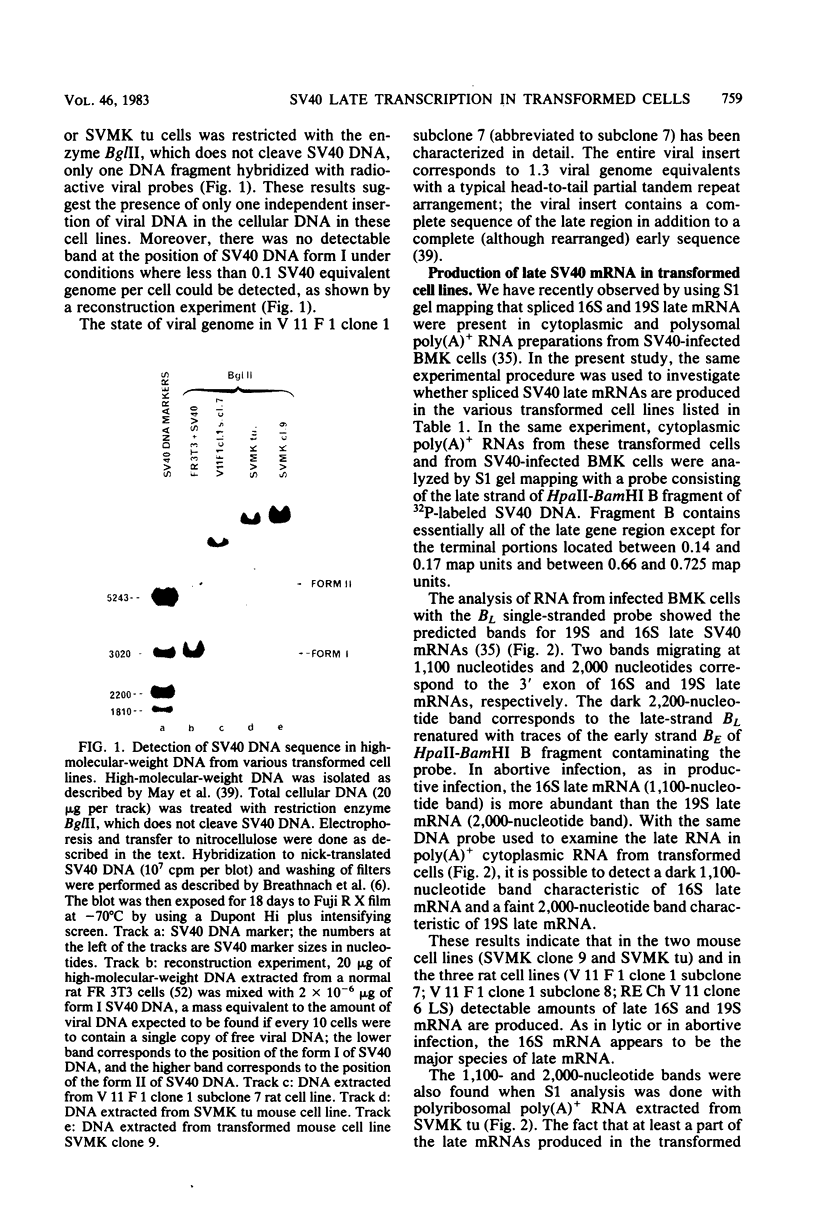
Abstract
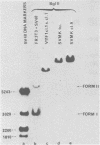
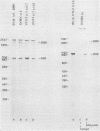
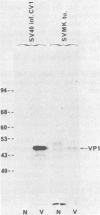
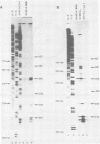
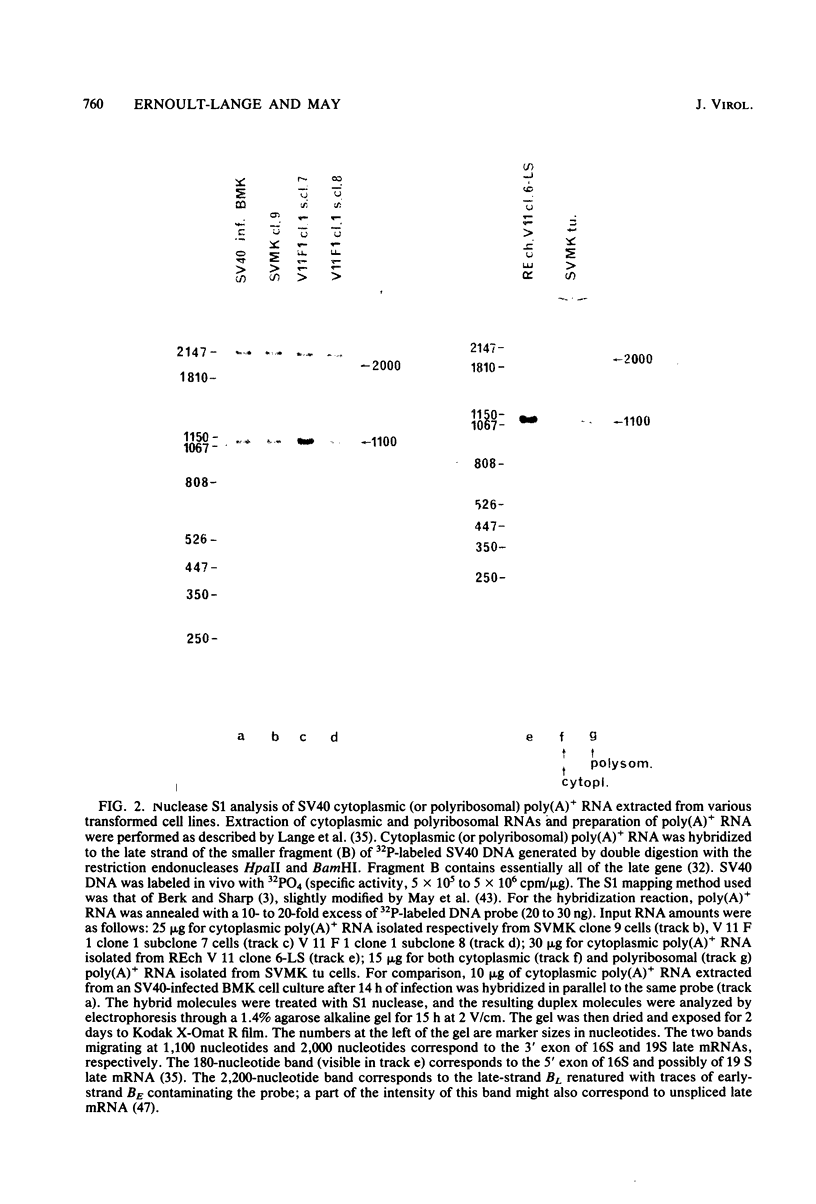
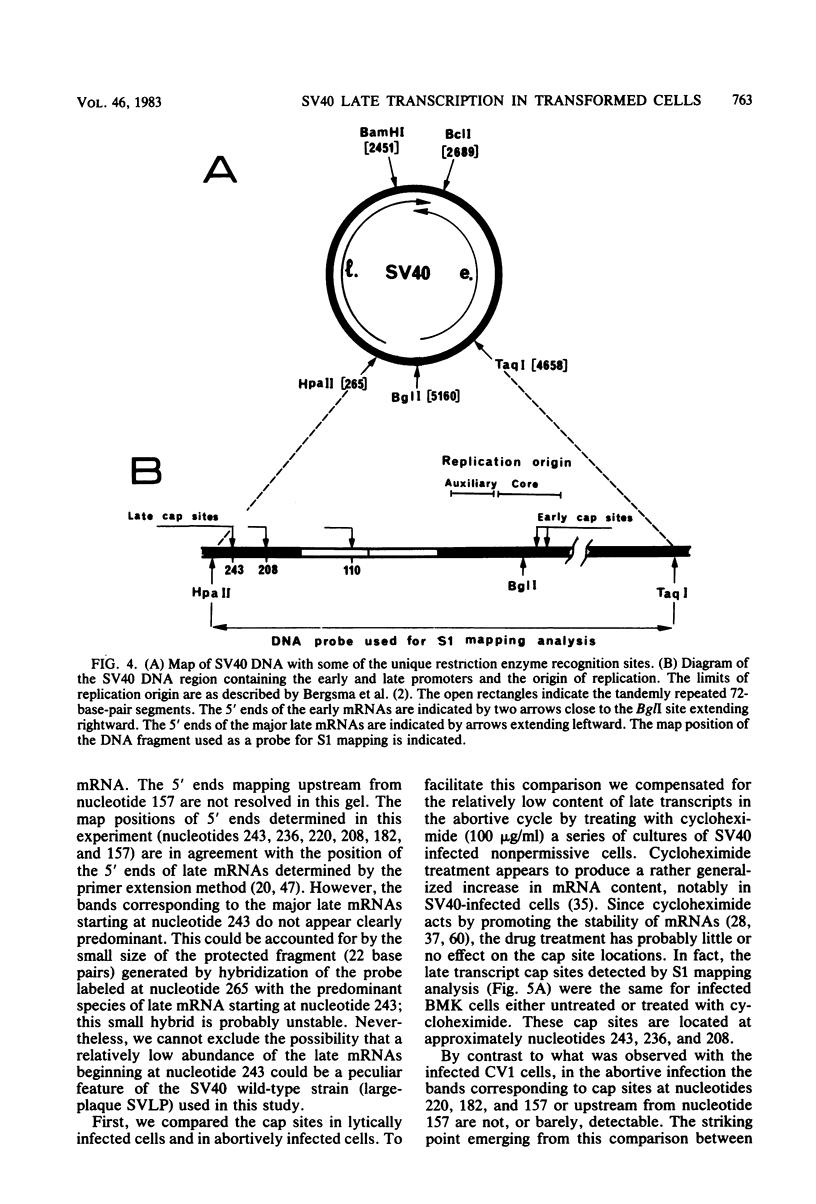
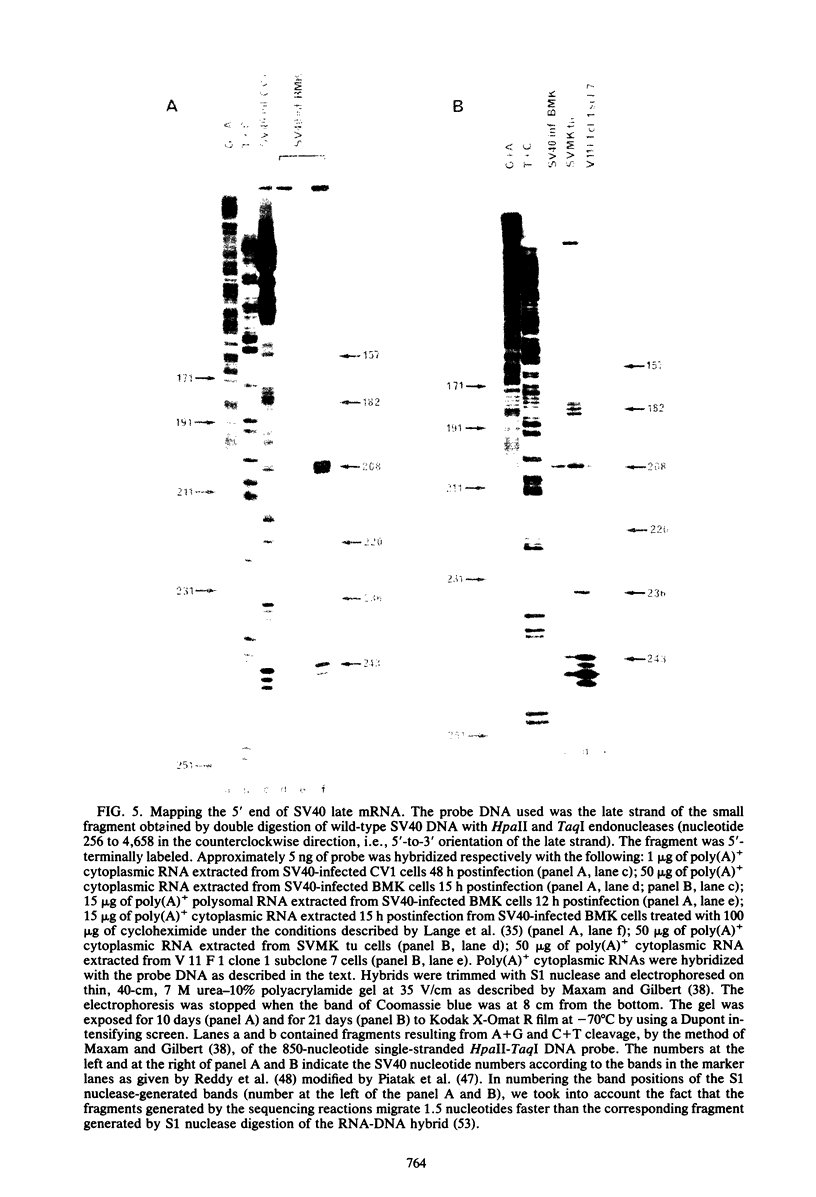
By means of S1 mapping, we observed that spliced 16S and 19S viral late mRNAs--in addition to early mRNAs--were present in cytoplasmic polyadenylated RNA preparations from simian virus 40-transformed cell lines of rat or mouse origin containing no detectable amount of free viral DNA. The amounts of early and late virus-specific mRNAs in these lines were quantified by hybridization of radioactive cytoplasmic polyadenylated RNA with cloned region-specific restriction fragments. The relative amount of late viral mRNA produced in these transformed cells was found to be of the same order as that produced in simian virus 40-infected, nonpermissive baby mouse kidney cells. Moreover, by using the S1 nuclease protection method, we compared the 5' ends of late mRNAs produced (i) in transformed cells, (ii) in abortively infected mouse cells, and (iii) in the late phase of the lytic cycle. The 5' ends of late mRNAs both in abortively infected and in transformed cells were less heterogeneous than the 5' ends of late mRNAs produced during the lytic cycle; however, they were a subset of the 5' ends of late transcripts produced in the lytic cycle.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Herisse J., Courtois G., Galibert F., Ziff E. Messenger RNA for the Ad2 DNA binding protein: DNA sequences encoding the first leader and heterogenity at the mRNA 5' end. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Chiu N., Radonovich M. F., May E., Salzman N. P. Regulation of simian virus 40 early and late gene transcription without viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):983–989. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.983-989.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene is split in chicken DNA. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):314–319. doi: 10.1038/270314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Kahana C., Mukamel A., Groner Y. Sequence heterogeneity at the 5' termini of late simian virus 40 19S and 16S mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassingena R., Suarez H. G., Lavialle C., Persuy M. A., Ermonval M. Transformation of normal diploid cells by isolated metaphase chromosomes of virus-transformed or spontaneous tumor cells. Gene. 1978 Dec;4(4):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov P. M. Transcription of the viral genome in cell lines transformed by simian virus 40. I. Mapping of virus-specific nuclear RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):111–125. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Fiers W. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in permeable, SV40-infected or noninfected, CVI cells; evidence for multiple promoters of SV40 late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):215–236. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya-Grosjean L., Lasne C., Nardeux P., Chouroulinkov I., Monier R. Oncogenic transformation of rat lung epitheloid cells by SV 40 DNA and restriction enzyme fragments. Arch Virol. 1979;62(2):87–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01318062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya-Grosjean L., Monier R. Presence of free viral DNA in simian virus 40-transformed nonproducer cells. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):307–312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.307-312.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Spritz R. A., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 as a eukaryotic cloning vehicle. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:295–340. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinand F. J., Brown M., Khoury G. Characterization of early simian virus 40 transcriptional complexes: late transcription in the absence of detectable DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5443–5447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Legon S., Kamen R. Multiple 5' terminal cap structures in late polyoma virus RNA. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon F., Jeltsch J. M., Perrin F. A detailed comparison of the 5'-end of the ovalbumin gene cloned from chicken oviduct and erythrocyte DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4405–4421. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kahana C., Canaani D., Groner Y. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription of simian virus 40 early and late genes occurs at the various cap nucleotides including cytidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2174–2178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Localization of the 5' terminus of late SV40 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2359–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., van Heuverswyn H., Gheysen D., Fiers W. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of late mRNA induced by a viable simian virus 40 deletion mutant. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.484-493.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Sharp P. A. Expression of early and late simian virus 40 transcripts in the absence of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):592–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.592-597.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Polyoma virus-specific 55K protein isolated from plasma membrane of productively infected cells is virus-coded and important for cell transformation. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Meister R. Rapid increase in poly(A) (+) mRNA content following inhibition of protein synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jul;92(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Byrne J. C., Martin M. A. Patterns of Simian Virus 40 DNA transcription after acute infection of permissive and nonpermissive cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1925–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P., Brown M., Martin M. The detection and quantitation of SV40 nucleic acid sequences using single-stranded SV40 DNA probes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):147–152. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., May E. Regulation of early and late simian virus 40 transcription: overproduction of early viral RNA in the absence of a functional T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.167-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange M., May E., May P. Ability of nonpermissive mouse cells to express a simian virus 40 late function(s). J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):940–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.940-951.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G. Simian virus 40 mutant with transposed T-antigen and VP1 genes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1025–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1025-1037.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Nathans D. A transcriptional map of the SV40 genome in transformed cell lines. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroun L. E., Miller E. T. Increased messenger RNA from protein synthesis inhibited human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Sep;92(3):375–379. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Jeltsch J. M., Gannon F. Characterization of a gene encoding a 115 K super T antigen expressed by a SV40-transformed rat cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4111–4128. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Kress M., Daya-Grosjean L., Monier R., May P. Mapping of the viral mRNA encoding a super-T antigen of 115,000 daltons expressed in simian virus 40-transformed rat cell lines. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.24-35.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Lasne C., Prives C., Borde J., May P. Study of the functional activities concomitantly retained by the 115,000 Mr super T antigen, an evolutionary variant of simian virus 40 large T antigen expressed in transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):901–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.901-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., May P., Weil R. "Early" virus-specific RNA may contain information necessary for chromosome replication and mitosis induced by Simian Virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1654–1658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., Kress M., Lange M., May E. New genetic information expressed in SV40-transformed cells: characterization of the 55K proteins and evidence for unusual SV40 mRNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):189–200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Transcription of simian virus 40. II. Hybridization of RNA extracted from different lines of transformed cells to the separated strands of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.90-98.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Kinetics of formation of 5' terminal caps in mRNA. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Subramanian K. N., Roy P., Weissman S. M. Late messenger RNA production by viable simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the leader region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):589–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Weil R., Frank G., Zuber H. Amino acid sequence analysis of fragments generated by partial proteolysis from large simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5627–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R., Cuzin F. Temperature-sensitive growth regulation in one type of transformed rat cells induced by the tsa mutant of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):721–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.721-728.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the Hind-C fragment of simian virus 40 DNA. Comparison of the 5'-untranslated region of wild-type virus and of some deletion Mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Nevins J. R., Blanchard J. M., Ginsberg H. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Metabolism of mRNA from the transforming region of adenovirus 2. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):447–455. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]