Konongo, and Nkawie (Ashanti Region), Nkawkaw and Atibie (Eastern Region), and Assin Fosu and Dunkwa (Central Region).
In a first step, 3128 patients with smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis were recruited. Symptoms including cough, haemoptysis, shortness of breath, chest pain, night sweats, fever, and weight loss were documented on structured questionnaires. Clinical and laboratory assessments included a physical examination, chest x ray, two sputum smears stained by the modified Ziehl/Neelsen staining technique, a culture of M tuberculosis on Löwenstein‐Jensen medium, and HIV‐1 and ‐2 testing (Capillus, Trinity Biotech, Bray, Co Wicklow, Ireland). All patients were treated in the framework of the DOTS programme (Directly Observed Treatment Short‐course strategy) organised by the National Tuberculosis Programme (NTP) of Ghana. A total of 1124 patients were excluded for the following reasons: HIV positivity (n = 490); lost to follow up (n = 74); refusal after enrolment (n = 33); deceased during the enrolment procedure (n = 33); age >60 not consistent with the age of 6–60 as specified in the study design (n = 25); evidence of alcoholism (n = 10), drug addiction (n = 7), or diabetes (n = 2); and various other reasons, mostly inappropriateness for matching with controls for sex and age, ambiguous bacteriological results, and incomplete documentation (n = 450). The final group of patients available for analyses comprised 2004 individuals.
For the recruitment of control groups, mobile teams enrolled 1715 unrelated personal contacts of patients and 2283 community members from neighbouring houses of patients and at public assemblies. Characterisation of participants included a medical history, clinical examination, chest x ray, and a tuberculin skin test (Tuberculin Test PPD Mérieux, bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany). According to the manufacturer's recommendations, the PPD test was considered positive if an induration of >1 mm was recorded between day 3 and 7 after inoculation. However, in a previous study comparing the Tuberculin Test PPD Mérieux with the Mendel‐Mantoux tuberculin test, skin indurations of 2 and 3 mm could not unambiguously be attributed to the individual PPD status.12 Another study proposed that reactions ⩾4 mm should be considered positive when tuberculosis was suspected and reactions ⩾8 mm highly specific.13 Accordingly, we have applied different thresholds of PPD positivity in the control group and performed statistical calculations with PPD positivity defined by skin indurations of ⩾2, ⩾4, and ⩾8 mm.
A total of 1632 controls were excluded for the following reasons: signs of actual or previous tuberculosis on chest x ray (n = 367); age not consistent with the age specified in the study design (n = 16); lost to follow up (n = 20); refusal after enrolment (n = 10); and ambiguous medical history as regards previous tuberculosis, incomplete documentation, or inappropriateness for matching with patients for sex and age (n = 1081). In addition, 138 PPD negative community controls below the age of 35 years were excluded to restrict the sample to persons with an increased probability of exposure to M tuberculosis transmission. The final control group consisted of 1231 unrelated personal contacts and 1135 community controls.
When considering a skin reaction >1 mm as PPD positivity, the male to female ratio was 1/0.5 in the patient group, 1/0.7 in the group of PPD positive controls, and 1/1.3 in the group of PPD negative controls. The mean age in the three groups was 34.1, 32.4, and 34.2 years, respectively. The study participants belonged to the following ethnic groups (patients/all controls/PPD positive controls/PPD negative controls): Akan including Ashanti, Fante, Akuapem (64.0%/59.3%/58.4%/75.2%); Ga‐Adangbe (14.6%/19.7%/20.4%/7.0%); Ewe (7.2%/9.3%/9.6%/3.9%); and ethnic groups of northern Ghana, including Mole Dagbane, Gurma, and Grusi (12.4%/10.4%/10.3%/12.4%). For 1.5% of study participants ethnicity was not clearly assignable. The final control group comprised 1117 PPD positive personal contacts, 1120 PPD positive community controls, 114 PPD negative personal contacts, and 15 PPD negative community controls.
The study protocol was approved by the Committee on Human Research, Publications and Ethics, School of Medical Sciences, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, and the Ethics Committee of the Ghana Health Services, Accra, Ghana. Samples were taken only after detailed explanation of the aims of the study, and consent was obtained by signature or thumb print.
Genetic analyses
The genomic reference sequence for Sp110 was AC009950.6 (MIM 604457; NCBI RefSeq database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq/). To supplement the design of SNP genotyping in addition to SNPs available from public databases, 1316 bp of the Sp110 5′‐UTR and the 18 transcribed exons of Sp110a, including the alternate exon 15 of the splice variant Sp110b and flanking intronic segments, were amplified from the genomic DNA of 12 patients and six PPD positive and six PPD negative control individuals. Amplicons were re‐sequenced unidirectionally on an ABI 3100 sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and sequences were aligned to the Sp110 consensus sequence AC009950.6. Alleles identified by DNA sequencing once only were confirmed in repeated independent PCR and sequencing reactions. All other alleles were found in more than one individual or confirmed by genotyping. Primer pairs and PCR conditions for DNA re‐sequencing are given in table 1.
