Abstract
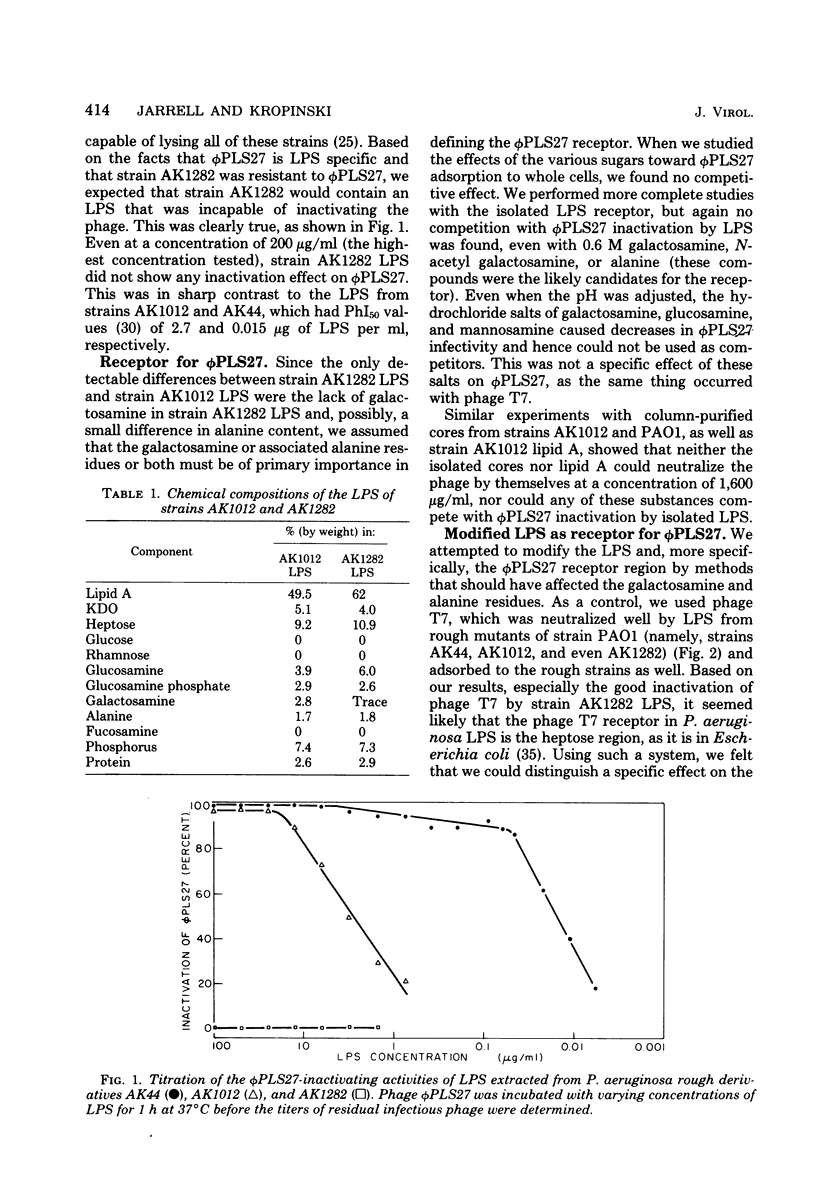
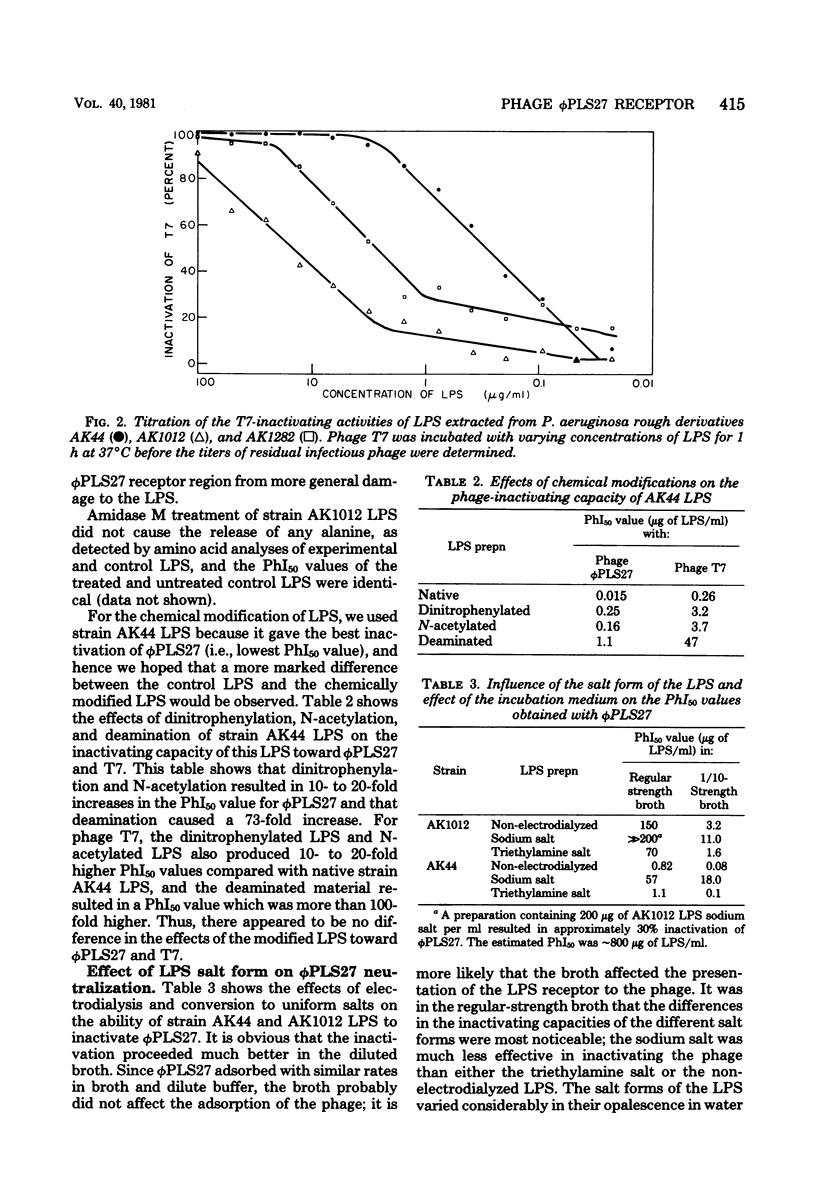
We investigated the phi PLS27 receptor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by analyzing a resistant mutant. This mutant, which was designated AK1282, had the most defective LPS yet reported for a P. aeruginosa rough mutant; this LPS contained only lipid A, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate, heptose, and alanine as major components. In addition, this LPS lacked galactosamine, which is present in the inner core of the LPS of other rough mutants. The loss of galactosamine but only a small decrease in the alanine content indicated that the core of strain PAO LPS differed from the core structure which has been suggested for the LPS of other well-characterized P. aeruginosa strains. Our analysis also indicated that galactosamine residues may be crucial for phi PLS27 receptor activity of the LPS. Electrodialysis of LPS and conversion to salt forms (sodium or triethylamine) influenced the phage-inactivating capacity of the LPS, as did the medium in which the inactivation occurred; experiments performed in 1/10-strength broth resulted in much lower PhI50 (concentration of LPS causing a 50% decrease in the titer of phage during 1 h of incubation at 37 degrees C) values than experiments performed in regular-strength broth. Sonication of the LPS also increased the phage-inactivating capacities of the LPS preparations.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E., Pitt T. L. Pilus-dependence of four Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages with non-contractile tails. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Melling J. Loss of sensitivity to EDTA by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown under conditions of Mg-limitation. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):439–444. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Melling J. Role of divalent cations in the action of polymyxin B and EDTA on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):263–274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Further studies of the chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):395–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1260395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M. Heterogeneity of the lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):273–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z., BORENFREUND E. A spectrophotometric method for the microdetermination of hexosamines. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jun;184(2):517–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T. The assay and characterization of amines by 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:783–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes J. Characterisation of the bacteriophage T4 receptor site. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):127–128. doi: 10.1038/256127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Low-molecular-weight solutes released during mild acid hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):289–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1300289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Symes K. C., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Studies of polysaccharide fractions from the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa N.C.T.C. 1999. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):93–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1490093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Gray G. W. The chemical composition of the lipopolyacarideof Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1140185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement in rats and its relation to endotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):875–882. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.875-882.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The role of the physical state of lipopolysaccharides in the interaction with complement. High molecular weight as prerequisite for the expression of anti-complementary activity. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):403–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Roppel J., Weckesser J., Rietschel E. T., Mayer H. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Rhodospirillaceae. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):407–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.407-412.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Reeves P. Lipopolysaccharide-deficient, bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):98–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.98-108.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., Kropinski A. M. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage specific for the lipopolysaccharide of rough derivatives of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):529–538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.529-538.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K., Kropinski A. M. Identification of the cell wall receptor for bacteriophage E79 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):461–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.461-466.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K., Kropinski A. M. The chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO and a spontaneously derived rough mutant. Microbios. 1977;19(76):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K., Kropinski A. M. The isolation and characterization of a lipopolysaccharide-specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):99–106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Meadow P. M. The isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAC1. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):387–398. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chadwick J. S. The pathogenicity of rough strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Galleria mellonella. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):2084–2088. doi: 10.1139/m75-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L. C., Milazzo F. H. The extraction and analysis of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO, and three rough mutants. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):390–398. doi: 10.1139/m79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L., Jarrell K., Milazzo F. H. The nature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO bacteriophage receptors. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):653–658. doi: 10.1139/m77-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Studies of a receptor for felix O-1 phage in Salmonella minnesota. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. F116: a DNA bacteriophage specific for the pili of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):558–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Beacham I. R. Bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Location of receptors within the lipopolysaccharide. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Oct;102(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praino M. D., Galanos C., Neter E. Attachment to erythrocytes of uniform salt forms of lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella abortus-equi and its inhibition by various animal sera. Immunol Commun. 1979;8(1):85–92. doi: 10.3109/08820137909044709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E., Anacker R. L., Brown R., Haskins W. T., Malmgren B., Milner K. C., Rudbach J. A. Reaction of endotoxin and surfactants. I. Physical and biological properties of endotoxin treated with sodium deoxycholate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1493–1509. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1493-1509.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C., Tanaka A., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biological activities of chemically modified endotoxins. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 24;22(2):218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan E. A., Kropinski A. M. Separation of amino sugars and related compounds by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jul 4;195(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)81550-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourek J., Tichý M., Levin J. Effects of certain cations (Fe, Zn, Mg, and Ca) on bacterial endotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):648–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.648-654.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T. Role of lipopolysaccharide in adsorption of coliphage T4D to Escherichia coli B. Can J Microbiol. 1976 May;22(5):745–751. doi: 10.1139/m76-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



