Abstract
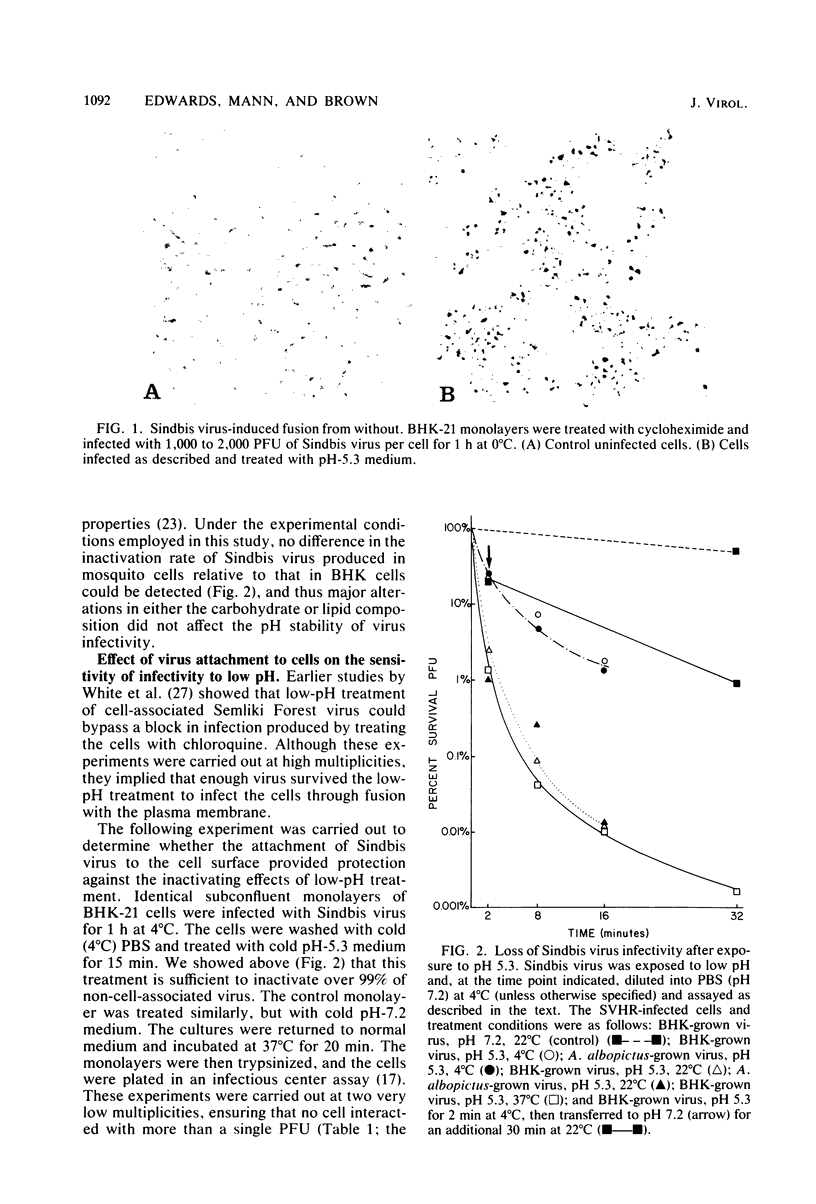
The attachment of high multiplicities of Sindbis virus to tissue-cultured cells followed by brief treatment at low pH has been shown to produce cell fusion (fusion from without). In this report, experiments to determine the effects of low pH on the physical and biological properties of Sindbis virus are described. Exposure of purified Sindbis virions to mildly acidic conditions resulted in a rapid and irreversible alteration in particle density and sedimentation characteristics, followed by a slower loss of infectivity. Infectivity was not restored by a return to neutral pH; rather, the loss of virus infectivity seemed to be initiated by exposure to low pH but continued at neutral pH. The formation of a virus-cell complex in which virions were attached to the cell surface protected the particles from low-pH inactivation, although low pH could still expose virus functions responsible for cell fusion. Low pH was found to induce a conformational change in the E2 polypeptide of the intact virion. These results are discussed with respect to the process of Sindbis virus infection of tissue-cultured cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. H., Brown D. T. Inhibition of Sindbis virus maturation after treatment of infected cells with trypsin. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):692–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.692-702.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs K., Mann E., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Effects of chloroquine and cytochalasin B on the infection of cells by Sindbis virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1060–1065. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1060-1065.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Review article initial stages in infection with animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):1–22. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M., White J. Inhibition of Semliki forest virus penetration by lysosomotropic weak bases. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):47–61. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Wahn K., Schmidt M. F., Rott R. Productive infection of chick embryo cells by influenza viruses tightly bound on substratum. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1981;170(2):91–98. doi: 10.1007/BF02122673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Philipson L. Early interaction between animal viruses and cells. Monogr Virol. 1974;9:1–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen A., von Bonsdorff C. H., Renkonen O. Characterization of Semliki Forest virus grown in mosquito cells. Comparison with the virus from hamster cells. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann E., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Polycaryocyte formation mediated by Sindbis virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1083–1089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1083-1089.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz D., Brown D. T. Characteristics of Sindbis virus temperature-sensitive mutants in cultured BHK-21 and Aedes albopictus (Mosquito) cells. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):775–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.775-781.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Yazaki P., Hostetler K. Y. The intracellular distribution and antiviral activity of amantadine. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel B., Brown D. T. Novel antiviral activity found in the media of Sindbis virus-persistently infected mosquito (Aedes albopictus) cell cultures. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.51-60.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel B., Brown D. T. Role of extracellular virus on the maintenance of the persistent infection induced in Aedes albopictus (mosquito) cells by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):554–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.554-561.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Eggers H. J. Early processes of echovirus 12-infection: elution, penetration, and uncoating under the influence of rhodanine. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheefers H., Scheefers-Borchel U., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Distribution of virus structural proteins and protein-protein interactions in plasma membrane of baby hamster kidney cells infected with Sindbis or vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7277–7281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. F., Brown D. T. Envelopments of Sindbis virus: synthesis and organization of proteins in cells infected with wild type and maturation-defective mutants. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):662–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.662-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V., Stollar B. D., Koo R., Harrap K. A., Schlesinger R. W. Sialic acid contents of sindbis virus from vertebrate and mosquito cells. Equivalence of biological and immunological viral properties. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):104–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Vance D. E. Evidence that Sindbis virus infects BHK-21 cells via a lysosomal route. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):1131–1137. doi: 10.1139/o80-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen P., Käriäinen L. Fusion and haemolysis of erythrocytes caused by three togaviruses: Semliki Forest, Sindbis and rubella. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):467–475. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