Table 1 PCR primer pairs for DNA sequencing of the Sp110 gene.
| Localisation | Forward primer | Reverse primer | Size (bp) | °C/MgCl2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5′ | Exon | 3′ | ||||
| 5′‐UTR3/4* | TCCCTGTAAACAGTTGTTAATTACG | GTTGCACAACTAGAGAGTGGAAGAG | 545 | 62/1.5 | ||
| 5′‐UTR1/2* | CTTGTTTAACCCAGATCAGTGTGG | GTTGCAGTAAGCCAAGATTGTG | 547 | 62/1.0 | ||
| Exon 2 | CAGAGAGAAGCTTCCCACATTC | TATGACACCCTCTCTCCTAACTAC | 356 | 147 | 139 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 3 | GAATTTCTTCTTAAAAGAGTAAGGTAGC | GATTAACGTGCATATTCCACAGG | 86 | 169 | 71 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 4 | ATCCTATTGGAAGGCATGTATTAAG | ATAAAAGTCAAGATGCTGGGATTG | 66 | 267 | 66 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 5 | TTGTGCCTTGATGCTCTATCTG | TCTGTTTCTTTTCCTTTGTATTGC | 79 | 84 | 107 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 6 | GTTGCTTACTTTCCCACTCTATGC | CTCTCTAGAAGATCCGAATGGC | 131 | 84 | 61 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 7 | CTGGGCTGCATGTACTTTCTAC | AGGACTGTGGTCACATAGTGGTG | 84 | 78 | 83 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 8 | CTAAGGTCACCAATGAACTTCTAGC | TAGAATAAAATTCAACCCTCCACAG | 99 | 69 | 65 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 9 | GAGAAGGGAAGTCACTGATTGG | GTTATACCCCATCCTCATTCTCTG | 62 | 150 | 112 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 10 | ATGCATTGTTAGGAGGGTAAGACC | GTTAAGAAATATTGCCTCAGTGTAAG | 109 | 81 | 61 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 11 | ATGGCAAGATAACTCCTGAAAGG | GTACGTCTCCCTCCTTCTACTATTG | 61 | 150 | 88 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 12 | TGCTACAAGGAAGTCCTTTCATAAG | GAGAACAACTTTGGAGGAGAAGG | 125 | 69 | 92 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 13 | GTACATTATTGGAATTCATGGAGGG | GTCCATTTCCTGATCAATTACACAC | 64 | 99 | 72 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 14 | GTAGAAGGCCACAATTAGGATGAAG | TCCTTATAAATCATGCTGTTGAATC | 60 | 143 | 92 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 15a† | CAGACTCTCTGCTTGTTGTGCC | TCCAGGGAATAGCATACTAGGAAAG | 169 | 116 | 189 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 15b† | ATCTAGAGAGGGAGAAATGGAAGG | ATCCTCCTACCTCAGCCTTAGC | 263 | 251 | 162 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 16 | TTGTCACACATTTCACCATAGTCTC | CCAGTCAGCATTCCAGCCATGC | 343 | 109 | 180 | 58/1.5 |
| Exon 17 | TATCATTATGACCCTGGAAATGAAG | GGCTGAAACTGAGTGTAATACTTGC | 79 | 141 | 71 | 62/1.5 |
| Exon 18 | ATGTGCCTGTAGTTTCAGCTTCTC | GTGATAATCCTATGAAGTGTCTGGG | 195 | 114 | 116 | 58/1.0 |
*5′‐UTR1/2 and 5′‐UTR3/4 are primer pairs to amplify 1092 bp of the 5′‐UTR proximal to the ATG; †primers for exons 15a and 15b are designed to amplify the alternative transcripts Sp110a and Sp110b, respectively.
AC009950.6 is the reference sequence for the design of all sequencing reactions and subsequent alignments. All primers anneal to 5′‐ and 3′ intronic regions of exons. Sequencing of exon 18 comprises 116 bp of the 3′‐UTR.
Variants selected for genotyping
A total of 21 SNPs were included in genotyping. Thirteen Sp110 variants, covering 5′‐UTR and exonic regions and one intronic variant, were selected on the basis of information provided by public databases (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db = snp) and re‐sequencing results, following reasonable inclusion criteria. All non‐synonymous exonic variants and variants suggestive of differences in frequencies between patients and the control groups of PPD positive and PPD negative individuals were included. In addition, SNPs in regions with binding sites for transcription factors as predicted by an in silico matrix search for transcription factor binding sites (Match, Gesellschaft für Biotechnik‐Forschung, Braunschweig, Germany; http://www.gene‐regulation.com/pub/programs/match/; after free registration) were tested. This applied to the 5′‐UTR variants g.2302C>T (at −745 of the ATG) (core match 0.996, matrix match 0.881), g.2755A>G (at −292 of the ATG) (core match 0.952, matrix match 0.785), and the newly identified variant g.3009C>A (at −38 of the ATG) (core match 1.0, matrix match 0.767). In order to capture common haplotypes segregating in the study population and to assess relevant haplotype related risks, out of 24 Sp110 SNPs occurring at allele frequencies of ⩾0.1 provided by the International HapMap Project (http://www.hapmap.org) for the West African Yoruba ethnic group, 10 tagging SNPs were additionally selected by the binning algorithm of LDSelect software (http://droog.gs.washington.edu/ldSelect.pl) at r2 thresholds of 0.5 and minor allele frequencies of 0.1.14 LDSelect analyses LD patterns between polymorphic sites in a locus, and bins SNPs with predefinable threshold levels. Two of the 10 tagging SNPs also met the aforementioned selection criterion of including non‐synonymous variants, resulting in the total of 21 variants to be genotyped.
SNPs were analysed by dynamic allele specific hybridisation with fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) in a LightTyper device (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Primer pairs and sensor/anchor oligonucleotides for Sp110 genotyping are listed in table 2.
