Abstract
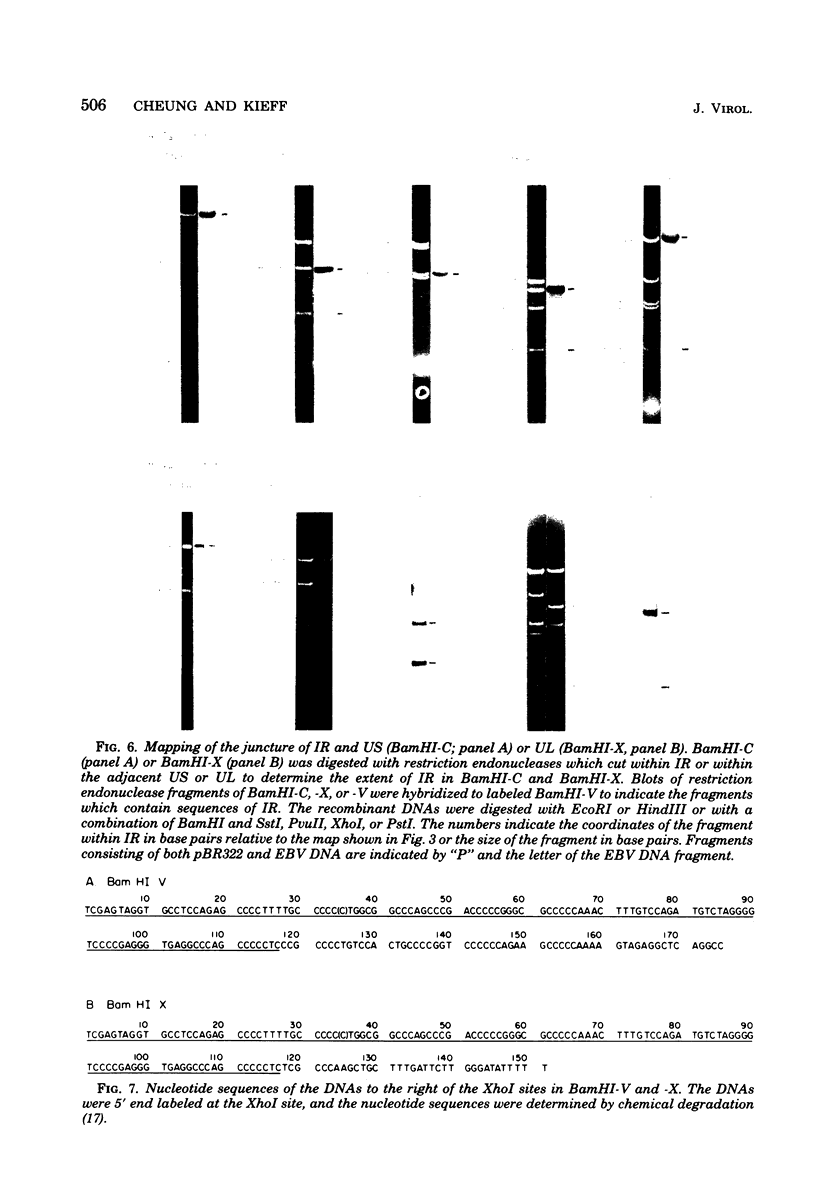
The 3,360-base-pair internal direct repeat (IR) in Epstein-Barr virus DNA separates the short and long unique DNA domains. IR has a single BamHI site. The juncture between the short unique domain and IR has been mapped by restriction endonucleases and is less than 2,600 nucleotides before the BamHI site in IR. The junction between IR and the long unique domain has been sequenced and is approximately 650 nucleotides after the BamHI site in IR. Thus, relative to the start of IR at the juncture with the short unique domain, the last repeat is at least 90 base pairs short of being complete. There is homology between the 250-nucleotide fragments to the left and the right of the unique BamHI site in IR. A 35-base-pair sequence of the left fragment is directly repeated within the right fragment, once fully and once partially. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Bjursell G., Kaschka-Dierich C., Lindahl T. Circular Epstein-Barr virus genomes of reduced size in a human lymphoid cell line of infectious mononucleosis origin. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):373–380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.373-380.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Delius H., Zimber U., Hudewentz J., Epstein M. A. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus strains of different origin by analysis of the viral DNAs. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):603–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.603-618.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Raab-Traub N., Heller M., Beisel C., Hummel M., Cheung A., Fennewald S., King W., Kieff E. Variations among isolates of Epstein-Barr virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:309–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Bornkamm G. W. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Comparison of a transforming and a nontransforming virus by partial denaturation mapping of their DNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given D., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. IV. Linkage map of restriction enzyme fragments of the B95-8 and W91 strains of Epstein-Barr Virus. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):524–542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.524-542.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given D., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. VI. Mapping of the internal tandem reiteration. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):315–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.315-324.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given D., Yee D., Griem K., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. V. Direct repeats of the ends of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):852–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.852-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. D., Nogee L., Hayward G. S. Organization of repeated regions within the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):507–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.507-521.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA. IX. Variation among viral DNAs from producer and nonproducer infected cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):632–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.632-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Gerber P., Kieff E. Herpesvirus papio DNA is similar in organization to Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):698–709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.698-709.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Kieff E. Colinearity between the DNAs of Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus papio. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.821-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Thomas-Powell A. L., Raab-Traub N., Hawke M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):506–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.506-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Queen C. L., Wegman M. N. Computer analysis of nucleic acid regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. S., Tanaka A., Lau R. Y., Nonoyama M., Rabin H. Linkage map of the fragments of herpesvirus papio DNA. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.710-720.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Weber H., Meyer F., Weissmann C. Site-directed mutagenesis in DNA: generation of point mutations in cloned beta globin complementary dna at the positions corresponding to amino acids 121 to 123. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus VIII: B95-8, the previous prototype, is an unusual deletion derivative. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L., Forsblom S. Cleavage of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by restriction endonucleases EcoRI, HindIII and BamI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1387–1402. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]