Abstract
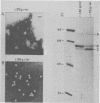
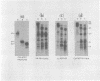
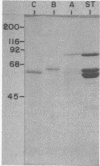
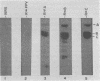
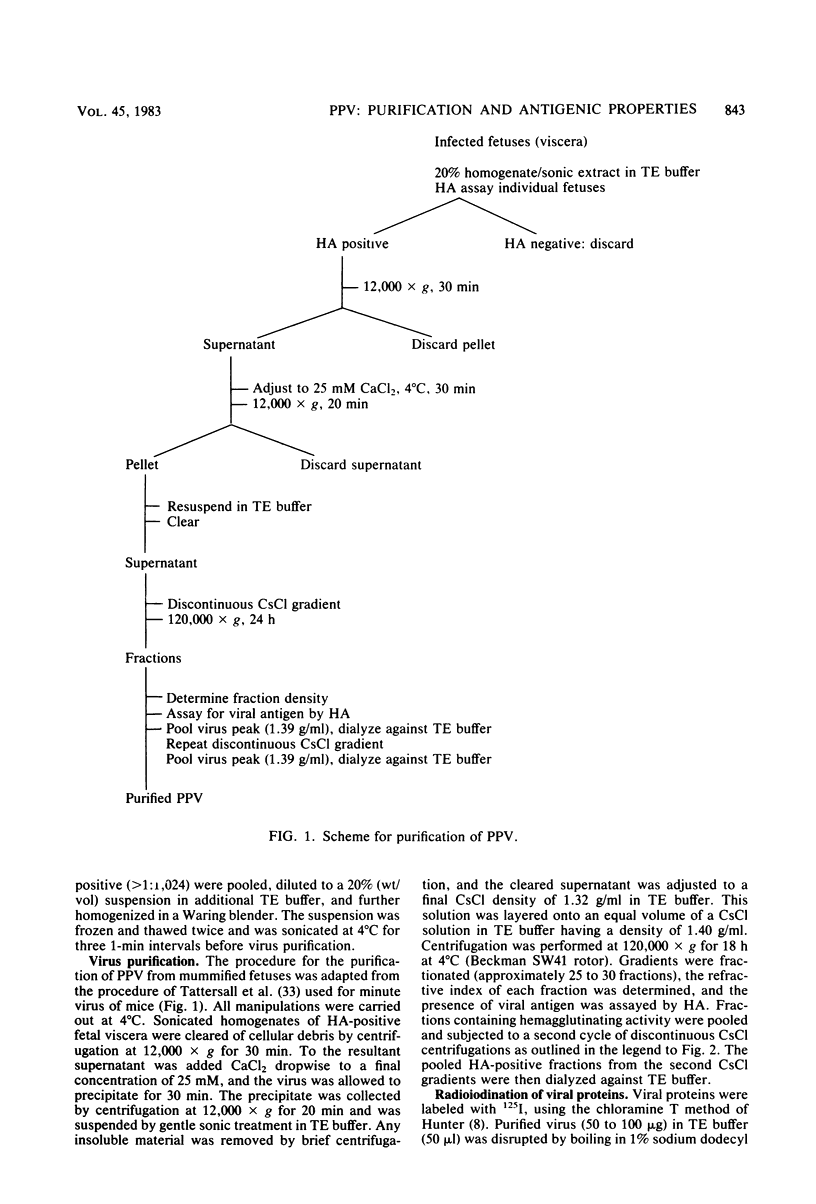
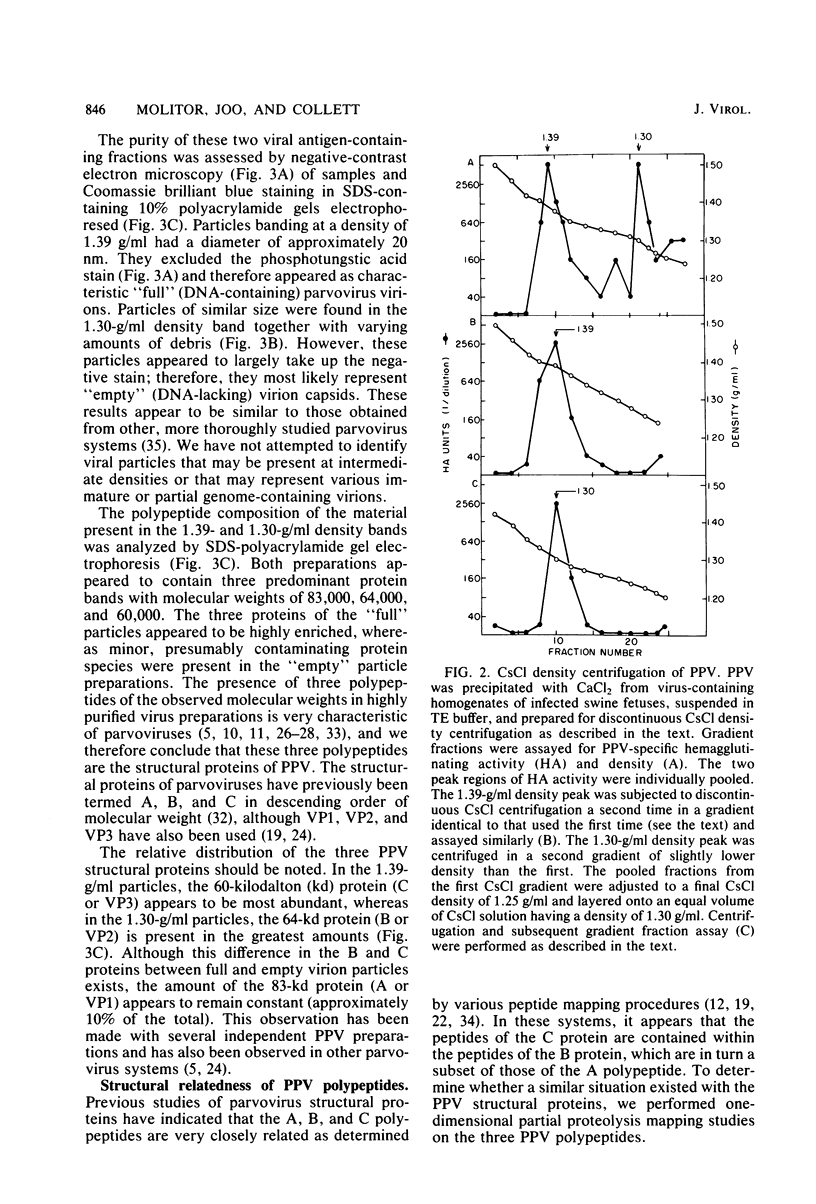
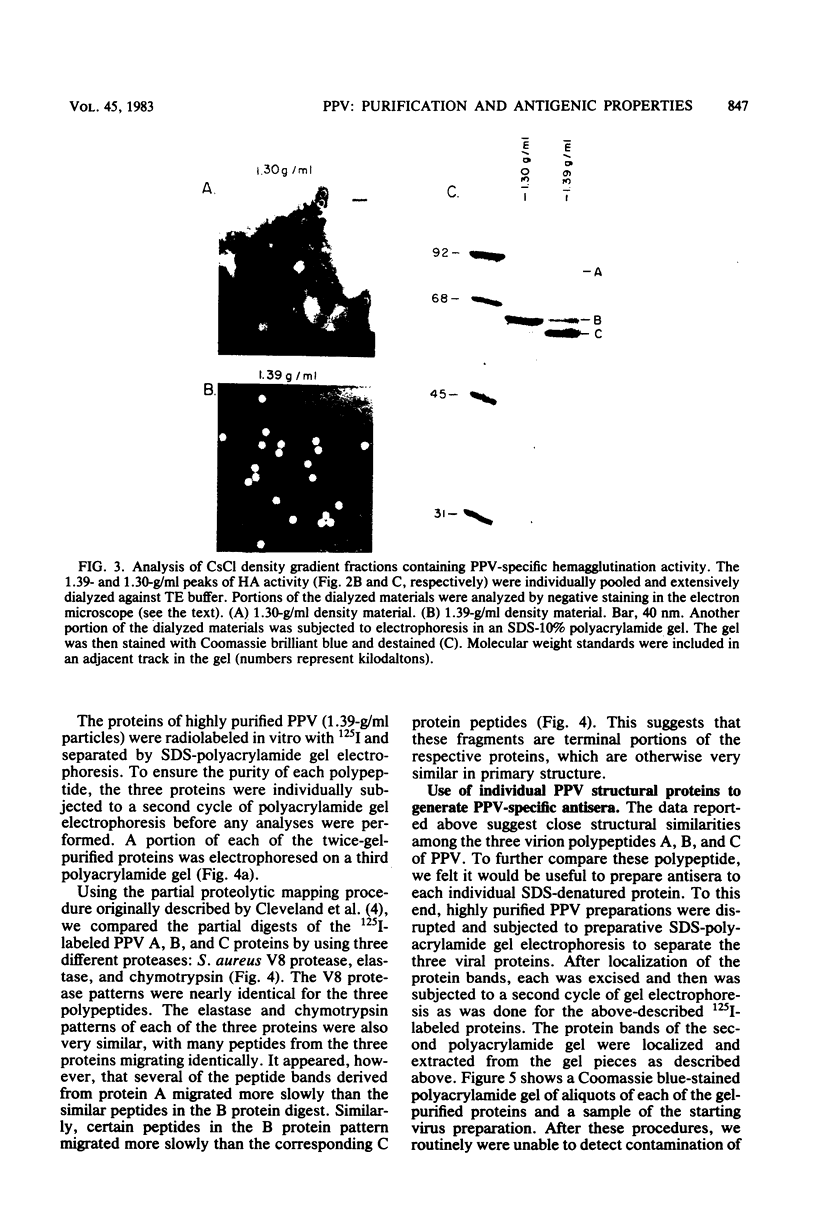
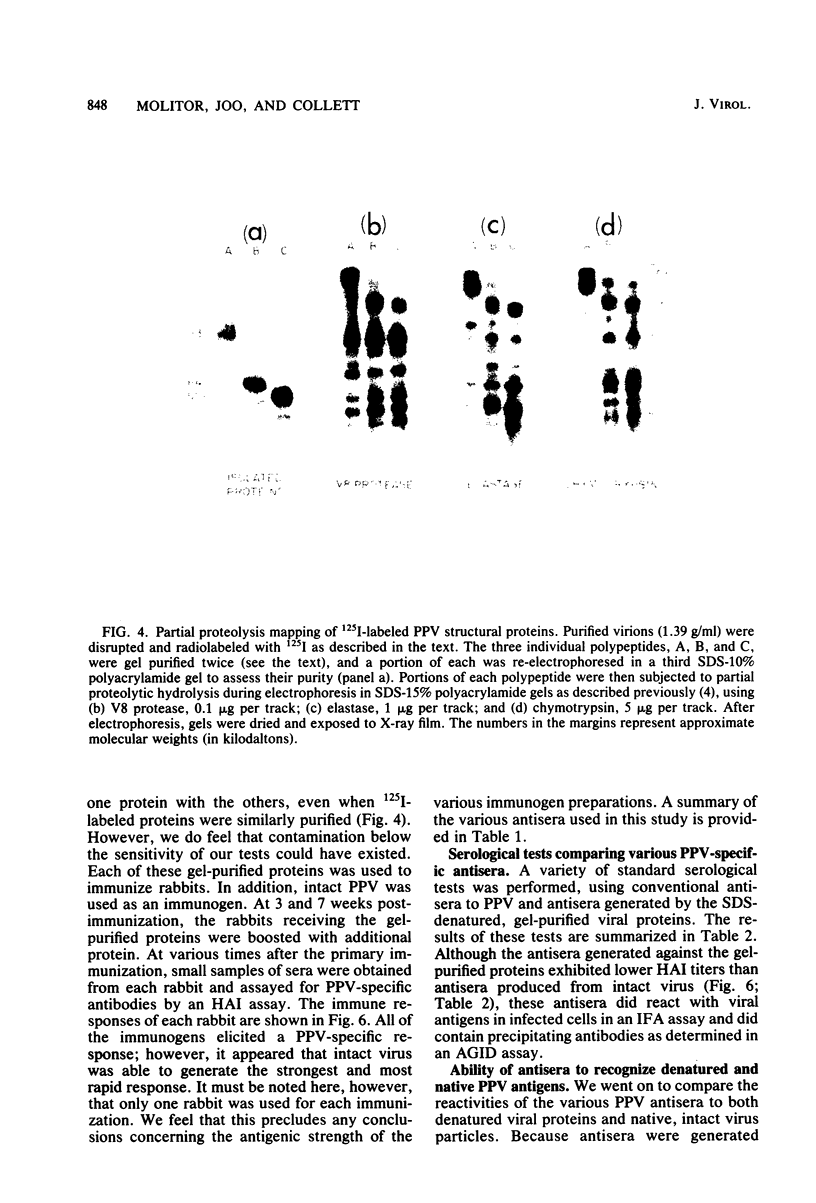
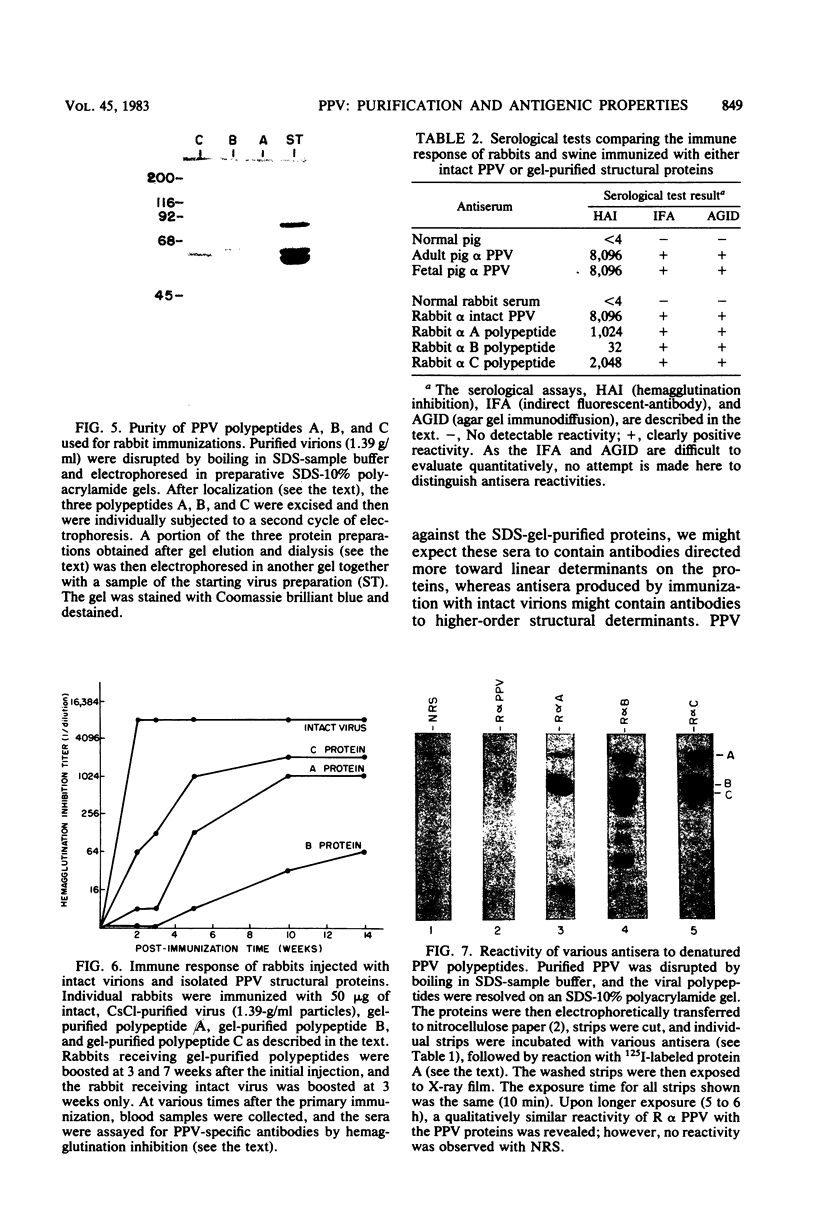
Porcine parvovirus (PPV) was extensively purified from infected swine fetal homogenates by CaCl2 precipitation followed by CsCl density centrifugation. Two species of particles possessing PPV-specific hemagglutinating activity were observed banding at densities of 1.39 and 1.30 g/ml, representing full and empty 20-nm virion particles, respectively. Both classes of particles contained three major polypeptides. A, B, and C, with respective molecular weights of 83,000, 64,000, and 60,000. The amount of polypeptide A was similar in both species (approximately 10%); however, the B protein was most abundant in the 1.30-g/ml particles, whereas the C protein was the major polypeptide found in the 1.39-g/ml particles. Antisera generated to each sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel-purified virion structural protein had reactivities qualitatively similar to those of conventional antisera raised against intact PPV in a variety of standard serological assays. The antisera generated against the individual sodium dodecyl sulfate-denatured PPV polypeptides were able to react with native, intact PPV virions and were capable of neutralizing virus infectivity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bier M., Cuddeback R. M., Kopwillem A. Preparative plasma protein fractionation by isotachophoresis in Sephadex columns. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 21;132(3):437–450. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82908-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommeli W., Kihm U., Zindel F., Fey H. Enzyme linked immunoassay and fluorescent antibody techniques in the diagnosis of viral diseases using staphylococcal protein-A instead of anti-gamma-globulins. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Feb;1(2):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(80)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Hayashi M. The parovivirus MVM: particles with altered structural proteins. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):261–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft G. F., Hoggan M. D., Johnson F. B. Production and reactivity of immune sera specific for HADEN virus polypeptide antigens. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):608–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.608-613.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England J. J., Reed D. E. Negative contrast electron microscopic techniques for diagnosis of viruses of veterinary importance. Cornell Vet. 1980 Apr;70(2):125–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Blacklow N. R., Hoggan M. D. Immunological reactivity of antisera prepared against the sodium dodecyl sulfate-treated structural polypeptides of adenovirus-associated virus. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):1017–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.1017-1026.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Hoggan M. D. Structural proteins of HADEN virus. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Ozer H. L., Hoggan M. D. Structural proteins of adenovirus-associated virus type 3. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):860–863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.860-863.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Thomson T. A., Taylor P. A., Vlazny D. A. Molecular similarities among the adenovirus-associated virus polypeptides and evidence for a precursor protein. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. S., Donaldson-Wood C. R., Johnson R. H. A standardised haemagglutination inhibition test for porcine parvovirus antibody. Aust Vet J. 1976 Sep;52(9):422–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1976.tb09517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. S., Donaldson-Wood C. R., Johnson R. H. Observations on the pathogenesis of porcine parvovirus infection. Arch Virol. 1976;51(1-2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01317841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. S., Johnson R. H. Serological responses in pigs vaccinated with inactivated porcine parvovirus. Aust Vet J. 1977 Nov;53(11):550–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1977.tb07945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. S., Johnson R. H., Watson D. L. Serological procedures to determine time of infection of pigs with porcine parvovirus. Aust Vet J. 1978 Mar;54(3):125–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb05524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Lee H. M., Hoggan M. D., Johnson F. B. Adenovirus-associated virus structural protein sequence homology. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):209–216. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengeling W. L., Brown T. T., Paul P. S., Gutekunst D. E. Efficacy of an inactivated virus vaccine for prevention of porcine parvovirus-induced reproductive failure. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Feb;40(2):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengeling W. L., Cutlip R. C. Pathogenesis of in utero infection: experimental infection of five-week-old porcine fetuses with porcine parvovirus. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Aug;36(08):1173–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore N. F., Kelly D. C. Interrelationships of the proteins of two parvoviruses (densonucleosis virus types 1 and 2). Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):160–166. doi: 10.1159/000149178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto T., Fujisaki Y., Ito Y., Tanaka Y. Biological and physicochemical properties of porcine parvovirus recovered from stillborn piglets. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1972 Fall;12(3):137–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R. Infectious process of the parvovirus H-1: correlation of protein content, particle density, and viral infectivity. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):800–807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.800-807.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Ferguson L. C. Porcine parvovirus: natural and experimental infections of the porcine fetus and prevalence in mature swine. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):718–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.718-723.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Inman J. K., Shatkin A. J. Structural proteins of adenovirus-associated viruses. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):766–770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.766-770.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo R. J., Mayor H. D. Structural polypeptides of parvoviruses. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman L. A., White W. L. Structural proteins of Kilham rat virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90564-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Lynch J., Cho H. J., Marusyk R. G. Studies on the multiplication of a porcine parvovirus. Vet Microbiol. 1982 May;7(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(82)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterzl J., Rejnek J., Trávnícek J. Impermeability of pig placenta for antibodies. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1966;11(1):7–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02877148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington J., Green M., Brackmann K. Immunoautoradiographic detection of proteins after electrophoretic transfer from gels to diazo-paper: analysis of adenovirus encoded proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Sequence homology between the structural polypeptides of minute virus of mice. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]