Table 2 Primer pairs and sensor/anchor oligonucleotides for LightTyper based Sp110 genotyping.
| Localisation | Primer oligonucleotides | Sensor/anchor oligonucleotides |
|---|---|---|
| 5′‐UTR g.394C>T (at −2653 of the ATG) rs6756352 | f‐CCGAGATTTGCCCTCTAC | s‐CGGCTCATCTGCTATCCATTGTG |
| r‐GTTCATGATACACTAGAGACGAAATTA | a‐AAATGACTAGAGGTACTTGGGAAGCTGGTGGAAA | |
| 5′‐UTR g.2302C>T (at −745 of the ATG) | f‐TTAATGGCTTCAGCCGTAG | s‐ACTCTCTAGTTGTGCAACCCTGG |
| r‐ATACTGTTGAGGAACTGAGAC | a‐GTAAGCCTGGAATCAGGATTTGCTCCCAGCTCTTC | |
| 5′‐UTR g.2755A>G (at −292 of the ATG) rs1966555 | f‐GAGAGAAGCTTCCCACAT | s‐CAGCCTGGGTGACAGAGTGAGA |
| r‐CTGAGGCGGGAAAATTG | a‐CAGTAAGCCAAGATTGTGCCACTGCACT | |
| 5′‐UTR g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG) | f‐CTTACCTTTAGATCTGCCCATT | s‐CCACCTCCCCGGTTCAAG |
| r‐TCTTGTCATGGTGAACATCCTAT | a‐AATTTTCCCGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAGTA | |
| 5′‐UTR g.3009C>A (at −38 of the ATG) | f‐CCAGGATGGTCTCAATCTC | s‐GCCCAGCCTTTGCTTCTATTTTTTATCATG |
| r‐TGCATGAAGTGCTGAAAAAG | a‐CTCTTTCCATAGGATGTTCACCATGACAAGAGCCA | |
| In2 g.3305 ex2+112C>T rs7580900 | f‐CCACCAATATGCCTGATTATTAAAG | s‐GAGTGGGCTTCCAAGAAATGCATTTACAAA |
| r‐GAGATAGGCAGCTATCGGA | a‐GTAGTCCTGGAGAACAGAGGGTCATCCTTCCTCAG | |
| Ex4 g.7013C>T [p.Val128Ala] rs11556887 | f‐AATGGCAGAGCAGAGAC | s‐TAGCAGAAGGAAGCTCCCTCCA |
| r‐TTCCAGGCTCACTGACT | a‐ACCCCACTGGCGCTGCC | |
| Ex5 g.7577C>T [p.Ala206Val] | f‐CATCCAGTCCCTGCAATC | s‐TGAATGCGGAAGAAGACTCAGAAGAGAT |
| Ex5 g.7579 A>G [p.Lys207Glu] rs11556888 | r‐GTCACCTTGAGCTAAGCG | a‐CCCAGCCTCCTCACTAGCACTGTGC |
| In5 g.8400 ex6–21G>T rs3820974 | f‐TCCCACTCTATGCCATCC | s‐TCCTGAGATCTAAACCTTTTTCTTCCTCC |
| r‐GTTGTCACTGGCCACTG | a‐TTCTCTTTTCTCCTCATTCTGGTCCCTGCTTGCTG | |
| Ex8 g.11980G>A [p.Gly299Arg] rs1365776 | f‐GATGTATCTGGTCAACTCCAAA | s‐TTGTACTCTCATCTTACCTCCTGGG |
| r‐CATTGTGTCACTTCACTGACTAA | a‐CTGTTTCCAGCCTCCAGCTTCCT | |
| In8 g.12828 ex8+845C>T rs10167116 | f‐GATGTAGAATGATGGATTTTTCTGTTTAG | s‐AGCAGCAAAGCTTTTTCTTTTCCTTT |
| r‐GGGTAAAGCCCAGAACTTG | a‐AGGAGGAAAGGATGATGGCTATCCCTCTCATGTAT | |
| Ex9 g17384. C>G [p.Ser346Ser] rs7606916 | f‐AAAGAAAGATGACTCAACTTGTAAC | s‐ATGTGCCCGAAAGTCCAGATCA |
| r‐TTAACTCTGTACCTGCTTCAGGA | a‐AGGGTAAGGCTGATGATGGAATCTGCCATTT | |
| Ex10 g.19059C>T [p.Thr367Met] | f‐ATTCTCCATGGTGTTTCCC | s‐AGGTCCCAGAAGACGCC |
| r‐GTACTCTGAGACCAGCAATC | a‐AGTACACCACGAAGGGTCACACAAGGT | |
| In10 g.20220 ex10+1132A>G rs1124534 | f‐CTGTCAAACCTTTGTCAATTCAC | s‐AGTTTATTTCCATTATCCATAGGATCTTGGAAGT |
| r‐TGGCATAATAACAGTAAGGTAACATCA | a‐TATGCTCTGCCCTGGGAGATTTTCCCAGAGA | |
| Ex11 g.33974C>T [p.Ser425Leu] rs3948464 | f‐CCAAGTGGTGGATAAGGTGA | s‐CATGATGAGGGTCCAAAAGGCAAGAACTAAATGTG |
| r‐TACGTCTCCCTCCTTCTACTA | a‐CCGAAAGTCCAGATCGAAAGG | |
| In11 g.34120 ex11+141C>T rs2114591 | f‐GGGTCAGATAGATATGTAAAGTCAATAGTA | s‐ACAGAGCACGGATCTGTTGATG |
| r‐TGTAAATCCACATGGCAAAGC | a‐GACAGTGGTTGTTGGAAGAAGTGTTCTCAGGG | |
| In13 g.41816 ex13+71G>A rs2241525 | f‐GGTCTTCTGCTCTTTGGAATC | s‐TACACACACGGGTATTTTCCTCCC |
| r‐ACCATGATGTGGAAGAGTTTG | a‐CAGTCTAGCTAGCAGGGTCCATTTCCTGATCAA | |
| Ex14 g.42413C>T [p.Thr523Met] rs1804027 | f‐CAGTGAAGTGCATTCGG | s‐GTTGTGAAGGAACGACCCTAGGA |
| r‐CCTGTCACCTATCTGTCCC | a‐AAGGAAGGAACGCAAAGAACTGGAAACGGAATATA | |
| Ex16 g.47823C>T [p.Cys577Cys] rs13018234 | f‐TCAGGATGCTGTGGAGTT | s‐ACCTCTTCATCCTGCAGAAGG |
| r‐CTCGTGTGAGAAGGGAAA | a‐GATACATGATGGCACTGTTGGCTTCCTGAA | |
| In17 g.50165 ex17+813G>T rs6436915 | f‐GCCTGGCATATCCGTAG | s‐TACAAAAATTGTTAAGCTATTTTGCATCA |
| r‐TTTAGGAGCCCAGCAGT | a‐CCTTCCTCAGCGAGTGGGCTTCCAAGAAATGCAT |
AC009950.6 is the reference sequence for all SNPs. The assay for SNPs in exon 5 is designed to detect two adjacent variants. a, anchor; ex, exon; f, forward primer; in, intron; r, reverse primer; s, sensor.
