Abstract
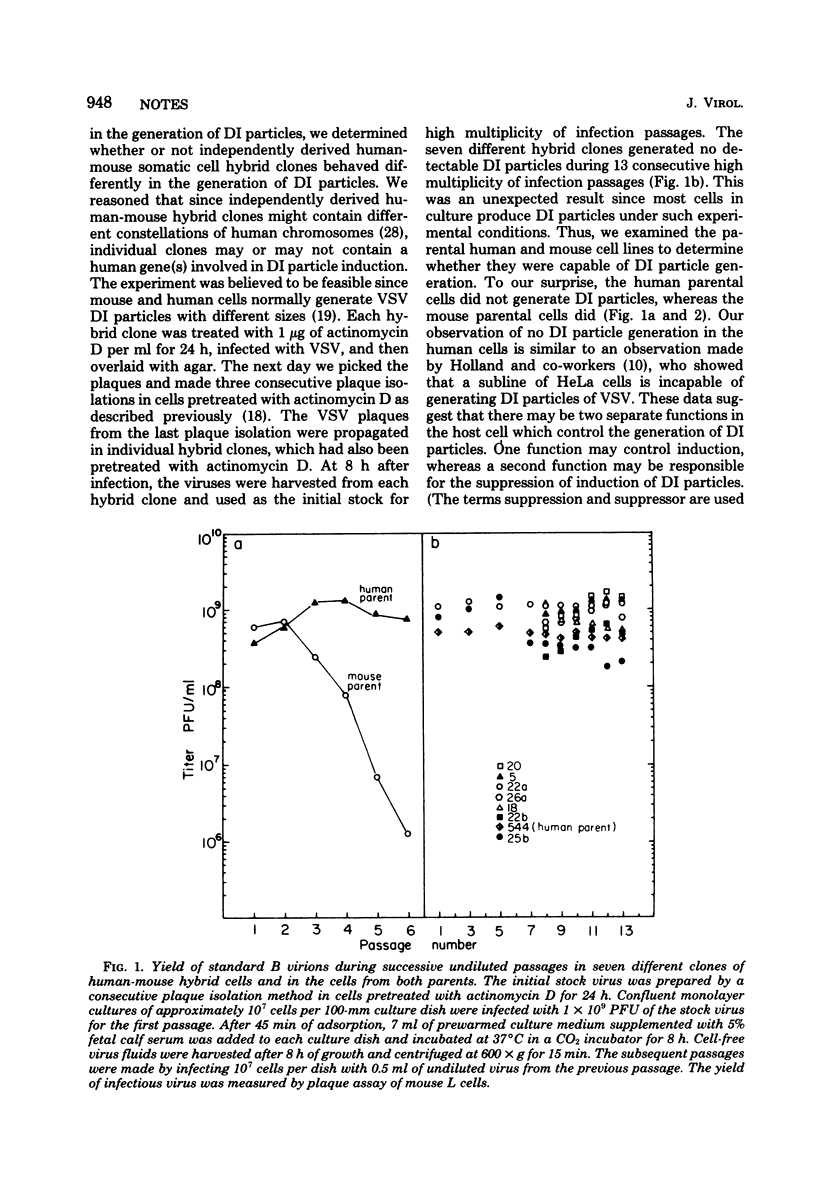
Human-mouse somatic cell hybrids were made between adenine phosphoribosyltransferase-deficient mouse L cells and a strain of human primary fibroblasts and selected in medium containing alanosine and adenine (J. A. Tischfield and F. H. Ruddle, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71:45-49, 1974). These hybrids were tested for the generation of defective interfering (DI) particles of vesicular stomatitis virus to determine whether or not a host gene controls the induction of DI particles. None of the seven independently arising hybrid clones tested generated detectable DI particles during 13 successive undiluted passages. In addition, the parental human cells also failed to generate DI particles. In contrast, the parental mouse cells generated a detectable level of DI particles during continuous passage. Thus, failure to generate DI particles appears to act in a dominant fashion in these hybrids. Human chromosome 16 and adenine phosphoribosyltransferase were present, as a direct consequence of the selection system, in all of the hybrid clones that failed to generate DI particles. It was the only human chromosome observed in the cells of every hybrid clone. This was verified by both isozyme and karyotype analyses. After hybrids were back-selected (with 2,6-diaminopurine) for loss of human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase and chromosome 16, they gained the ability to generate DI particles. Replication of DI particles already present in virus stocks, however, was normal in all of the hybrid clones and the parental human cells. This suggests that the induction, but not the replication, of DI particles is affected by the human genome and that a factor on human chromosome 16 seems to selectively suppress the mouse cell's ability to generate DI particles in the hybrids. These results support the idea that the induction of DI particles is controlled in part by host cell function(s), as suggested previously (C. Y. Kang and R. Allen, J. Virol. 25:202-206, 1978).
