Abstract
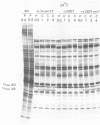
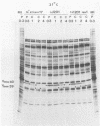
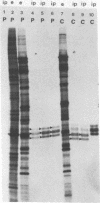
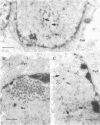
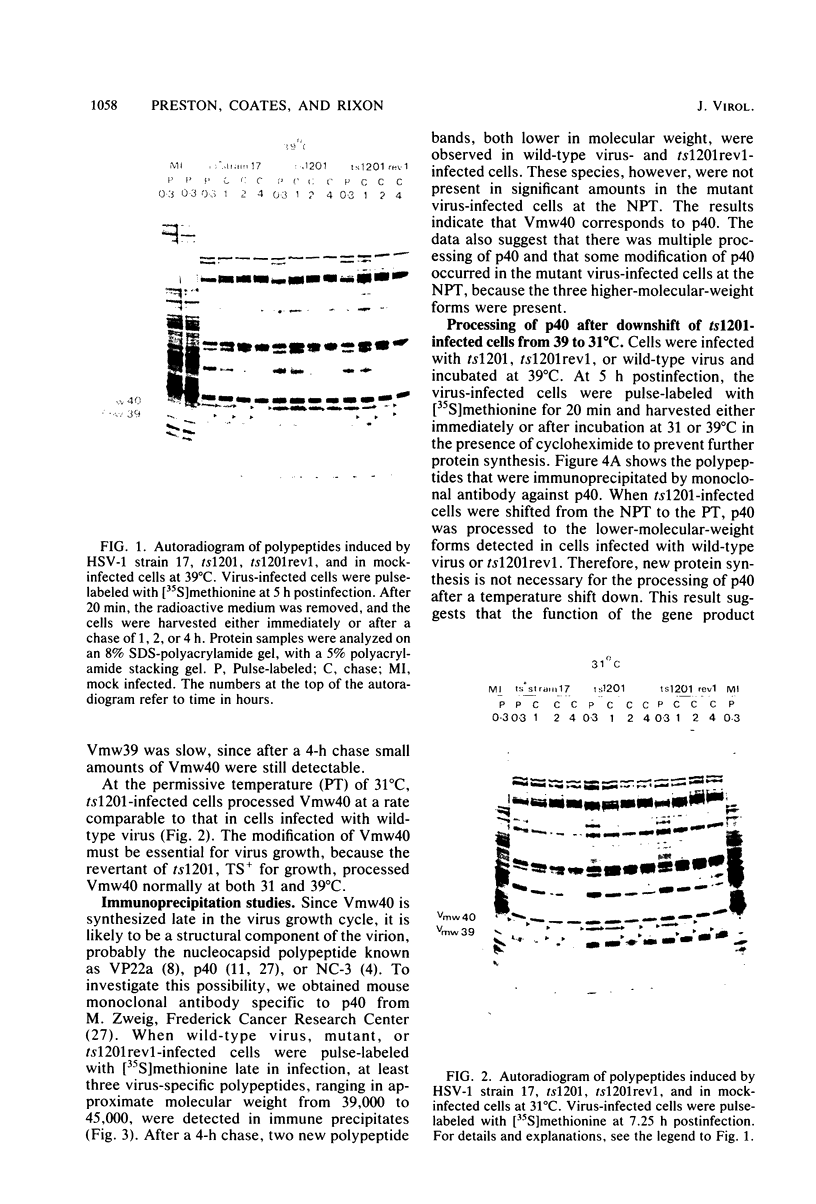
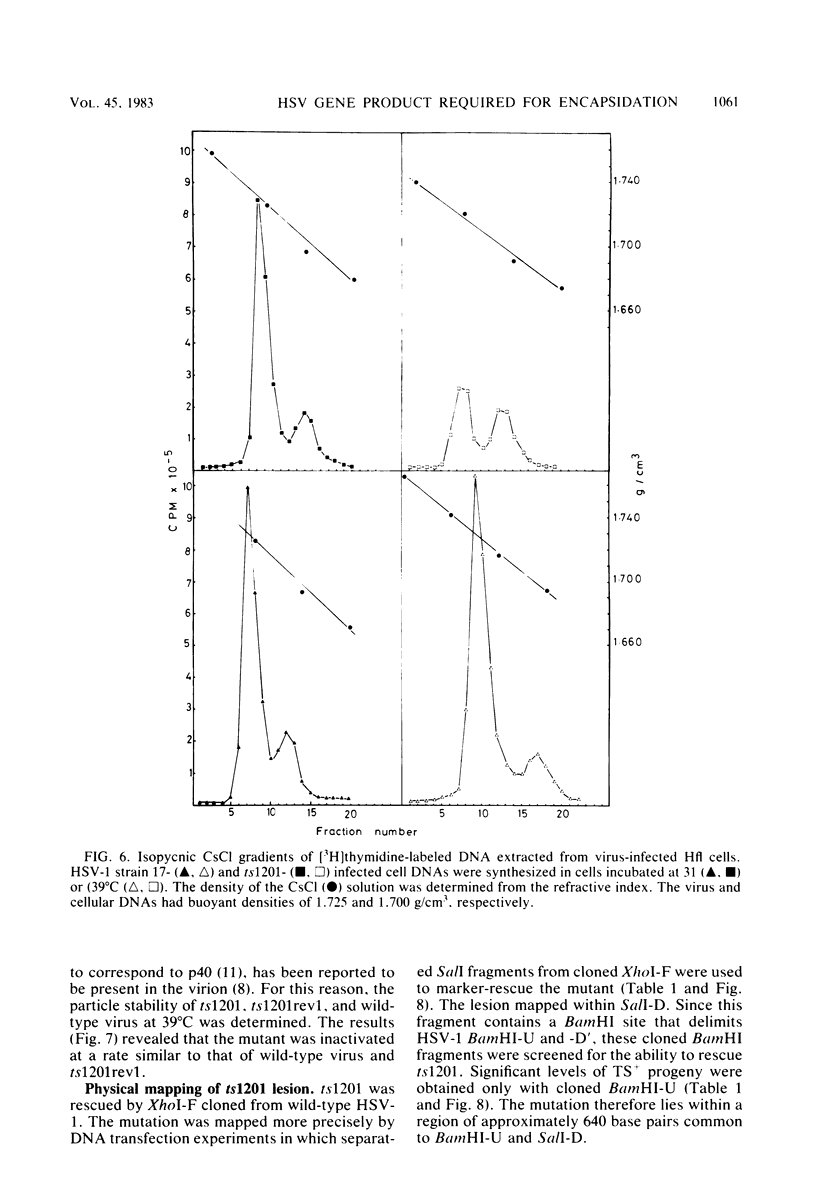
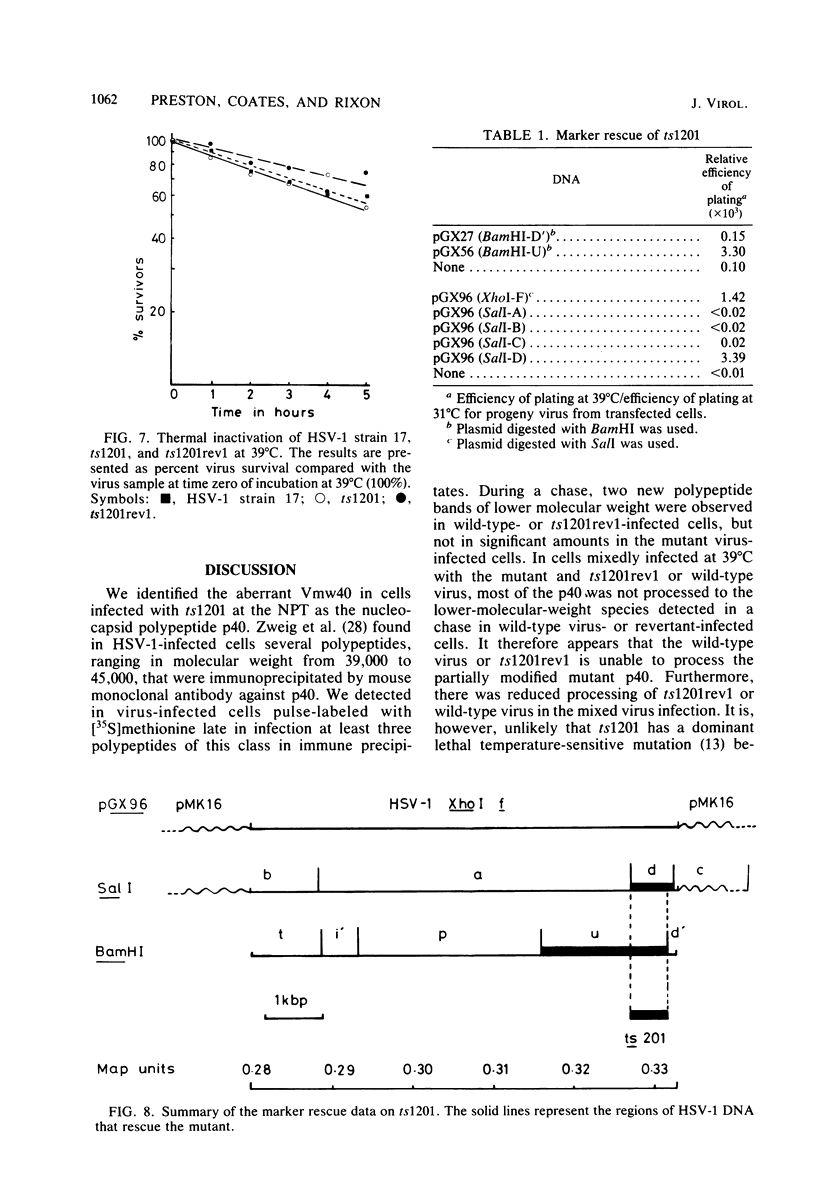
A mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1, 17tsVP1201, has a temperature-sensitive processing defect in a late virus polypeptide. Immunoprecipitation studies with monoclonal antibodies showed that the aberrant polypeptide in mutant virus-infected cells was the nucleocapsid polypeptide known as p40. Since a revertant, TS+ for growth, processed the polypeptide normally under conditions restrictive for the mutant, the processing event must be essential for virus replication. Electron microscopic analysis of mutant virus-infected cells grown at the nonpermissive temperature revealed that the nuclei contained large aggregations of empty nucleocapsids possessing some internal structure. Therefore, although the mutant synthesized virus DNA at the nonpermissive temperature, the DNA was not packaged into nucleocapsids. When mutant virus-infected cells were shifted from 39 to 31°C in the presence of cycloheximide, the polypeptide p40 was processed to lower-molecular-weight forms, and full nucleocapsids were detected in the cell nuclei. The aberrant polypeptide of the mutant, however, was not processed in cells mixedly infected with 17tsVP1201 and a revertant at the nonpermissive temperature, suggesting that the defect of the mutant was in the gene encoding p40 rather than in a gene of a processing enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Barr S., Timbury M. C. The fine structure of cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):103–119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. IV: analysis of concatemers. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Genetic studies with herpes simplex virus type 1. The isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants, their arrangement into complementation groups and recombination analysis leading to a linkage map. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):329–346. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Diggelmann H., Lawrence W. C., Vernon S. K., Eisenberg R. J. Structural analysis of the capsid polypeptides of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):521–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.521-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Coward J. E., Rosenkranz H. S., Morgan C. Electron microscopic studies on assembly of herpes simplex virus upon removal of hydroxyurea block. J Gen Virol. 1975 Feb;26(2):171–181. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong D., Swift H., Roizman B. Arrangement of herpesvirus deoxyribonucleic acid in the core. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1071–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1071-1074.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. Staining and radiolabeling properties of B capsid and virion proteins in polyacrylamide gels. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):155–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.155-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Timbury M. C. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: description of three new complementation groups and studies on the inhibition of host cell DNA synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):207–221. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. J., Jr, Zweig M., Stephenson J. R., Hampar B. Isolation of a nucleocapsid polypeptide of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 possessing immunologically type-specific and cross-reactive determinants. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):34–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.34-42.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Morse L. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XII. Accumulation of head-to-tail concatemers in nuclei of infected cells and their role in the generation of the four isomeric arrangements of viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):448–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.448-457.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A dominant lethal temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):173–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90663-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. V. Maturation of concatemeric DNA of pseudorabies virus to genome length is related to capsid formation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1151–1164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1151-1164.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Ihara S., Hampl H., Ben-Porat T. Pathway of assembly of herpesvirus capsids: an analysis using DNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):544–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ELLISON S. A., ROSE H. M., MOORE D. H. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. I. Herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1954 Aug 1;100(2):195–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G. Fine-structure mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutations within the short repeat region of the genome. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):150–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.150-161.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutations by marker rescue. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Green N., Liu F. T., Niman H. L., Lerner R. A. Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide predicted from nucleotide sequence allows detection of a new retroviral gene product. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):801–805. doi: 10.1038/287801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Cortini R. Sequence arrangement in herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA: identification of terminal fragments in restriction endonuclease digests and evidence for inversions in redundant and unique sequences. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.211-221.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hampar B. Shared antigenic determinants between two distinct classes of proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):644–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.644-652.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Hampar B. Production of monoclonal antibodies against nucleocapsid proteins of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):676–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.676-678.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]