Statistics
Analyses to calculate χ2 tests, odds ratios, Hardy‐Weinberg equilibria, linkage disequilibria, and haplotypes were performed with Stata 8 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA), COCAPHASE (version 2.404; Frank Dudbridge, http://www.mrc‐bsu.cam.ac.uk/personal/frank/software/unphased/), and Haploview (version 3.2; http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/) software with additional Stata 8 modules (David Clayton, Cambridge, UK). Mantel‐Haenszel χ2 tests were used to adjust p values after stratification according to ethnic groups. An 80% power of detection (software at http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/˜purcell/gpc/) was achieved for a dominant model, assuming a tuberculosis prevalence of 0.004 in West Africa, a frequency of 0.1 for high risk alleles, and a genotype relative risk (GRR) of 2 (α = 0.05) with our sample size (case‐control ratio = 1), whereby a higher risk allele frequency would provide sufficient power in a recessive model. With a GRR of 4 and a high risk allele frequency of 0.1, the power was 80% in a recessive model.
Results
DNA re‐sequencing and novel Sp110 variants
Re‐sequencing of 1316 bp of the Sp110 5′‐UTR and of all exons with adjacent intronic regions in 12 patients and in six PPD positive and six PPD negative controls yielded a total of 27 polymorphisms, including 13 variants previously unrecognised. Three novel variants in the 5′‐UTR, six intronic variants, and two synonymous and two non‐synonymous exonic variants were identified. Details of the novel variants, including the frequencies of their occurrence in our West African study population, are summarised in table 3. The allele frequencies given for the newly identified variants not included in the Sp110 genotyping design are not necessarily representative for our West African study population, since they were obtained from DNA sequencing of 24 samples only.
Table 3 Genotyping of Sp110 variants and novel variants identified by DNA sequencing.
| Localisation | Exchange | AF | Assay | Inclusion criterium | GenBank accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5′‐UTR | *g.394T>C (at −2653 of the ATG) | 0.10 | rs6756352 | Tagging SNP (1) | |
| *g.2302C>T (at −745 of the ATG) | 0.20 | rs1346311 | Transcription factor binding site¶ | ||
| *g.2755A>G (at −292 of the ATG) | 0.34 | rs1966555 | Transcription factor binding site¶ | ||
| *g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG)† | 0.18 | This report (table 2) | More frequent among patients | DQ124709 | |
| g.2978C>T (at −69 of the ATG)† | 0.02‡ | – | DQ124709 | ||
| *g.3009C>A (at −38 of the ATG)† | 0.09 | This report (table 2) | 5′‐UTR; transcription factor binding site¶ | DQ124709 | |
| Intron 2 | *g.3305+112C>T | 0.34 | rs7580900 | Tagging SNP (2) | |
| Exon 4 | *g.7013C>T [p.Val128Ala] | 0.01 | rs11556887 | Non‐synonymous mutation | |
| Exon 4 | g.7152C>T [p.Pro174Pro]† | 0.02‡ | – | DQ124710 | |
| Intron 4 | g.7213+322C>T† | 0.35‡ | – | DQ124711 | |
| Exon 5 | *g.7577C>T [p.Ala206Val]† | 0.20 | This report (table 2) | Non‐synonymous mutation | DQ124711 |
| *g.7579A>G [p.Lys207Glu] | 0.06 | rs11556888 | Non‐synonymous mutation | ||
| Intron 5 | *g.8400‐21G>T | 0.42 | rs3820974 | Tagging SNP (3) | |
| Intron 5 | g.7627+726T>C† | 0.04‡ | – | DQ124712 | |
| Exon 8 | *g.11980G>A [p.Gly299Arg] | 0.98 | rs1365776 | Non‐synonymous mutation | |
| Intron 8 | *g.12828+845T>C | 0.10 | rs10167116 | Tagging SNP (4) | |
| Exon 9 | *g.17384G>C [p.Ser346Ser] | 0.30 | rs7606916 | Tagging SNP (5) | |
| Intron 9 | g.17394+1573T>A† | 0.21‡ | – | DQ124713 | |
| Exon 10 | *g.19059C>T [p.Thr367Met]† | 0.09 | This report (table 2) | Non‐synonymous mutation | DQ124713 |
| Intron 10 | *g.20220+1132C>T | 0.24 | rs1124534 | Tagging SNP (6) | |
| Exon 11 | *g.33974C>T [p.Ser425Leu] | 0.14 | rs3948464 | Tagging SNP (7); non‐synonymous mutation | |
| Intron 11 | *g.34120+141C>T | 0.46 | rs2114591 | Tagging SNP (8) | |
| Intron 13 | *g.41816+71G>A | 0.15 | rs2241525 | More frequent among controls | |
| Exon 14 | *g.42413T>C [p.Thr523Met] | 0.19 | rs1804027 | Tagging SNP (9); non‐synonymous mutation | |
| Exon 15a | g.47070C>T [p.Cys549Cys]† | 0.04‡ | – | DQ124714 | |
| Intron 15 | g.47129+77G>A† | 0.04‡ | – | DQ124714 | |
| g.47129+115C>T† | 0.02‡ | – | DQ124714 | ||
| Exon 16 | *g.47823C>T [p.Cys577Cys] | 0.06 | rs13018234 | More frequent among patients | |
| Intron 16 | g.47906+28C>T† | 0.15‡ | – | DQ124715 | |
| Intron 17 | *g.50165+813G>T | 0.28 | rs6436915 | Tagging SNP (10) |
AC009950.6 is the Sp110 reference sequence. Tagging SNPs 1–10 were genotyped following the selection of bins provided by LDSelect software. The numbering of tagging SNPs (1–10) refers to the order of SNPs as given in haplotypes in table 4. AF, allele frequency. GenBank accession numbers are given only for novel variants identified in this study by re‐sequencing.
