Abstract
A cDNA clone containing the entire vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid gene was assembled by fusing portions of two partial clones. When the cDNA clone was inserted into a new general-purpose eucaryotic expression vector and introduced into appropriate host cells, abundant N-protein synthesis ensued. The expressed protein was indistinguishable from authentic N protein produced during vesicular stomatitis virus infections. The recombinant N protein was recognized by a polyclonal antibody and two different monoclonal antibodies and could not be resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis from authentic N. Our results suggest that the recombinant N protein produced in transfected cells rapidly aggregates into high-molecular-weight complexes in the absence of vesicular stomatitis virus genomic RNA.
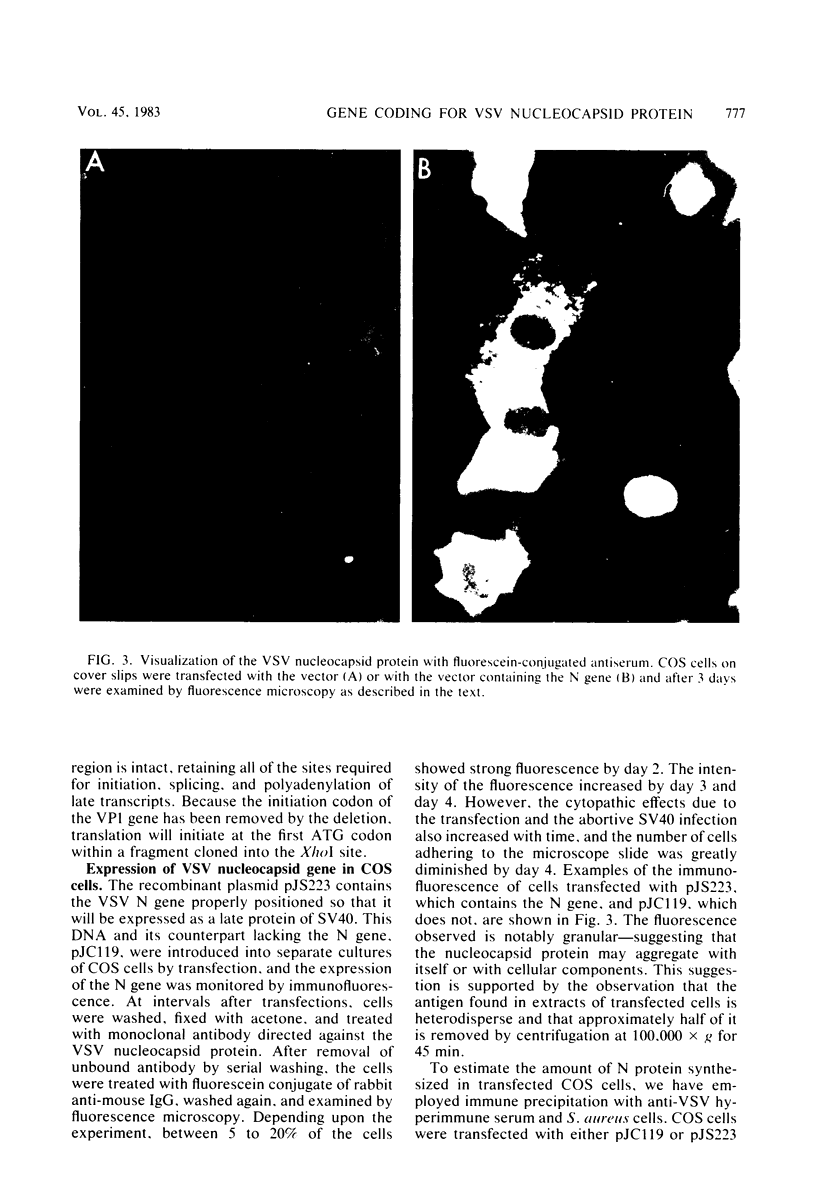
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. M., Leppert M., Kolakofsky D. Interaction of VSV leader RNA and nucleocapsid protein may control VSV genome replication. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90448-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F., Hull R. Model for vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):256–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.256-260.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. A unique RNA species involved in initiation of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcription in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the leader RNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Nayak D. P. Defective interfering influenza viruses and host cells: establishment and maintenance of persistent influenza virus infection in MDBK and HeLa cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):847–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.847-859.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng G., Wu R. An improved procedure for utilizing terminal transferase to add homopolymers to the 3' termini of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4173–4188. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Dierks P. M., Parsons J. T. In vitro synthesis of a unique RNA species by a T particle of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.708-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Greene J. R., Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus N and NS proteins. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.529-535.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A., Rosenberg M. Nucleotide sequence homology at the 3' termini of RNA from vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective interfering particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. R., Lazzarini R. A. The relationship between autointerference and the replication of defective interfering particle. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. The molecular biology of paramyxoviruses. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1974;160(2-3):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02121714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Keene J. D., Schubert M. The origins of defective interfering particles of the negative-strand RNA viruses. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Weber G. H., Johnson L. D., Stamminger G. M. Covalently linked message and anti-message (genomic) RNA from a defective vesicular stomatitis virus particle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 25;97(3):289–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. P., Cohen S. N. 3'-end labeling of DNA with [alpha-32P]cordycepin-5'-triphosphate. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Ryffel G. U., Wyler T., Jaggi F. B., Weber R., Dawid I. B. Cloning and characterization of synthetic sequences from the Xenopus iaevis vitellogenin structural gene. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac B. A., Hummeler K. Morphogenesis of the nucleoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):243–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.243-252.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





