Abstract
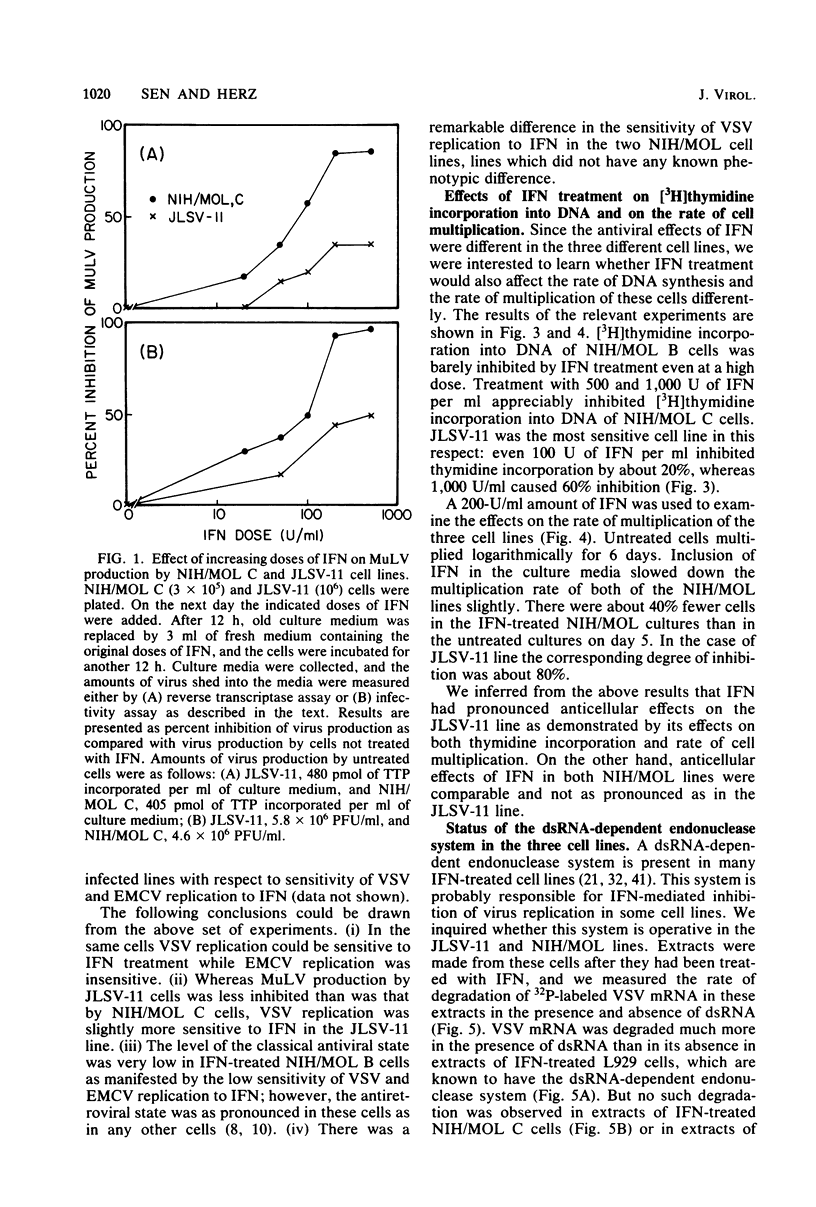
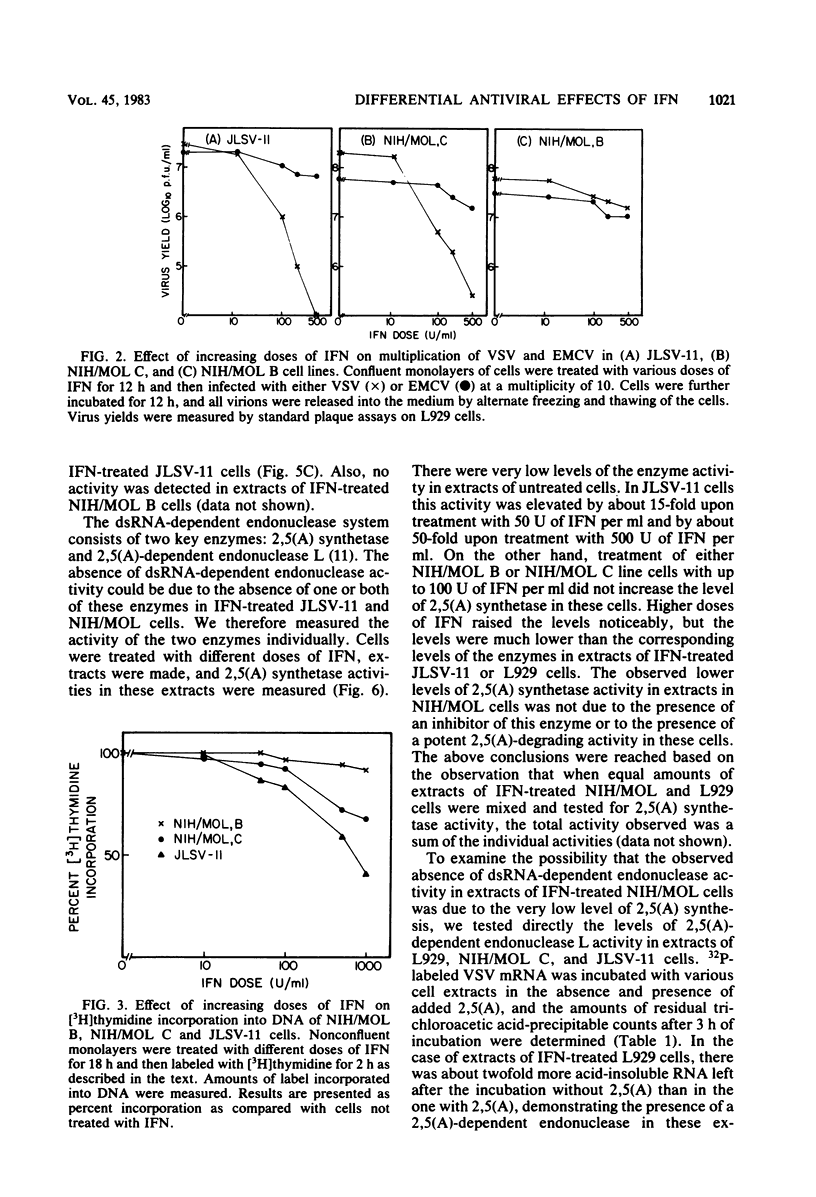
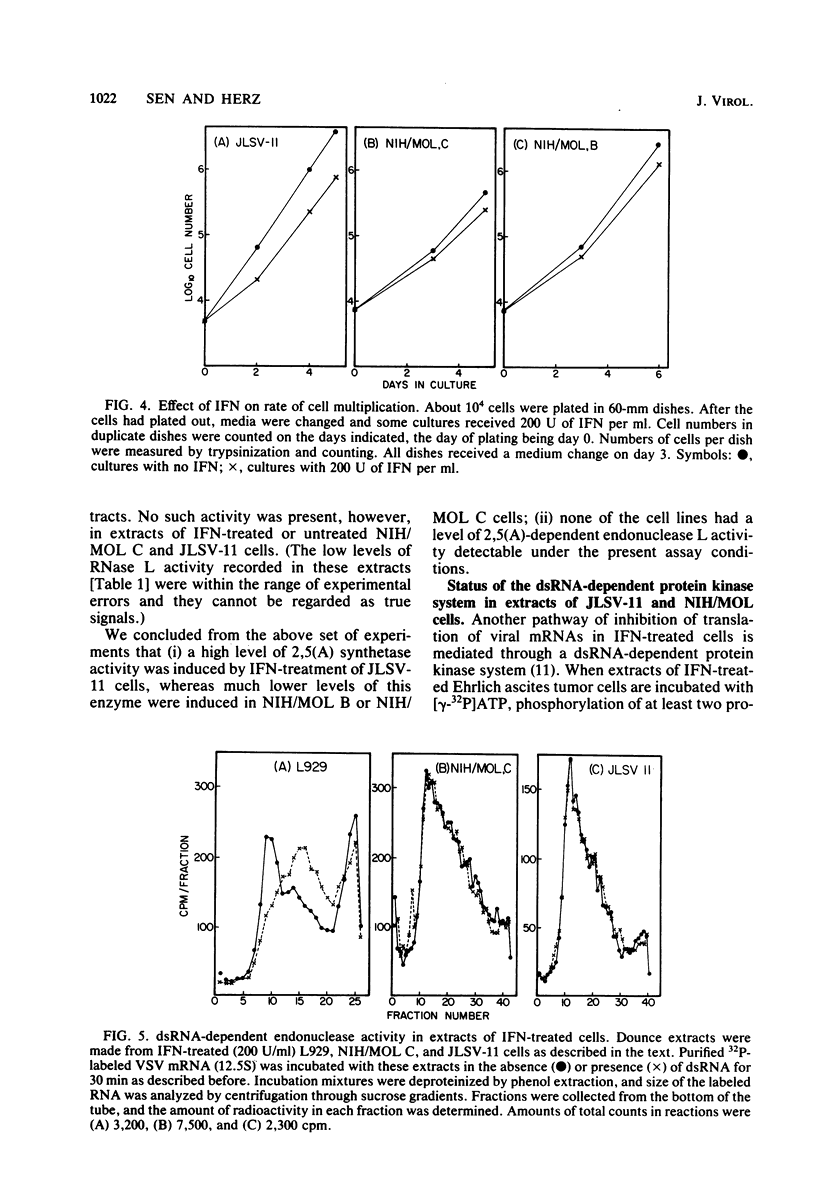
Infectious leukemia virus production by two chronically infected NIH/MOL lines was strongly inhibited by interferon treatment of the cells. The corresponding degree of inhibition in JLSV-11 cells was much lower. Multiplication of encephalomyocarditis virus in all three cell lines was barely affected by interferon treatment. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus, on the other hand, was highly sensitive to interferon in the JLSV-11 line and in one NIH/MOL line but was practically insensitive in the other NIH/MOL line. Anticellular actions of interferon were more pronounced in the JLSV-11 line than in the others. In response to interferon treatment, 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity was induced to a high level in JLSV-11 cells and to lower levels in the NIH/MOL lines. We failed to detect any 2',5'-oligoadenylate-dependent endonuclease activity in extracts of these cells. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activity was present in extracts of interferon-treated NIH/MOL cells, but it was barely detectable in extracts of interferon-treated JLSV-11 cells. The above studies demonstrated that interferon could differentially affect the replication of three different viruses in three different cell lines, including two seemingly identical NIH/MOL lines, and that certain tentative conclusions can be drawn regarding the roles of different interferon-inducible enzyme markers in the different antiviral actions of interferons.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Gresser I., Hovanessian A. G., Bandu M. T., Blanchard B., Blangy D. Specific high-affinity binding of 125I-labeled mouse interferon to interfevon resistant embryonal carcinoma cells in vitro. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):585–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. T., Schellekens H., Van Griensven L. J., Billiau A. Differential sensitivity of Rauscher murine leukaemia virus (MuLV-R) to interferons in two interferon-responsive cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):429–435. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:35–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. C., Graham C. F., Lehman J. M. Appearance of interferon inducibility and sensitivity during differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Sreevalsan T., Friedman R. M., Panet A. Dissociation of interferon effects on murine leukemia virus and encephalomyocarditis virus replication in mouse cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):827–831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.827-831.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. A., Czarniecki C. W., Jacobsen H., Friedman R. M., Panet A. A mouse cell line, which is unprotected by interferon against lytic virus infection, lacks ribonuclease F activity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Dubois M. F., Ratner L., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two distinct pathways for inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Antiviral activity of interferons. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):543–567. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.543-567.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Chang E. H., Ramseur J. M., Myers M. W. Interferon-directed inhibition of chronic murine leukemia virus production in cell cultures: lack of effect on intracellular viral markers. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):569–574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.569-574.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L. Specific protein phosphorylation in interferon-treated uninfected and virus-infected mouse L929 cells: enhancement by double-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):301–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.301-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. L., Gupta S. L. Interferon action in human fibroblasts: induction of 2', 5'-oligoadenylate synthetase in the absence of detectable protein kinase activity. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01314459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
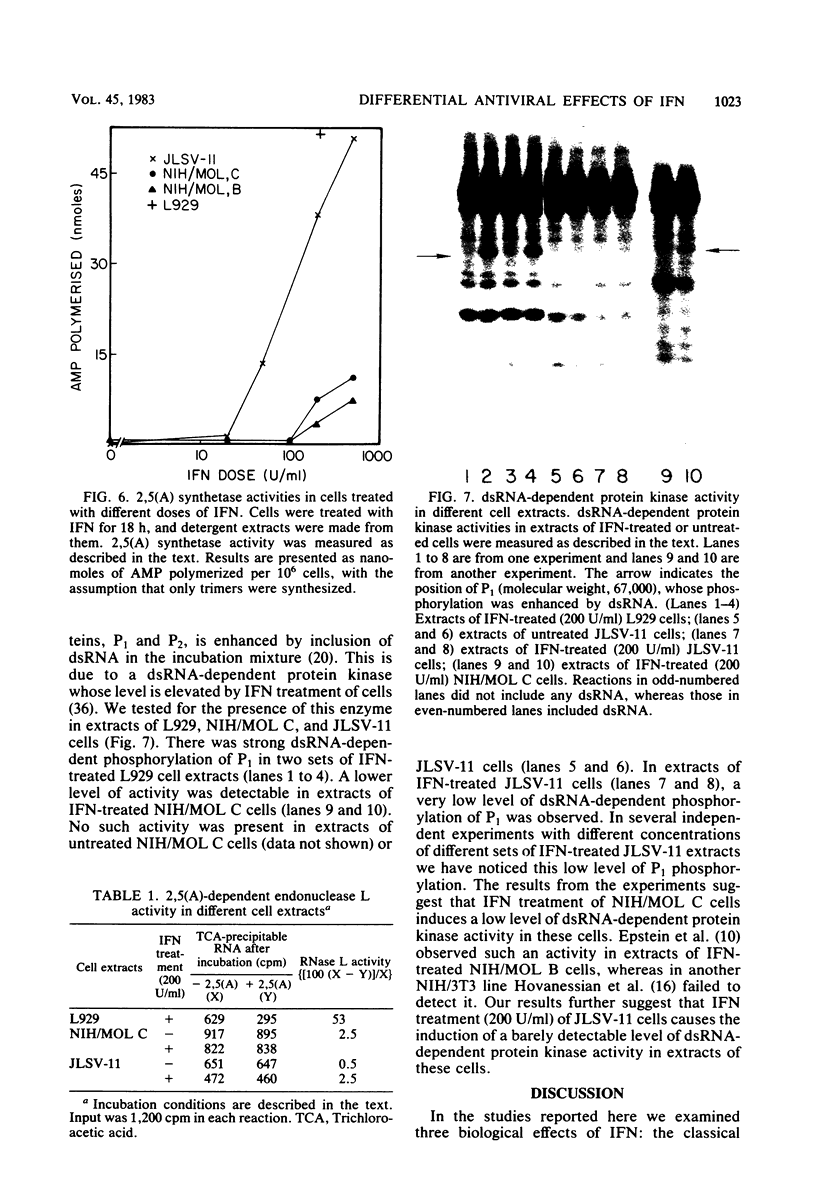
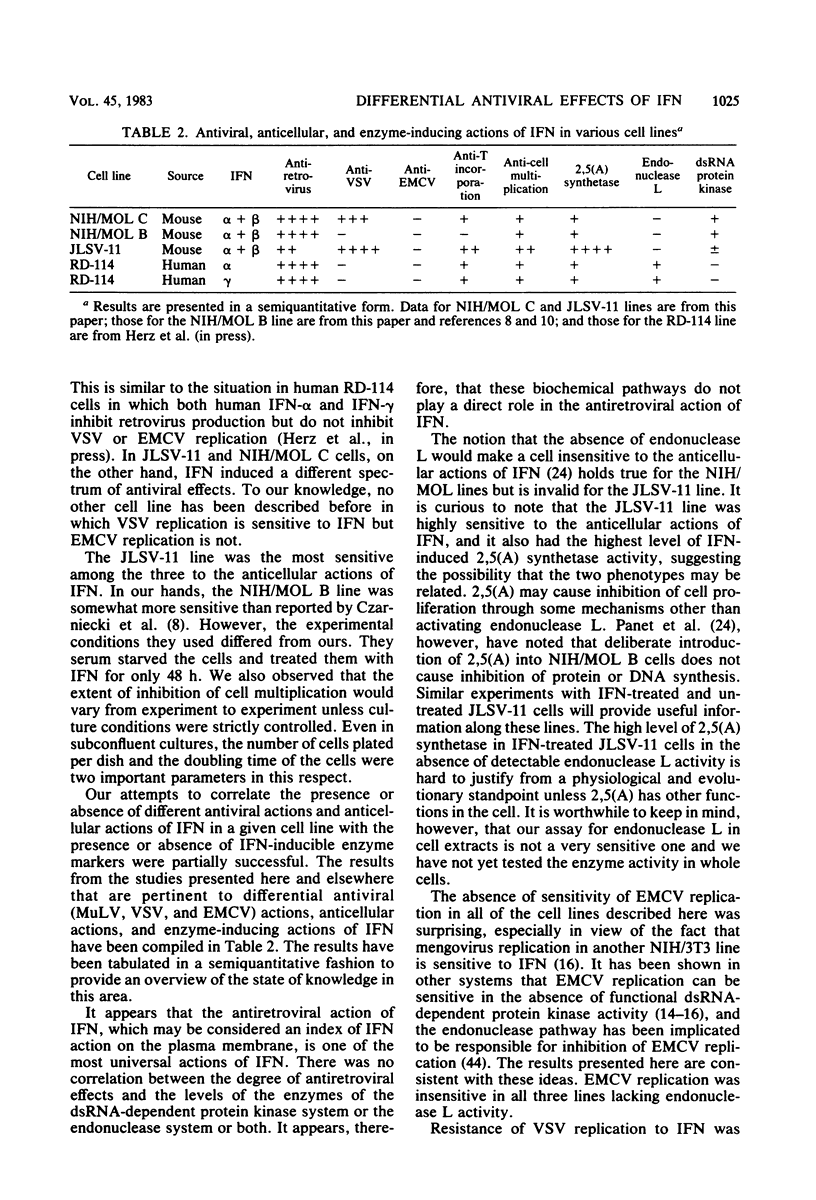
- Hovanessian A. G., Meurs E., Montagnier L. Lack of systematic correlation between the interferon mediated antiviral state and the levels of 2-5A synthetase and protein kinase in three different types of murine cells. J Interferon Res. 1981 Feb;1(2):179–190. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Wood J., Meurs E., Montagnier L. Increased nuclease activity in cells treated with pppA2'p5'A2'p5' A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3261–3265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. P., White C., Ball A., Gupta S. L., Ratner L., Sen G. C., Colby C. Interferon-associated, dsRNA-dependent enzyme activities in a mutant 3T6 cell engaged in the semiconstitutive synthesis of interferon. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Shure H., Revel M. Regulation of lymphocyte mitogenesis by (2'--5') oligo-isoadenylate. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):849–851. doi: 10.1038/282849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naso R. B., Wu Y. H., Edbauer C. A. Antiretroviral effect of interferon: proposed mechanism. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(1):75–96. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Wood D. L., Baglioni C. Virus-specific effects of interferon in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):178–180. doi: 10.1038/286178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Czarniecki C. W., Falk H., Friedman R. M. Effect of 2'5'-oligoadenylic acid on a mouse cell line partially resistant to interferon. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M., Rowe W. P., Oxman M. N. Effect of interferon on exogenous, endogenous, and chroniv murine leukemia virus infection. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):324–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M., Wivel N. A., Fernie B. F., Harper H. P. Effect of interferon on murine leukaemia virus infection. IV. Formation of non-infectious virus in chronically infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):467–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Sen G. C., Brown G. E., Lebleu B., Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA and RNA degradation. Characteristics of an endonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):565–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Wallach D., Merlin G., Schattner A., Schmidt A., Wolf D., Shulman L., Kimchi A. Interferon-induced enzymes: microassays and their applications: purification and assay of (2'-5')-oligoadenylate synthetase and assay of 2'-phosphodiesterase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):149–161. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Gupta S. L. Differential efficacies of human type I and type II interferons as antiviral and antiproliferative agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5928–5932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Gupta S. L., Brown G. E., Lebleu B., Rebello M. A., Lengyel P. Interferon treatment of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells: effects on exogenous mRNA translation and tRNA inactivation in the cell extract. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):191–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.191-203.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C. Mechanism of interferon action: progress toward its understanding. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:105–156. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60599-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Sarkar N. H. Effects of interferon on the production of murine mammary tumor virus by mammary tumor cells in culture. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Shaila S., Lebleu B., Brown G. E., Desrosiers R. C., Lengyel P. Impairment of reovirus mRNA methylation in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrilich ascites tumor cells: further characteristics of the phenomenon. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):69–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.69-83.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaegen M., Divizia M., Vandenbussche P., Kuwata T., Content J. Abnormal behavior of interferon-induced enzymatic activities in an interferon-resistant cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4479–4483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Kerr I. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis by 2'-5' linked adenine oligonucleotides in intact cells. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):88–90. doi: 10.1038/276088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Yuen P. H., MacLeod R., Chang E. H., Myers M. W., Friedman R. M. The effect of interferon on de novo infection of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hovanessian A. G. Interferon enhances 2-5A synthetase in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):74–76. doi: 10.1038/282074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreschner D. H., James T. C., Silverman R. H., Kerr I. M. Ribosomal RNA cleavage, nuclease activation and 2-5A(ppp(A2'p)nA) in interferon-treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1571–1581. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. S., O'Brien P. A., Shibley G. P., Mayyasi S. A., Lasfargues J. C. Infection of an established mouse bone marrow cell line (JLS-V9) with Rauscher and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Cancer Res. 1967 Sep;27(9):1672–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Baglioni C. Viral messenger RNA unmethylated in the 5'-terminal guanosine in interferon-treated HeLa cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):426–435. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]