*SNPs included in Sp110 genotyping; †novel Sp110 variants identified in this study; ‡AF as observed in 24 samples that underwent DNA sequencing; ¶putative transcription factor binding site predicted by a matrix search for transcription factor binding sites (Match).
The allele frequencies of variants described previously did not differ significantly from those reported in the dbSNP database (see http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db = snp) (table 3).
Comparisons between subgroups
With the exception of the SNPs in exons 5 and 10, g.7577C>T [p.Ala206Val] and g.19059C>T [p.Thr367Met], all variants were in Hardy‐Weinberg equilibrium. Statistical analyses were carried out to compare patients with all controls, patients with PPD positive controls, and patients with PPD negative controls. Analyses were also done applying different thresholds of PPD positivity/negativity and under the assumption of recessive and dominant modes of inheritance. The genotyping results are given in table 5.
Table 5 Haplotypes of tagging SNPs.
| Haplotype (tagging SNPs 1–10) | Frequency (patients) | Frequency (controls) | OR | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 1.1 | 0.75 |
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐2 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.07 | 0.79 |
| 1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐2 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 1.14 | 0.66 |
| 2‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.11 | 0.88 |
| 1‐1‐2‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.86 | 0.17 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.66 |
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.02 | 0.69 |
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.34 | 0.36 |
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 0.31 |
| 1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐2‐1 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 1.61 | 0.12 |
| 1‐2‐2‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.02 | 0.76 |
| 2‐2‐2‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.2 | 0.66 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 0.46 |
| 1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.68 | 0.12 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.83 | 0.04* |
| 1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0.21 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.28 | 0.57 |
| 1‐2‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.31 |
| 1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1‐1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.69 |
| 1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐2‐2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.12 |
| 1‐2‐2‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1‐2‐2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 0.46 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.59 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐2‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.3 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.76 | 0.29 |
| 1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.29 | 0.6 |
| 1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐2‐2‐1‐1‐1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.95 |
Haplotype defining tagging SNPs were derived by LD selection on the basis of HapMap data available for the West African Yoruba ethnic group. The order of SNPs (1–10) corresponds to the numbering given in table 3. Cumulative frequencies are 99% and 98% for patients and controls, respectively.
*p value not corrected for multiple testing.
After adjusting p values for ethnicity and correcting for multiple testing (Bonferroni correction), the frequencies of the 21 SNPs did not differ significantly between patients and the two control subgroups. This applied also after stratifications for different thresholds of PPD positivity and negativity. When, however, uncorrected p values <0.05 adjusted for ethnicity were considered indicative of a trend of association, trends were observed in several comparisons of patients with all controls, with PPD negative controls, and with PPD positive controls (table 4).
Table 4 Genotyping results.
| Sp110 variant | Gt | Patients | All controls | Controls grouped according to size of skin induration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPD negativity | PPD positivity | ||||||||
| ⩽1 mm | ⩽3 mm | ⩽7 mm | ⩾2 mm | ⩾4 mm | ⩾8 mm | ||||
| g.394T>C (at −2653 of the ATG) | n = 1009 | n = 1138 | n = 76 | n = 387 | n = 1017 | n = 1062 | n = 751 | n = 121 | |
| g.2302C>T (at−745 of the ATG) | n = 984 | n = 1248 | n = 128 | n = 501 | n = 1129 | n = 1120 | n = 747 | n = 119 | |