Full text
PDF

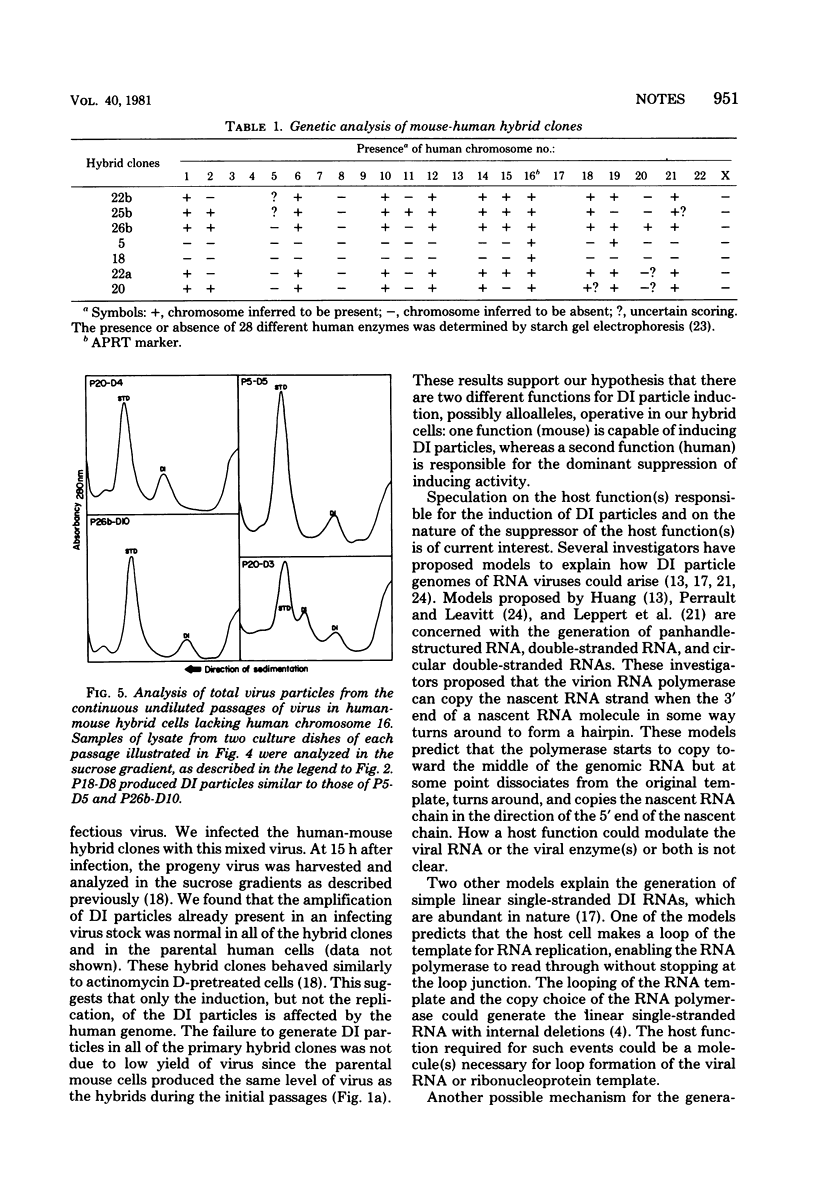

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choppin P. W., Pons M. W. The RNAs of infective and incomplete influenza virions grown in MDBK and HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W. Replication of influenza virus in a continuous cell line: high yield of infective virus from cells inoculated at high multiplicity. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell M. B., Koprowski H. Genetically determined resistance to infection with group B arboviruses. II. Increased production of interfering particles in cell cultures from resistant mice. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):248–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. A., Herman R. C., Chien I., Lazzarini R. A. Defective interfering particle generated by internal deletion of the vesicular stomatitis virus genome. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):818–829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.818-829.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN G. T., KOPROWSKI H. Macrophages as a cellular expression of inherited natural resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Feb;48:160–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.2.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN G. T., KOPROWSKI H. Study of the mechanism of innate resistance to virus infection. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:333–373. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Grabau E. A., Jones C. L., Semler B. L. Evolution of multiple genome mutations during long-term persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Breindl M. Factors involved in the generation and replication of rhabdovirus defective T particles. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):805–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.805-815.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B., Kohne D., Lazzarini R., Scolnick E. Long-term persistent vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus infection of cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):193–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Viral pathogenesis and molecular biology. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):811–821. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.811-821.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi A., Stollar V. Failure of defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus produced in BHK or chicken cells to affect viral replication in Aedes albopictus cells. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):398–408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.398-408.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Allen R. Host function-dependent induction of defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):202–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.202-206.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Glimp T., Clewley J. P., Bishop D. H. Studies on the generation of vesicular stomatitis virus (indiana serotype) defective interfering particles. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):142–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W., Portner A. On the genesis of incomplete Sendai virions. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):872–879. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Kort L., Kolakofsky D. Further characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs: a model for their generation. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):539–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A., Ruddle F. H. The status of the gene map of the human chromosomes. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):390–405. doi: 10.1126/science.850784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. A review of enzyme polymorphism, linkage and electrophoretic conditions for mouse and somatic cell hybrids in starch gels. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Dec;21(12):1066–1081. doi: 10.1177/21.12.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J., Leavitt R. W. Inverted complementary terminal sequences in single-stranded RNAs and snap-back RNAs from vesicular stomatitis defective interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):35–50. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman J. M., Simon E. H. Defective interfering particles in monolayer-propagated Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Tischfield J. A., Schneider E. L. Appearance of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase activity as a consequence of mycoplasma contamination. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):329–331. doi: 10.1038/256329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Bernhard H. P., Ruddle F. H. A new electrophoretic-autoradiographic method for the visual detection of phosphotransferases. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the gene for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to human chromosome 16 by mouse-human somatic cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):45–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON MAGNUS P. Incomplete forms of influenza virus. Adv Virus Res. 1954;2:59–79. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Prevention of virus-induced cerebellar diseases by defective-interfering lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):391–399. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]