Abstract
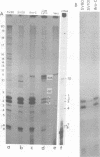
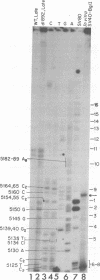
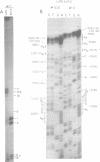
We have used primer-directed synthesis, separation, and sequencing of cDNA's to identify and localize the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNA's. We have examined polyadenylated RNAs obtained from whole cytoplasm and polysomes of two transformed lines and from the cytoplasm of infected cells early and late in the lytic cycle, and we have attempted to correlate the results of our cDNA analyses with recent analyses of early cap structures. We have found that early mRNA's from transformed cells have three principal 5' termini, at residues 5,150, 5,154, and 5,155, with terminal transcribed sequences of CU, GC, and GG, respectively. These termini lie 21 to 26 nucleotides downstream from the early Hogness-Goldberg sequence. Transformed cell early mRNA's also contain a series of less abundant 5' termini that are copied from DNA sequences as far as 80 nucleotides downstream and a minimum of 70 to 75 nucleotides upstream from the Hogness-Goldberg sequence. The templates for the upstream 5' termini and the late simian virus 40 mRNA's overlap by a minimum of 60 to 65 nucleotides. Early mRNA's isolated from cells early in infection contain the same three principal 5' termini and downstream minor 5' termini as transformed cell mRNA's, but they lack 5' termini upstream from the Hogness-Goldberg sequence. With the onset of the late lytic phase, there is a progressive decreases in the utilization of the three principal 5' termini and additional downstream 5' termini and a progressive increase in the utilization of four major termini at residues 5,190 to 5,194, which are 10 to 15 nucleotides upstream from the Hogness-Goldberg sequence. With the onset of the late lytic phase, there is a progressive decrease in the utilization of the three principal 5' termini and additional downstream 5' termini and a progressive increase in the utilization of four major termini at residues 5,190 to 5,194, which are 10 to 15 nucleotides upstream from the Hogness-Goldberg sequence. This shift is evident in cells infected with a tsA mutant at the permissive temperature, but is aborted by growth at or shift-up to a restrictive temperature. Thus, this shift is mediated by the gene A product, large T antigen. We present two models, which are mutually exclusive, to account for the role of T antigen in the early-late shift. One involves transcription late in infection on a new DNA template synthesized during DNA replication. The second involves inhibition of initiation of early transcription at residues 5,150 to 5,155 and other downstream sites and a shift of transcription initiation principally to the upstream sites as a result of the binding of T antigen to two sites on simian virus 40 DNA downstream from the Hogness-Goldberg sequence.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Van De Voorde A., Warnaar S. O., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of primary rat kidney cells by fragments of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.818-823.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Herisse J., Courtois G., Galibert F., Ziff E. Messenger RNA for the Ad2 DNA binding protein: DNA sequences encoding the first leader and heterogenity at the mRNA 5' end. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of human alpha-and beta-globin mRNA. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. Deletions covering the putative promoter region of early mRNAs of simian virus 40 do not abolish T-antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Kahana C., Mukamel A., Groner Y. Sequence heterogeneity at the 5' termini of late simian virus 40 19S and 16S mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Fiers W. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in permeable, SV40-infected or noninfected, CVI cells; evidence for multiple promoters of SV40 late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):215–236. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of a fragment of SV40 DNA that contains the origin of DNA replication and specifies the 5' ends of "early" and "late" viral RNA. IV. Localization of the SV40 DNA complementary to the 5' ends of viral mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Arrand J. R., Kamen R. Localization of three major cappe 5' ends of polyoma virus late mRNA's within a single tetranucleotide sequence in the viral genome. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.902-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Legon S., Kamen R. Multiple 5' terminal cap structures in late polyoma virus RNA. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Frisque R. J., Gluzman Y. Identification of a promoter component involved in positioning the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Piatak M., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Transcription of the SV40 genome in virus-transformed cells and early lytic infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):31–39. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Piatak M., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Determination of RNA sequences by primer directed synthesis and sequencing of their cDNA transcripts. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):580–595. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Roy P., Barkan A., Mertz J. E., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P. Unspliced functional late 19S mRNAs containing intervening sequences are produced by a late leader mutant of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1386–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kahana C., Canaani D., Groner Y. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription of simian virus 40 early and late genes occurs at the various cap nucleotides including cytidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2174–2178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Characterization of the 5'-terminal cap structures of early simian virus 40 mRNA. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):955–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.955-961.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Characterization of the 5'-terminal capped structures of late simian virus 40-specific mRNA. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):824–830. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.824-830.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Kaufman R. J., Manley J., Gefter M., Sharp P. A. Transcription of Simian virus 40 DNA in a HeLa whole cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):478–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Green M. Methylated 5'-terminal caps of adenovirus type 2 early mRNA: evidence for at least six 5'-termini. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):254–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Pursley M. H., Wold W. S., Green M. Characterization of distinct 5'-terminal cap structures of adenovirus type 2 early messenger ribonucleic acid and KB cell messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):294–300. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Gidoni D., Canaani D., Groner Y. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's in lytically infected and transformed cells contain six 5'-terminal caps. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):7–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.7-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., May E. Regulation of early and late simian virus 40 transcription: overproduction of early viral RNA in the absence of a functional T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.167-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Hofstetter H., Di Capua E., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. A tRNA gene of Xenopus laevis contains at least two sites promoting transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Stern R., Ghosh P. K., Weissman S. M. Specificity of initiation of transcription of simian virus 40 DNA I by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: identification and localization of five sites for initiation with [gamma-32P]ATP. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):430–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.430-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Organization and transcription of the simian virus 40 genome. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;87:43–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67344-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse D. S., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation on a purified mouse beta-globin DNA fragment in a cell-free system. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Gaps and duplicated sequences in the leaders of SV40 16S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4195–4213. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D., Robbins A., Myers R., Tjian R. Regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro by a purified tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5706–5710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Construction of an adenovirus-SV40 recombinant producing SV40 T antigen from an adenovirus late promoter. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90509-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Shenk T. Definition of the boundaries of the origin of DNA replication in simian virus 40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3635–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Radonovich M. F., Salzman N. P. Characterization of the 5'-terminal structure of simian virus 40 early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):437–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.437-446.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the Hind-C fragment of simian virus 40 DNA. Comparison of the 5'-untranslated region of wild-type virus and of some deletion Mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Kédinger C., Corden J., Brison O., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):367–373. doi: 10.1038/285367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Dhar R., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P., Lewis A. M., Jr Preferred site for initiation of RNA transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase within the simian virus 40 DNA segment of the nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses Ad2 + ND 1 and Ad2 + ND 3 . J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):682–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.682-693.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]