| CC | 63.5% | 65.7% | 64.1% | 62.5% | 65.2% | 65.9% | 67.9% | 70.6% | |
| CT | 33.2% | 29.4% | 32.0% | 32.7% | 29.8% | 29.1% | 27.2% | 26.0% | |
| TT | 3.3% | 4.9% | 3.9% | 4.8% | 5.0% | 5.0% | 4.9% | 3.4% | |
| prec 0.04 | |||||||||
| prec/adj 0.045 | |||||||||
| OR 0.63 | |||||||||
| (CI 0.41 to 0.98) | |||||||||
| g.2755A>G (at −292 of the ATG) | n = 1010 | n = 1143 | n = 78 | n = 388 | n = 1018 | n = 1065 | n = 755 | n = 125 | |
| g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG) | n = 1360 | n = 1388 | n = 123 | n = 521 | n = 1237 | n = 1265 | n = 867 | n = 151 | |
| CC | 67.0 % | 66.3 % | 65.9% | 66.6% | 66.9% | 66.4% | 66.2% | 62.2% | |
| CT | 30.4% | 29.7% | 30.9% | 30.1% | 29.1% | 29.6% | 29.4% | 33.8% | |
| TT | 2.6% | 4.0% | 3.2% | 3.3% | 4.0% | 4.0% | 4.4% | 4.0% | |
| prec 0.041 | prec 0.046 | prec 0.036 | prec 0.019 | ||||||
| prec/adj 0.040 | prec/adj 0.045 | prec/adj 0.036 | prec/adj 0.018 | ||||||
| OR 0.64 | OR 0.64 | OR 0.63 | OR 0.58 | ||||||
| (CI 0.41 to 0.99) | (CI 0.41 to 1.00) | (CI 0.41 to 0.97) | (CI 0.36 to 0.92) | ||||||
| g.3009C>A (at −38 of the ATG) | n = 1013 | n = 1265 | n = 129 | n = 507 | n = 1140 | n = 1136 | n = 758 | n = 125 | |
| g.3305+112C>T | n = 987 | n = 1119 | n = 76 | n = 381 | n = 998 | n = 1043 | n = 738 | n = 121 | |
| g.7013C>T [p.Val128Ala] | n = 1041 | n = 1380 | n = 123 | n = 515 | n = 1249 | n = 1257 | n = 865 | n = 131 | |
| g.7577C>T [p.Ala206Val] | n = 1262 | n = 1378 | n = 128 | n = 531 | n = 1227 | n = 1250 | n = 847 | n = 151 | |
| g.7579A>G [p.Lys207Glu] | n = 1262 | n = 1378 | n = 128 | n = 531 | n = 1227 | n = 1250 | n = 847 | n = 151 | |
| g.8400‐21G>T | n = 999 | n = 1120 | n = 74 | n = 377 | n = 997 | n = 1046 | n = 743 | n = 123 | |
| g.11980G>A [p.Gly299Arg] | n = 1055 | n = 1409 | n = 127 | N = 530 | n = 1276 | n = 1282 | n = 879 | n = 133 | |
| g.12828+845T>C | n = 1007 | n = 1145 | n = 8 | n = 389 | n = 1022 | n = 1067 | n = 756 | n = 123 | |
| TT | 82.7 % | 79.7 % | 85.9 % | 81.7 % | 80.4 % | 79.3 % | 78.7% | 74.0% | |
| CT | 16.2% | 18.7% | 11.5% | 16.0% | 17.8% | 19.2% | 20.1% | 26.7% | |
| CC | 1.1% | 1.6% | 2.6% | 2.3% | 1.8% | 1.5% | 1.2% | 0% | |
| pdom 0.033 | p 0.014 | ||||||||
| pdom/adj 0.039 | padj 0.021 | ||||||||
| OR 0.77 | ORCTvTT 0.56 | ||||||||
| (CI 0.61 to 0.98) | (CI 0.36 to 0.86) | ||||||||
| pdom 0.018 | |||||||||
| pdom/adj 0.021 | |||||||||
| OR 0.59 | |||||||||
| (CI 0.38 to 0.92) | |||||||||
| g.17384G>C [p.Ser346Ser] | n = 1008 | n = 1142 | n = 78 | n = 388 | n = 1017 | n = 1064 | n = 754 | n = 125 | |
| g.19059C>T [p.Thr367Met] | n = 985 | n = 1098 | n = 77 | n = 373 | n = 981 | n = 1021 | n = 725 | n = 117 | |
| g.20220+1132C>T | n = 999 | n = 1137 | n = 78 | n = 387 | n = 1013 | n = 1059 | n = 750 | n = 124 | |
| g.33974C>T [p.Ser425Leu] | n = 1051 | n = 1269 | n = 79 | n = 410 | n = 1138 | n = 1190 | n = 859 | n = 131 | |
| g.34120+141C>T | n = 1010 | n = 1143 | n = 77 | n = 386 | n = 1019 | n = 1066 | n = 757 | n = 124 | |
| CC | 29.9% | 29.1% | 16.9% | 24.9% | 28.8% | 30.0% | 31.3% | 31.4% | |
| CT | 48.5% | 49.8% | 57.1% | 50.8% | 50.0% | 49.3% | 49.3% | 48.4% | |
| TT | 21.6% | 21.1% | 26.0% | 24.3% | 21.2% | 20.7% | 19.4% | 20.2% | |
| pdom 0.015 | |||||||||
| pdom/adj 0.02 | |||||||||
| OR 0.47 | |||||||||
| (CI 0.26 to 0.88) | |||||||||
| g.41816+71G>A | n = 1891 | n = 2284 | n = 129 | n = 695 | n = 2044 | n = 2155 | n = 1589 | n = 240 | |
| GG | 72.3% | 73.0% | 77.5% | 74.1% | 73.5% | 72.8% | 72.5% | 69.2% | |
| AG | 25.1% | 25.1% | 21.7% | 25.0% | 24.7% | 25.3% | 25.2% | 29.2% | |
| AA | 2.6% | 1.9% | 0.8% | 0.9% | 1.8% | 1.9% | 2.3% | 1.6% | |
| prec 0.006 | |||||||||
| prec/adj 0.006 | |||||||||
| OR 3.12 | |||||||||
| (CI 1.33 to 7.32) | |||||||||
| g.42413T>C [p.Thr523Met] | n = 1000 | n = 1304 | n = 121 | n = 500 | n = 1186 | n = 1183 | n = 804 | n = 118 | |
| CC | 86.2% | 88.9% | 87.9% | 90.0% | 88.8% | 89.0% | 88.2% | 89.6% | |
| CT | 13.2% | 10.7% | 12.1% | 9.8% | 11.0% | 10.6% | 11.3% | 8.9% | |
| TT | 0.6% | 0.4% | 0.0% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 1.5% | |
| pdom 0.034 | pdom 0.046 | ||||||||
| pdom/adj 0.035 | pdom/adj 0.047 | ||||||||
| OR 1.44 | OR 1.29 | ||||||||
| (CI 1.03 to 2.0) | (CI 1.0 to 1.65) | ||||||||
| g.50165+813G>T | n = 974 | n = 1100 | n = 73 | n = 374 | n = 982 | n = 1027 | n = 726 | n = 118 | |
p values (not corrected for multiple testing) and odds ratios (OR) given refer to comparisons with the group of patients. adj, p obtained after adjustment for ethnic groups by Mantel‐Haenszel χ2 tests; CI, confidence interval; Gt, genotypes; dom, dominant mode of inheritance assumed; rec, recessive mode of inheritance assumed.
Assuming a recessive mode of inheritance, the 5′‐UTR variant g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG) was more frequent among all controls than among patients. When considering a skin induration ⩽1 mm as PPD negative, the tagging variant g.34120+141C>T occurred more frequently among PPD negative individuals than among patients in a dominant model. When considering a skin induration ⩽3 mm as PPD negative, the intronic g.41816+71G>A and the exon 16 g.47823C>T [p.577Cys] variants were more prevalent in patients than in PPD negative controls in a recessive and a dominant model, respectively. When considering a skin induration ⩽7 mm as PPD negative in a recessive model, the g. 2302C>T (at −745 of the ATG) and the g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG) variants were less frequent among patients than among controls.
The proportion of individuals carrying the g.2804C>T (at −243 of the ATG) 5′‐UTR variant was higher in PPD positive controls than in patients. This applied for the thresholds of skin reactions of ⩾2 mm and ⩾4 mm defining the PPD status in recessive models.
The synonymous variant g.47823C>T was more frequent in patients than in PPD positive controls (PPD positivity ⩾2 mm, dominant model) and g.12828+845T>C occurred more frequently in PPD negative controls than in patients (PPD positivity ⩾4 and ⩾8 mm, dominant model).
Linkage disequilibria and haplotypes
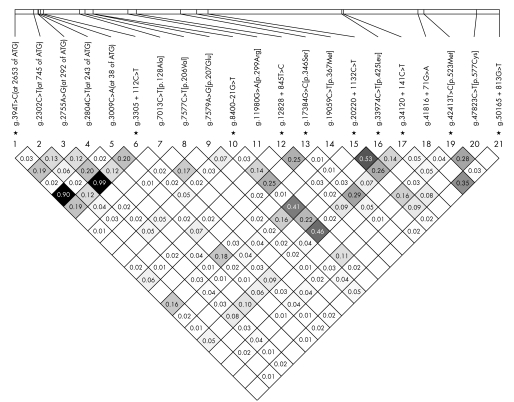
The 10 tagging SNPs that were representative of bins of SNPs were selected to cover the complete Sp110 gene and to exhibit pairwise LDs below the threshold of r2 = 0.5. Nevertheless, the combination of the tagging variants g.20220+1132A>G (intron 10) and g.33974C>T [p.425Leu] (exon 11) exceeded, with r2 = 0.53, that threshold in our study population. Other LDs with r2>0.5 were those between the putative promoter variants g.394C>T (at −2653 of the ATG) and g.3009C>A (at −38 of the ATG) (r2 = 0.90) and between g.394C>T (at −2653 of the ATG) and g.3305+112C>T (intron 2; r2 = 0.99). r2 values for the Sp110 SNPs typed in this study are given in the LD plot of fig 1.
Figure 1 Estimates of pairwise linkage disequilibria between Sp110 variants with the LD measure of r2 assuming Hardy‐Weinberg equilibrium. r2 values <0.01 are not shown. *Tagging SNPs.
Significant differences between patients and the two subgroups of controls were not observed when comparing the frequencies of variant haplotypes of tagging SNPs (table 5).
Differential sliding window haplotype analyses with three adjacent markers performed for (i) all markers, (ii) tagging SNPs, and (iii) for markers other than tagging SNPs (5′‐UTR and exonic regions, one intronic variant) did not reveal significant differences between groups.
Discussion
After the recent report on the role of the mouse locus sst1 and the gene Ipr1 in innate immunity to tuberculosis in mice,2 the human homologue of Ipr1, Sp110, was considered a promising candidate for association studies in human M tuberculosis infection. This hypothesis was based on the presumed function of Ipr1 in the pathogenesis of murine tuberculosis, where transcription in macrophages was activated in response to signals of intracellular pathogens, and pathways were initiated that eventually induced apoptosis and conferred innate immunity. The results of the present study on associations of Sp110 gene variants with distinct phenotypes of human M tuberculosis infection in a West African population, however, argue against a major role of Sp110 variants and haplotypes in resistance or susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis. None of the comparisons performed between patients and PPD positive and PPD negative controls after adjustment for ethnicity, and with an assumed statistical power of 80%, reached statistical significance when p values were subjected to Bonferroni corrections. This was also true when different sizes of the skin reaction were used to define PPD status as recommended by the manufacturer of the PPD test and by both Lunn et al12 and Fourie et al.13 Taking into account the number of samples tested, these results appear conclusive.
With the stringent criteria for enrolment of study participants, it appears most unlikely that deficits in phenotyping patients and controls account for the lack of any association. Rather, failure to establish a major role of Sp110 variants in human phenotypes of M tuberculosis infection might be due to the limited 69% and 41% Sp110 identity at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, respectively, with its mouse homologue Ipr1. Furthermore, and as predicted by computerised UniProtKB/Swiss‐Prot database adjustments (http://www.expasy.uniprot.org/), among those variants causing amino acid substitutions only the exon 14 variant g.42413C>T [p.523Met] is located within the functional DNA‐binding SAND domain, while all other non‐synonymous variants tested do not map to any functional site. Lastly, by re‐sequencing 1316 bp of the Sp110 5′‐UTR and transcribed exons with flanking intronic segments in 24 samples only, rare but potentially essential alleles and significant genetic effects might have gone unnoticed.<1?tpb=3pt?>
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to the patients and control individuals who participated in the study. We thank all field workers, nurses, and physicians involved in the recruitment of patients and controls and gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Lincoln Gankpala, Emmanuel Abbeyquaye, Gerd Ruge, Sandra Engels, Birgit Förster, Christa Flessner, and Birgit Muntau and appreciate the logistics provided by the staff of the Kumasi Centre for Collaborative Research in Tropical Medicine, Kumasi, Ghana.
Electronic‐database information
The following URLs have been mentioned: Gene Regulation: http://www.gene‐regulation.com/; UniProt: http://www.expasy.uniprot.org/; NCBI Entrez SNP: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db = snp; NCBI RefSeq: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq/; UNPHASED: http://www.mrc‐bsu.cam.ac.uk/personal/frank/software/unphased/; Genetic Power Calculator: http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/˜purcell/gpc/; Haploview: http://www.broad.mit.edu/personal/jcbarret/haploview/; International HapMap Project: http://www.hapmap.org/; LDSelect: http://droog.gs.washington.edu/ldSelect.pl.
Abbreviations
DOTS - Directly Observed Treatment Short‐course strategy
FRET - fluorescence resonance energy transfer
GRR - genotype relative risk
Ipr1 - intracellular pathogen resistance‐1 gene
PPD - purified protein derivative
SAND - Sp100, AIRE‐1, NucP41/75, and DEAF‐1/suppressin
sst - super‐susceptibility to tuberculosis
Footnotes
The study has been supported by the German National Genome Research Network (project NIE‐S17T20)
Competing interests: none declared
The following URLs have been mentioned: Gene Regulation: http://www.gene‐regulation.com/; UniProt: http://www.expasy.uniprot.org/; NCBI Entrez SNP: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db = snp; NCBI RefSeq: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq/; UNPHASED: http://www.mrc‐bsu.cam.ac.uk/personal/frank/software/unphased/; Genetic Power Calculator: http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/˜purcell/gpc/; Haploview: http://www.broad.mit.edu/personal/jcbarret/haploview/; International HapMap Project: http://www.hapmap.org/; LDSelect: http://droog.gs.washington.edu/ldSelect.pl.
References
- 1.Bellamy R. Genetic susceptibility to tuberculosis. Clin Chest Med 200526233–246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pan H, Yan B S, Rojas M, Shebzukhov Y V, Zhou H, Kobzik L, Higgins D E, Daly M J, Bloom B R, Kramnik I. Ipr1 gene mediates innate immunity to tuberculosis. Nature 2005434767–772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bloch D B, Nakajima A, Gulick T, Chiche J D, Orth D, de La Monte S M, Bloch K D. Sp110 localizes to the PML‐Sp100 nuclear body and may function as a nuclear hormone receptor transcriptional coactivator. Mol Cell Biol 2000206138–6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kadereit S, Gewert D R, Galabru J, Hovanessian A G, Meurs E F. Molecular cloning of two new interferon‐induced, highly related nuclear phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem 199326824432–24441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wasylyk C, Schlumberger S E, Criqui‐Filipe P, Wasylyk B. Sp100 interacts with ETS‐1 and stimulates its transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol 2002222687–2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sternsdorf T, Jensen K, Reich B, Will H. The nuclear dot protein sp100, characterization of domains necessary for dimerization, subcellular localization, and modification by small ubiquitin‐like modifiers. J Biol Chem 199927412555–12566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bottomley M J, Collard M W, Huggenvik J I, Liu Z, Gibson T J, Sattler M. The SAND domain structure defines a novel DNA‐binding fold in transcriptional regulation. Nat Struct Biol 20018626–633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Surdo P L, Bottomley M J, Sattler M, Scheffzek K. Crystal structure and nuclear magnetic resonance analyses of the SAND domain from glucocorticoid modulatory element binding protein‐1 reveals deoxyribonucleic acid and zinc binding regions. Mol Endocrinol 2003171283–1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Watashi K, Hijikata M, Tagawa A, Doi T, Marusawa H, Shimotohno K. Modulation of retinoid signaling by a cytoplasmic viral protein via sequestration of Sp110b, a potent transcriptional corepressor of retinoic acid receptor, from the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol 2003237498–7509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Saito T, Ji G, Shinzawa H, Okumoto K, Hattori E, Adachi T, Takeda T, Sugahara K, Ito J I, Watanabe H, Saito K, Togashi H, Ishii K, Matsuura T, Inageda K, Muramatsu M, Kawata S. Genetic variations in humans associated with differences in the course of hepatitis C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004317335–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nicewonger J, Suck G, Bloch D, Swaminathan S. Epstein‐Barr virus (EBV) SM protein induces and recruits cellular Sp110b to stabilize mRNAs and enhance EBV lytic gene expression. J Virol 2004789412–9422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lunn J A, Johnson A J, Fry J S. Comparison of multiple puncture liquid tuberculin test with Mantoux test. Lancet 198128695–698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fourie P B, Swanevelder J P, Lancaster J. Diagnostic efficiency of the disposable Monotest in detecting tuberculosis infection by setting objective‐specific cut‐off points for positivity. S Afr Med J 199686151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carlson C S, Eberle M A, Rieder M J, Yi Q, Kruglyak L, Nickerson D A. Selecting a maximally informative set of single‐nucleotide polymorphisms for association analyses using linkage disequilibrium. Am J Hum Genet 200474106–120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]